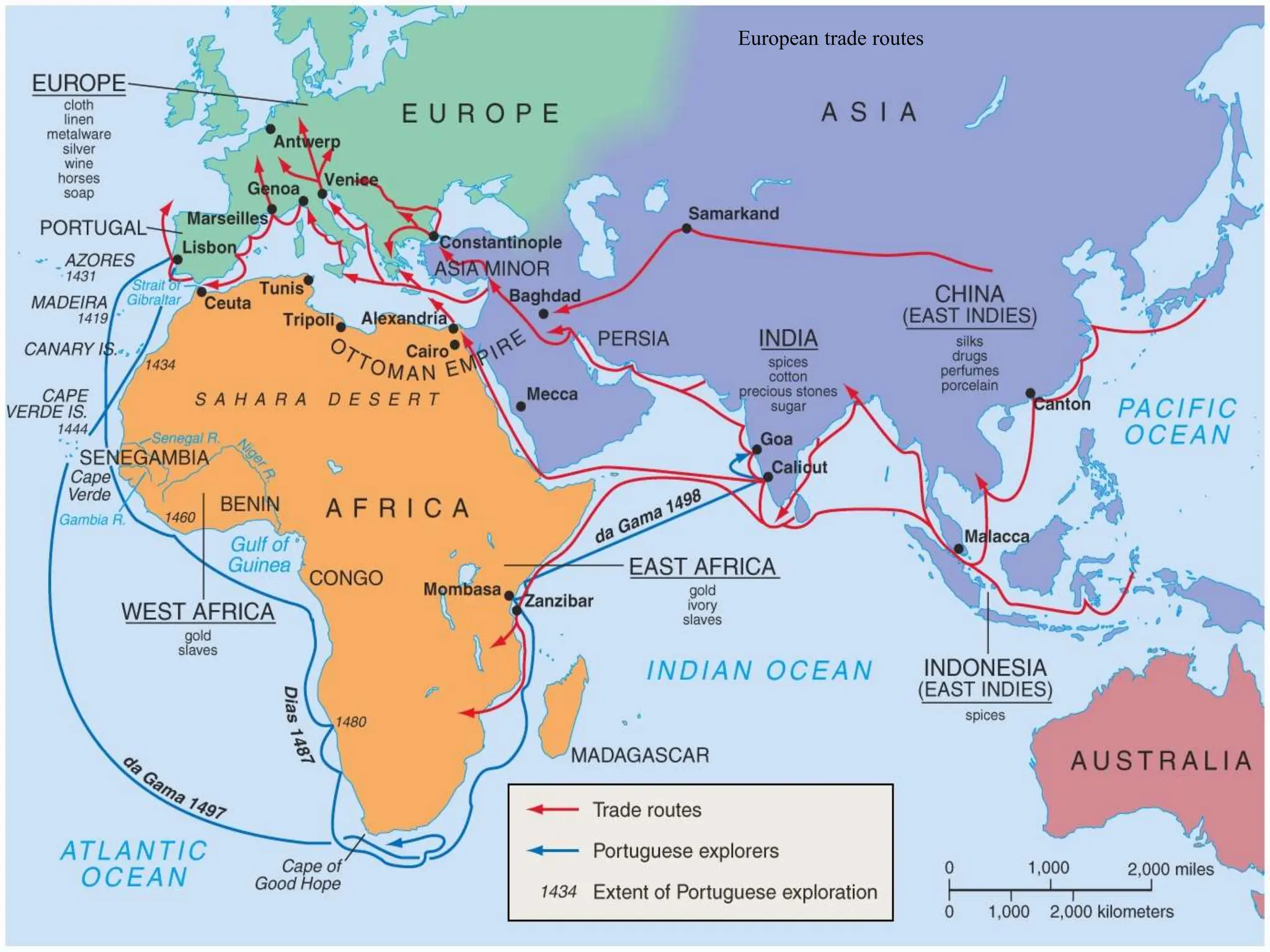
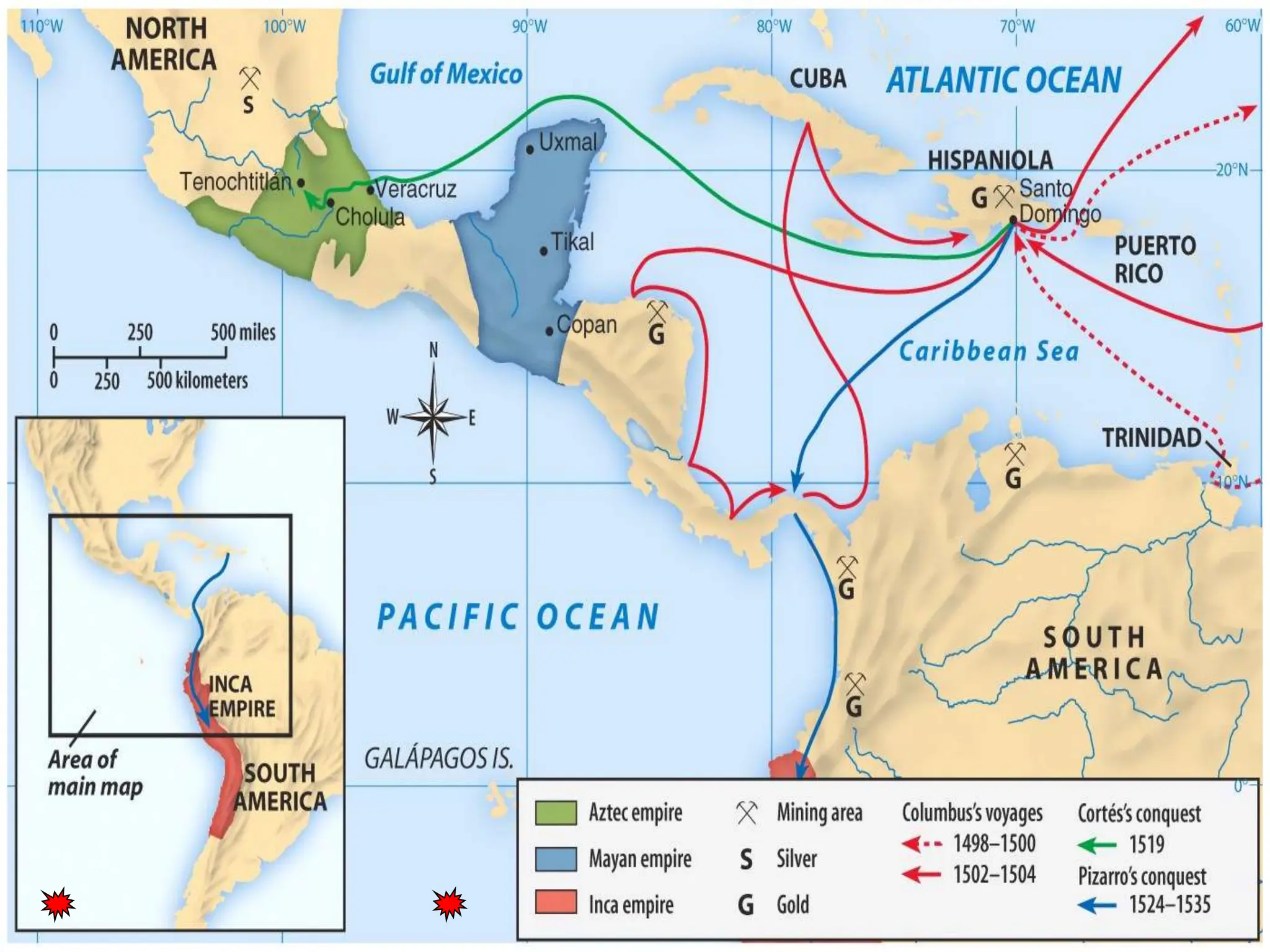
