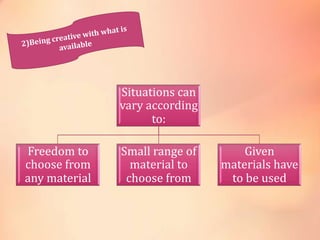
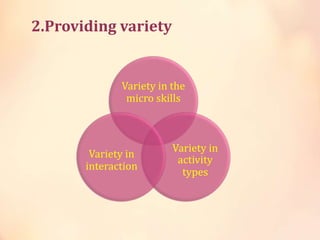
The document discusses the role and purpose of materials in language teaching. It explains that materials should maximize language exposure, support learning through engaging activities, and motivate and stimulate learners. Good materials also serve as references for self-study. The document discusses teacher-generated and learner-generated materials and how technology continues to change language teaching materials.