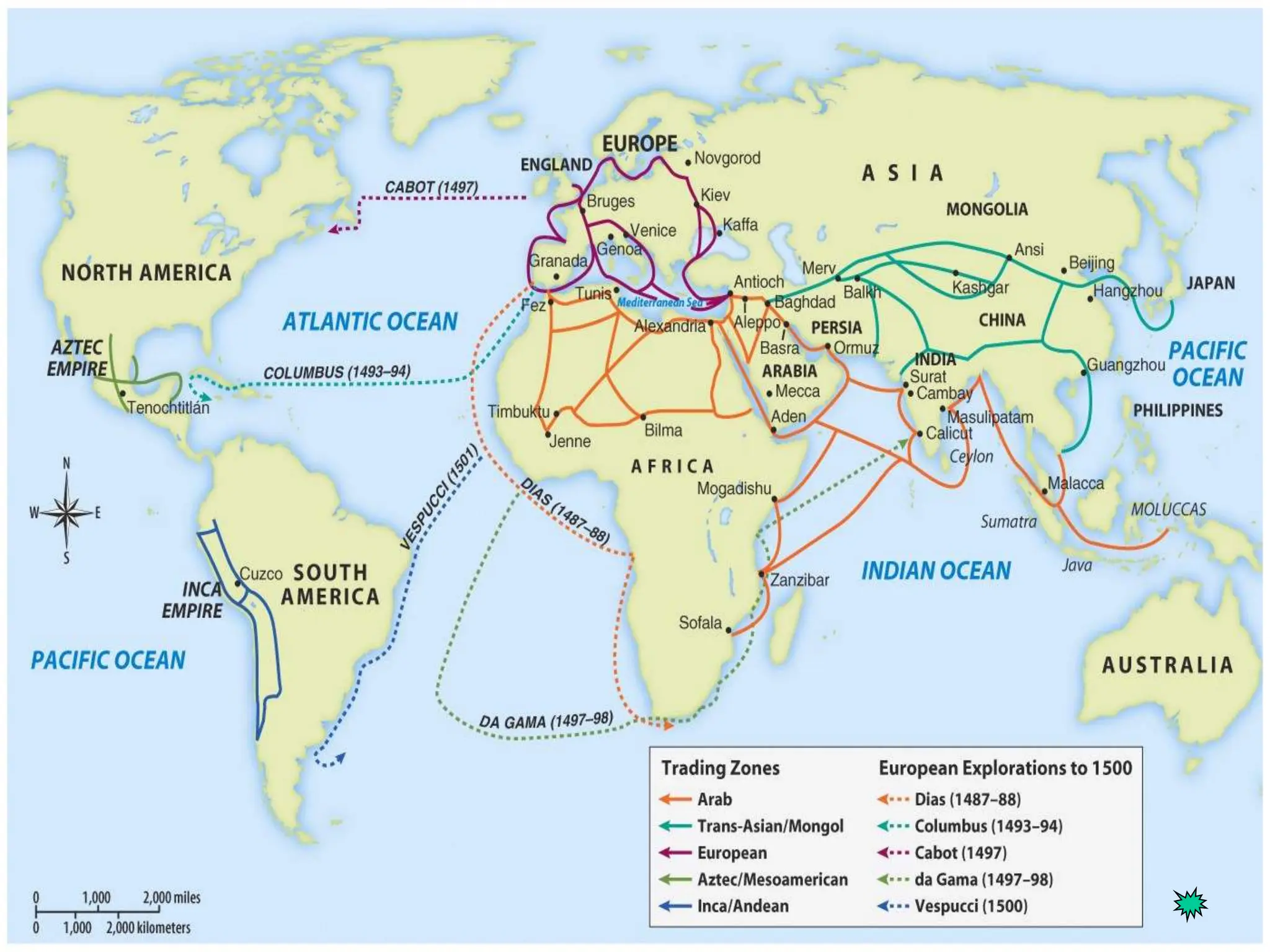
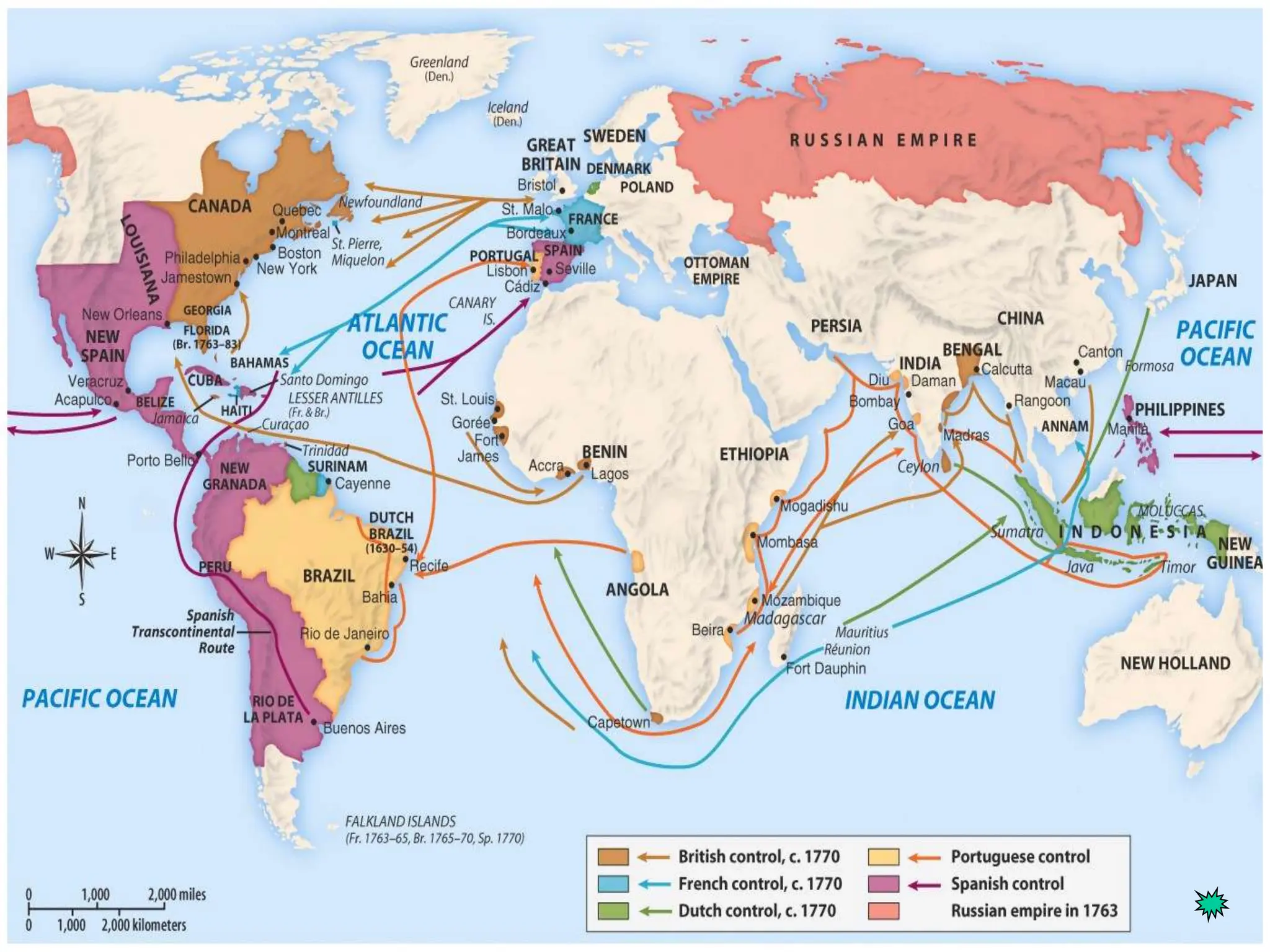
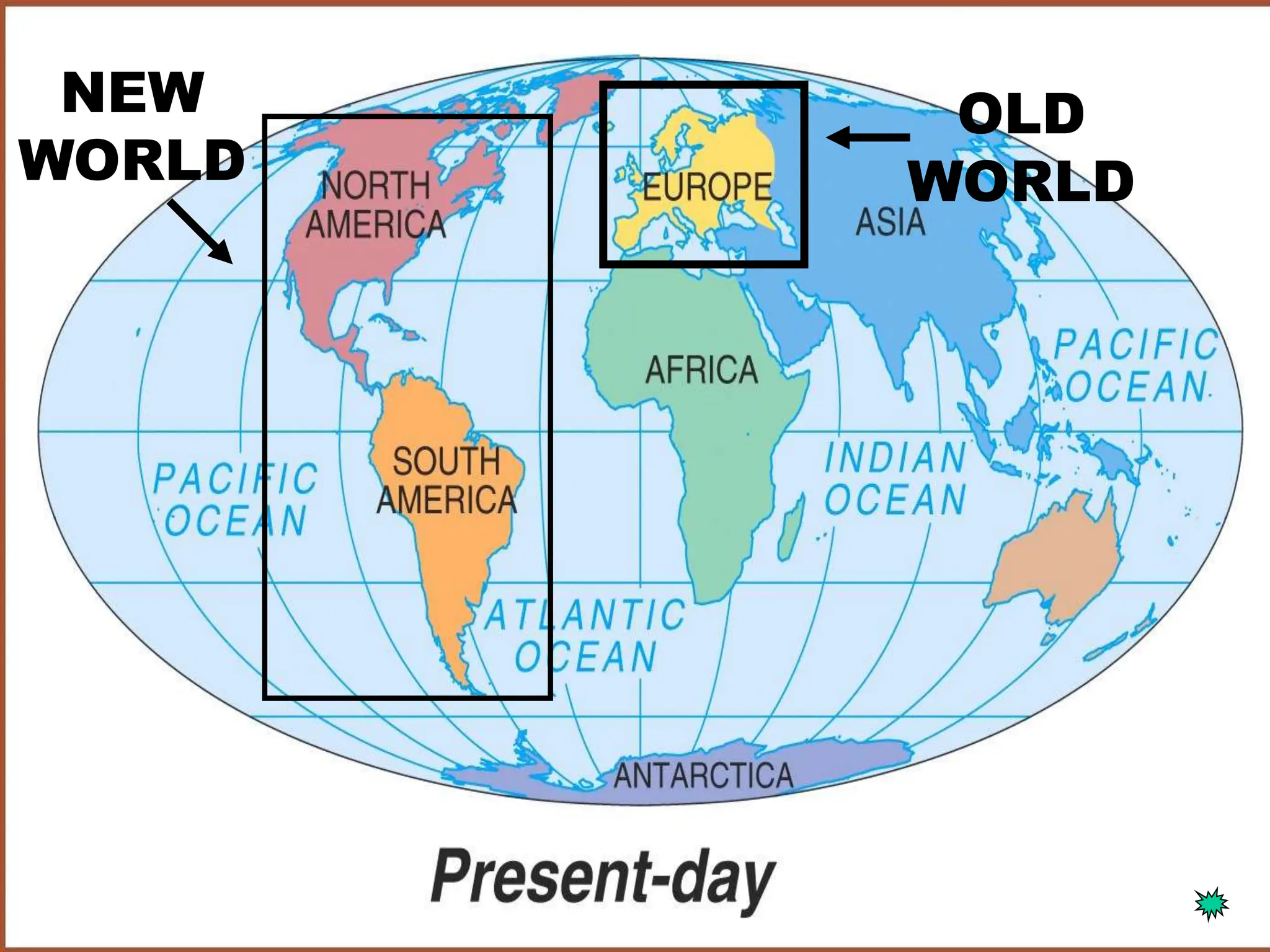
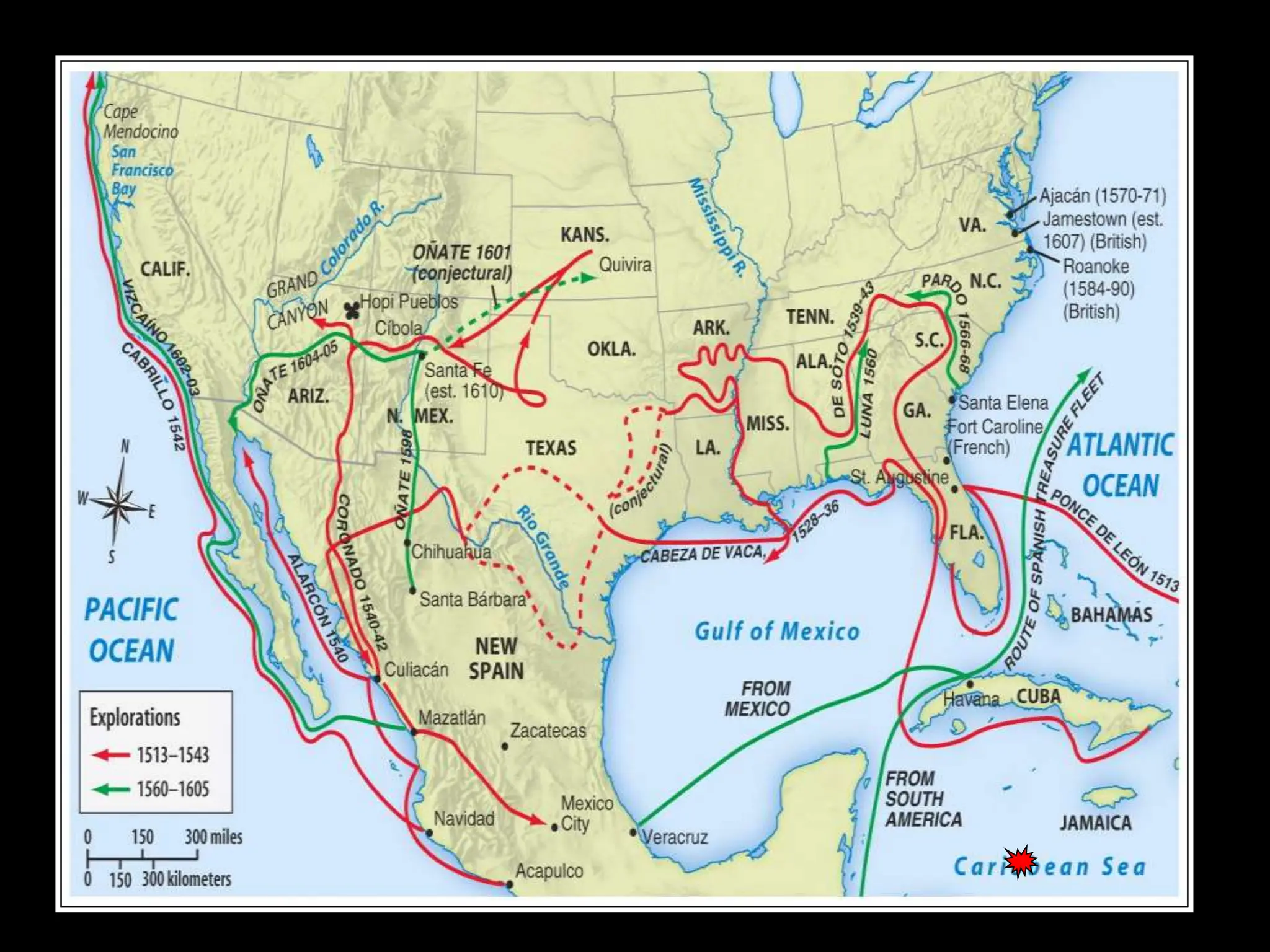
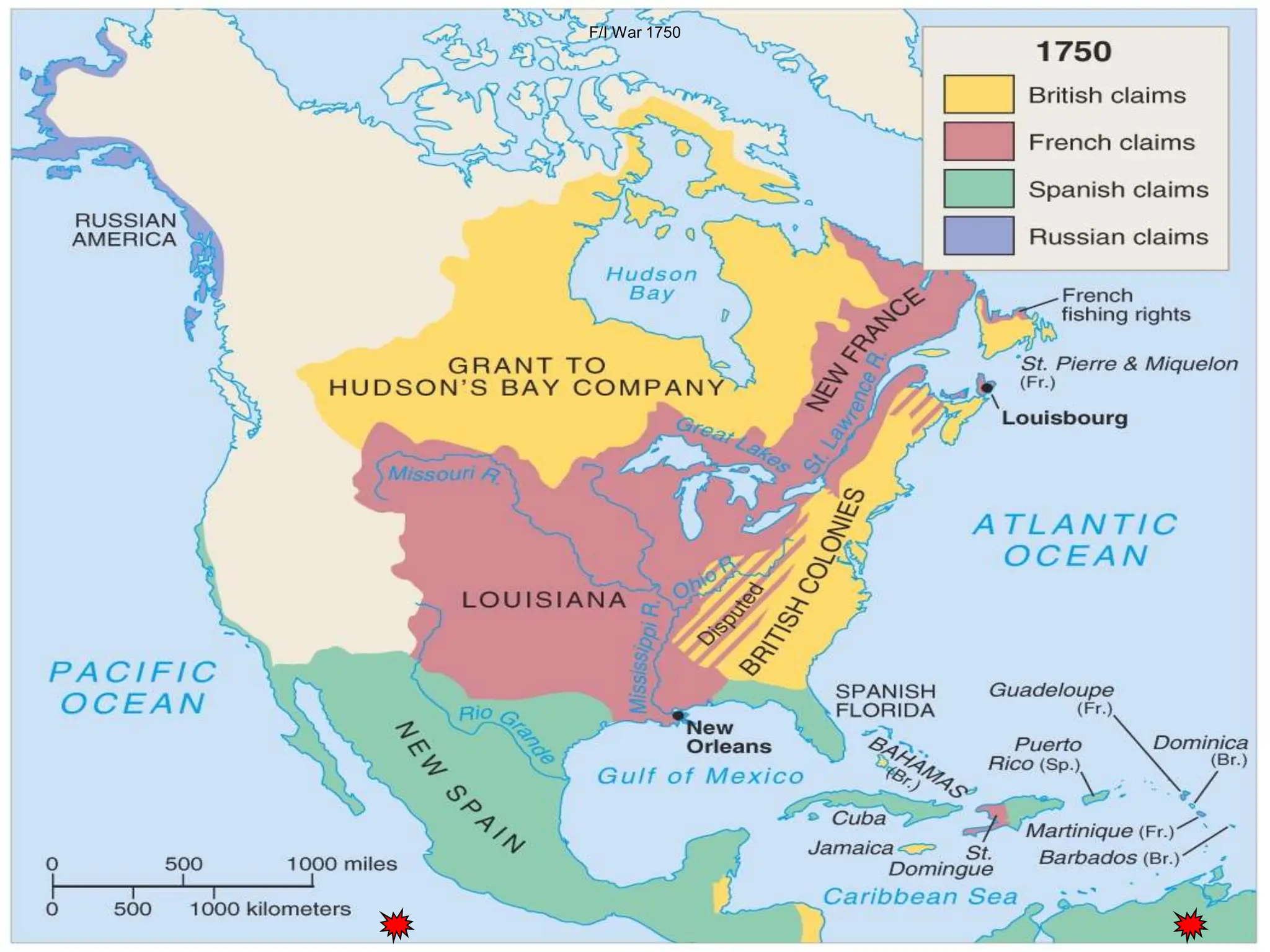
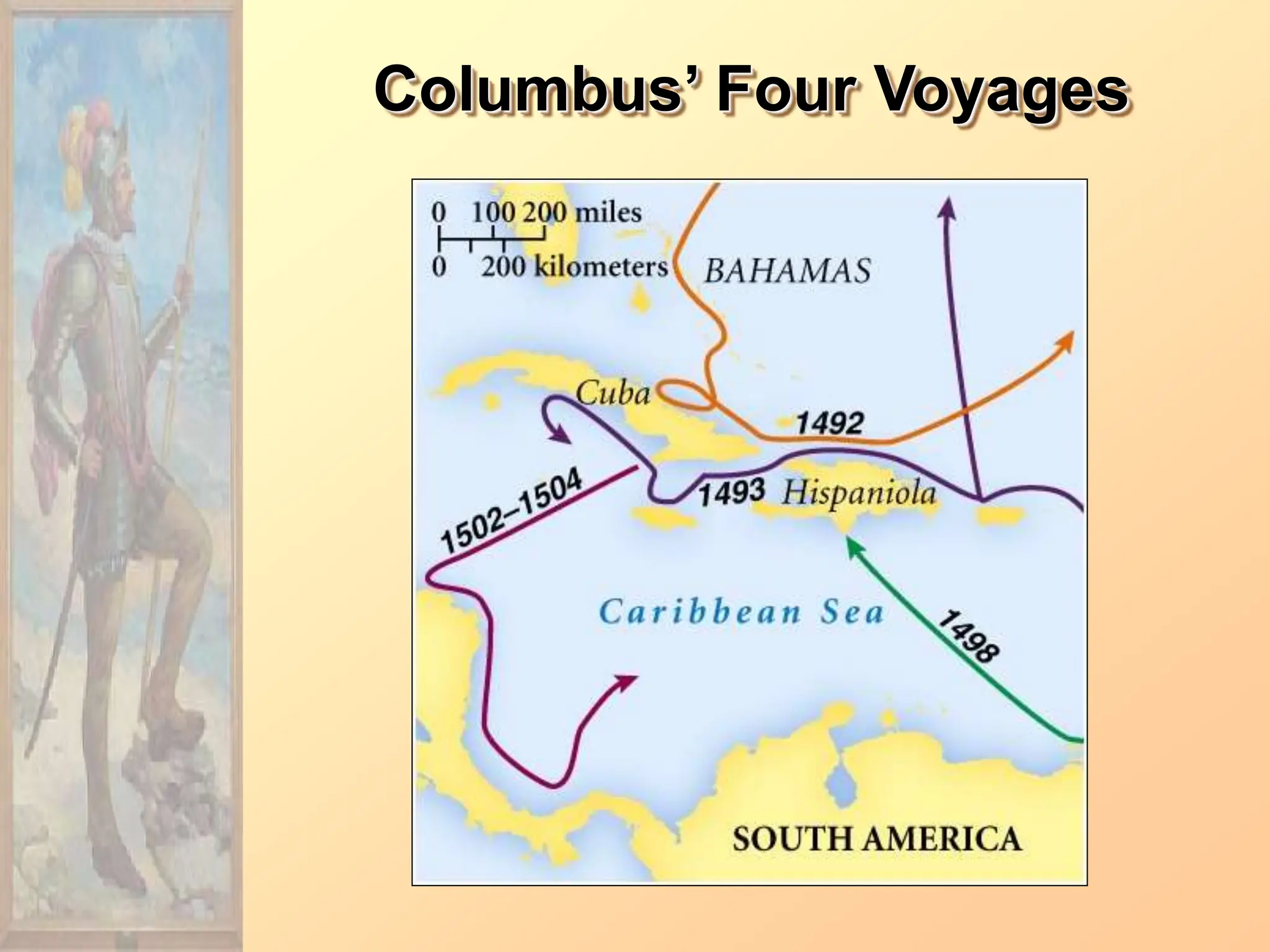
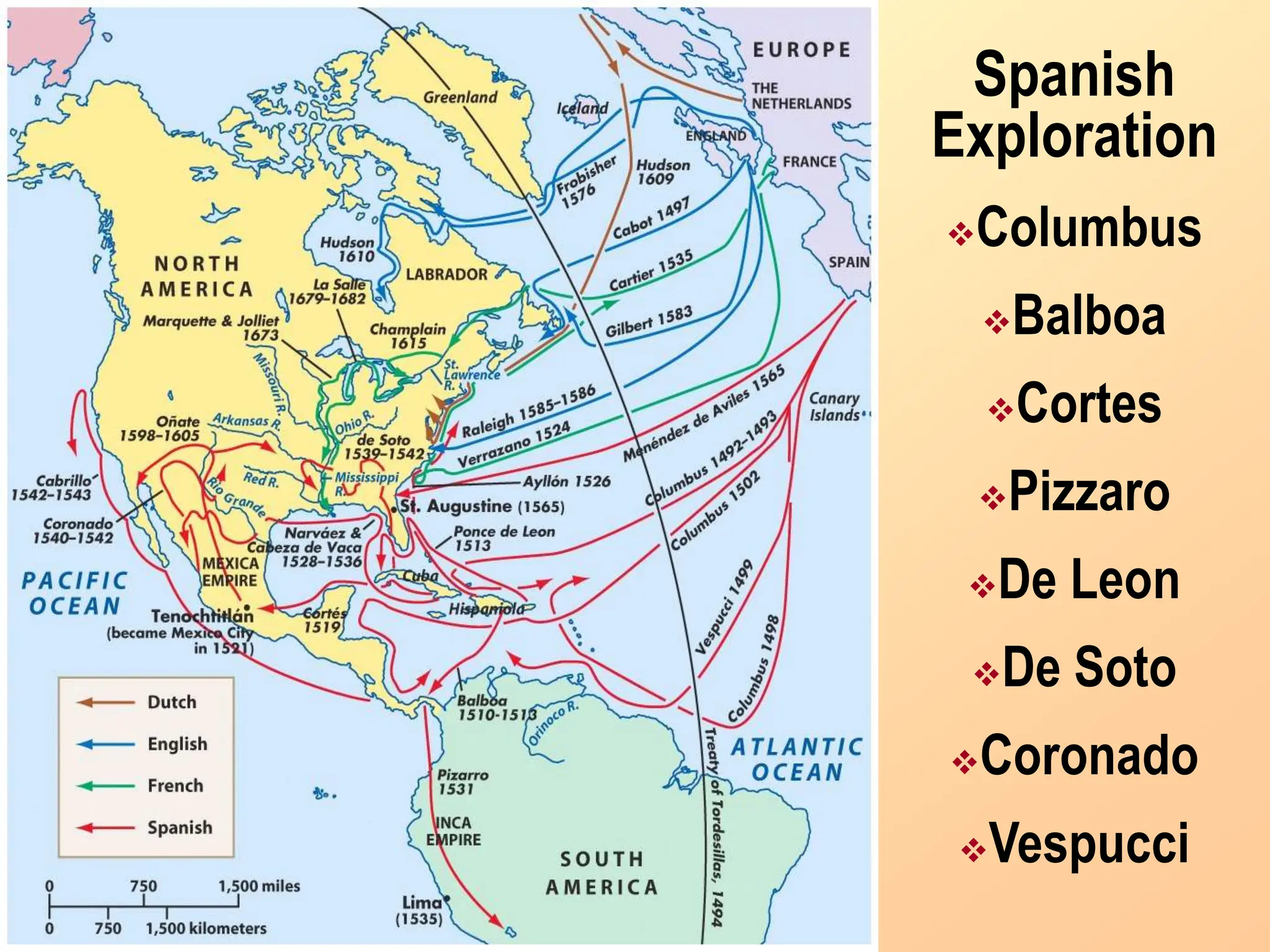
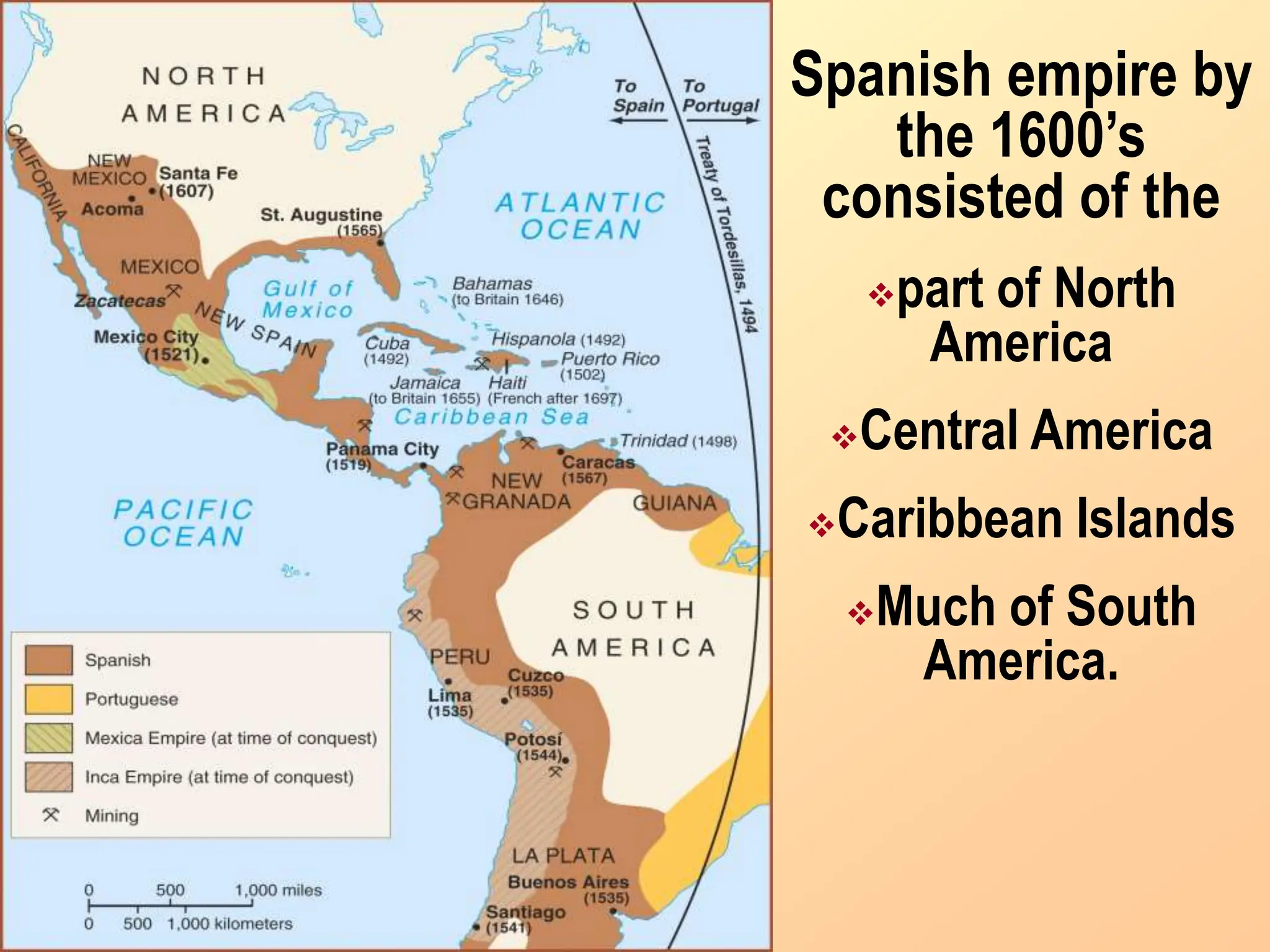
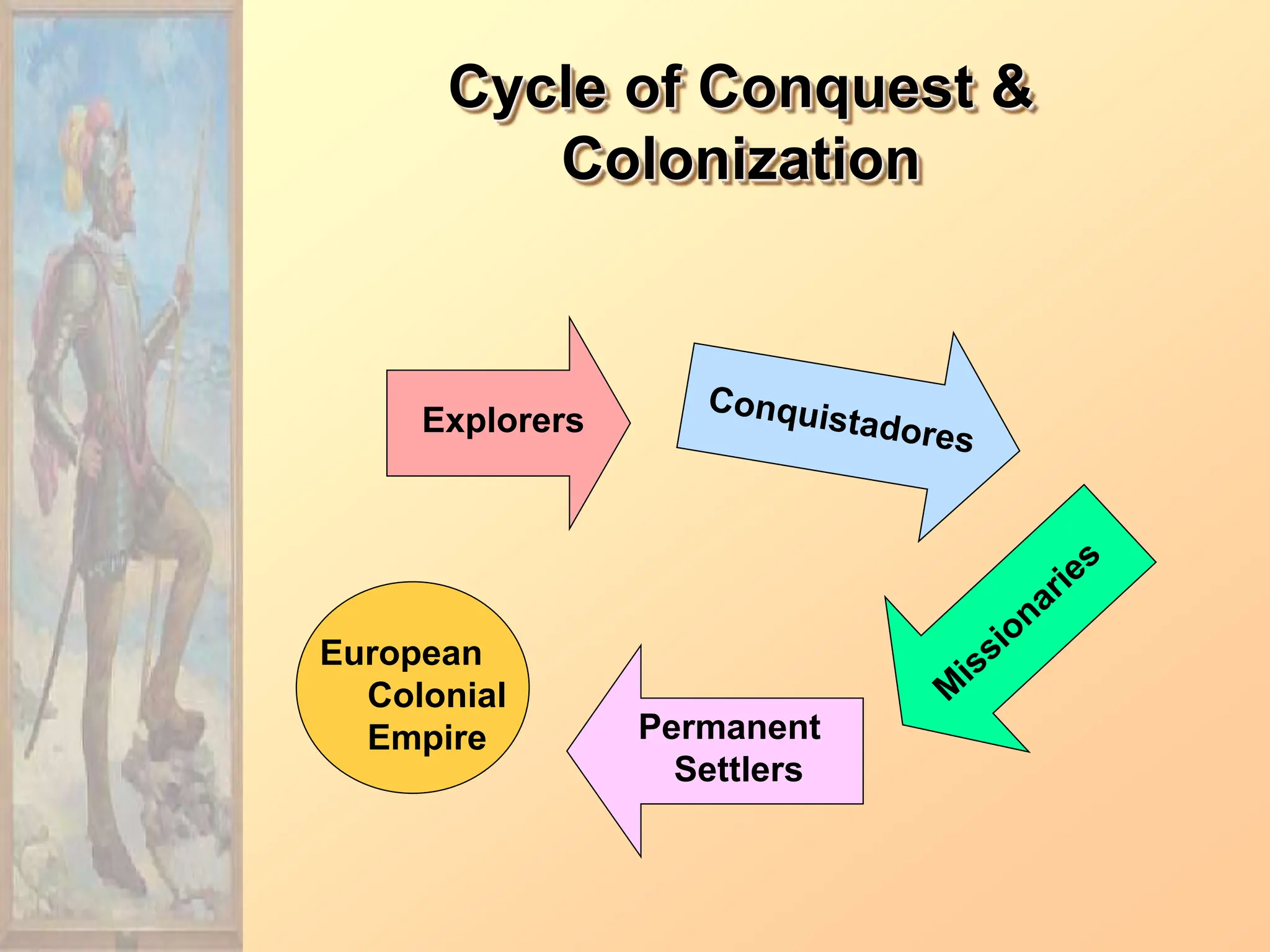
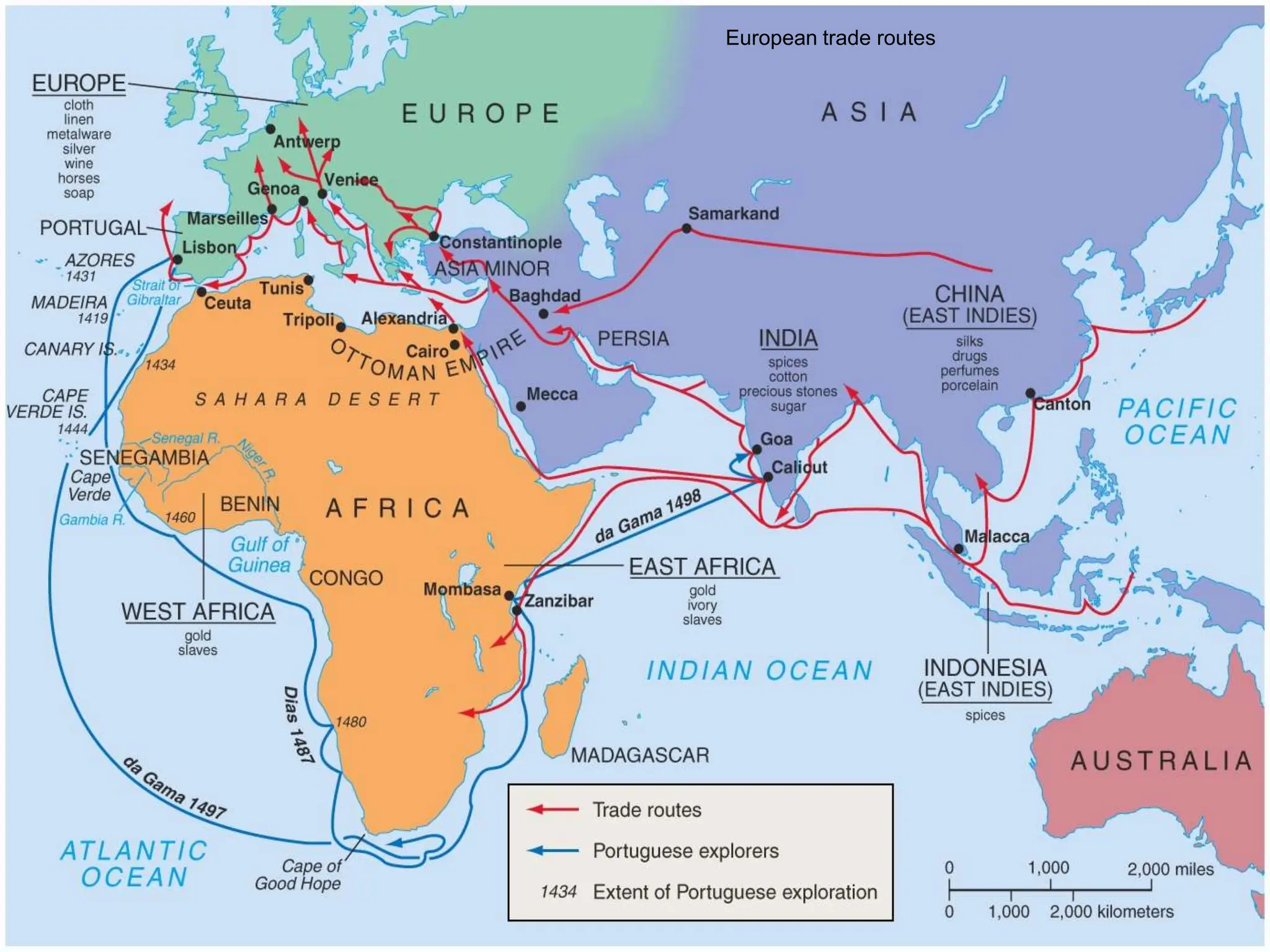
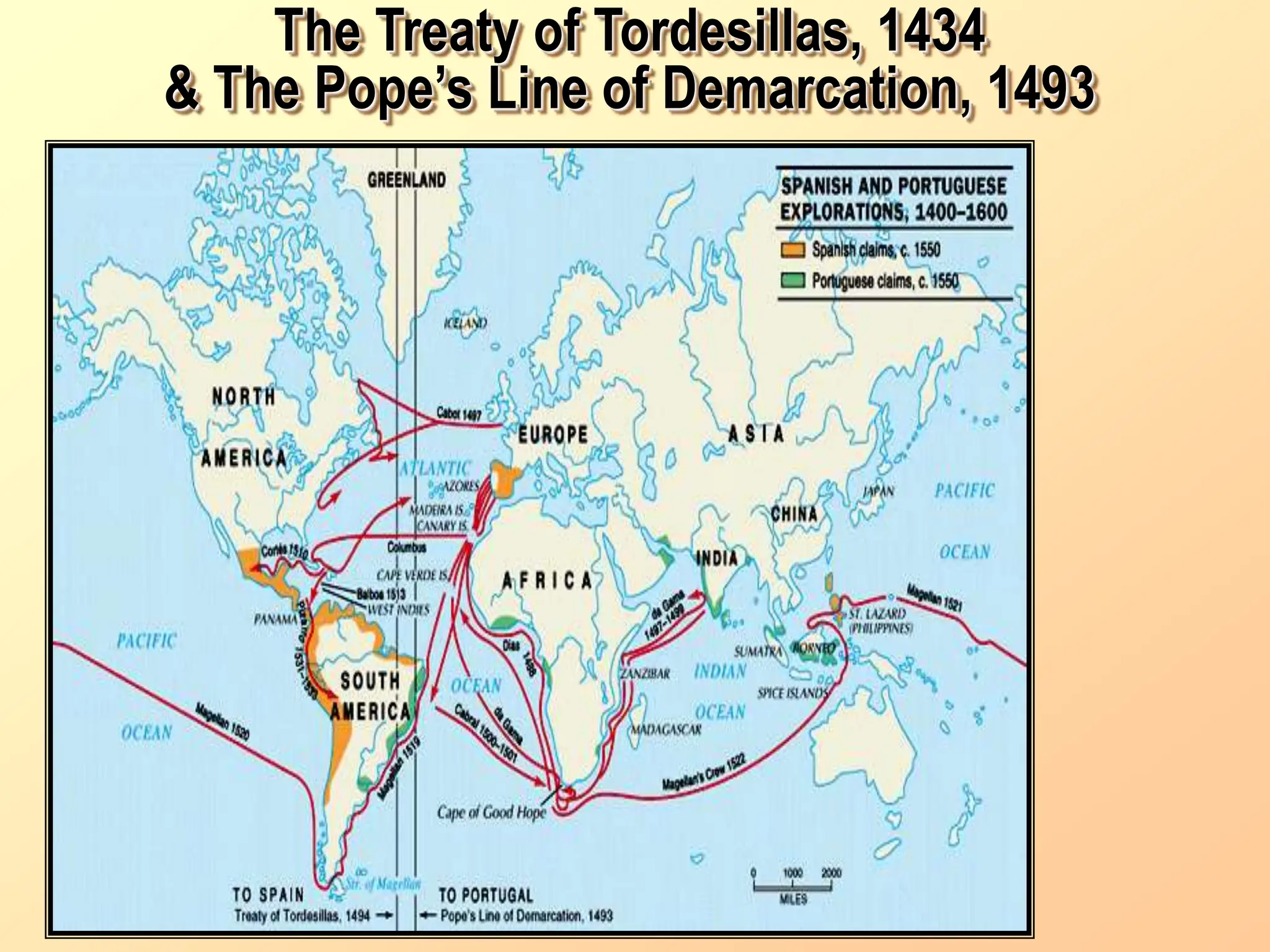
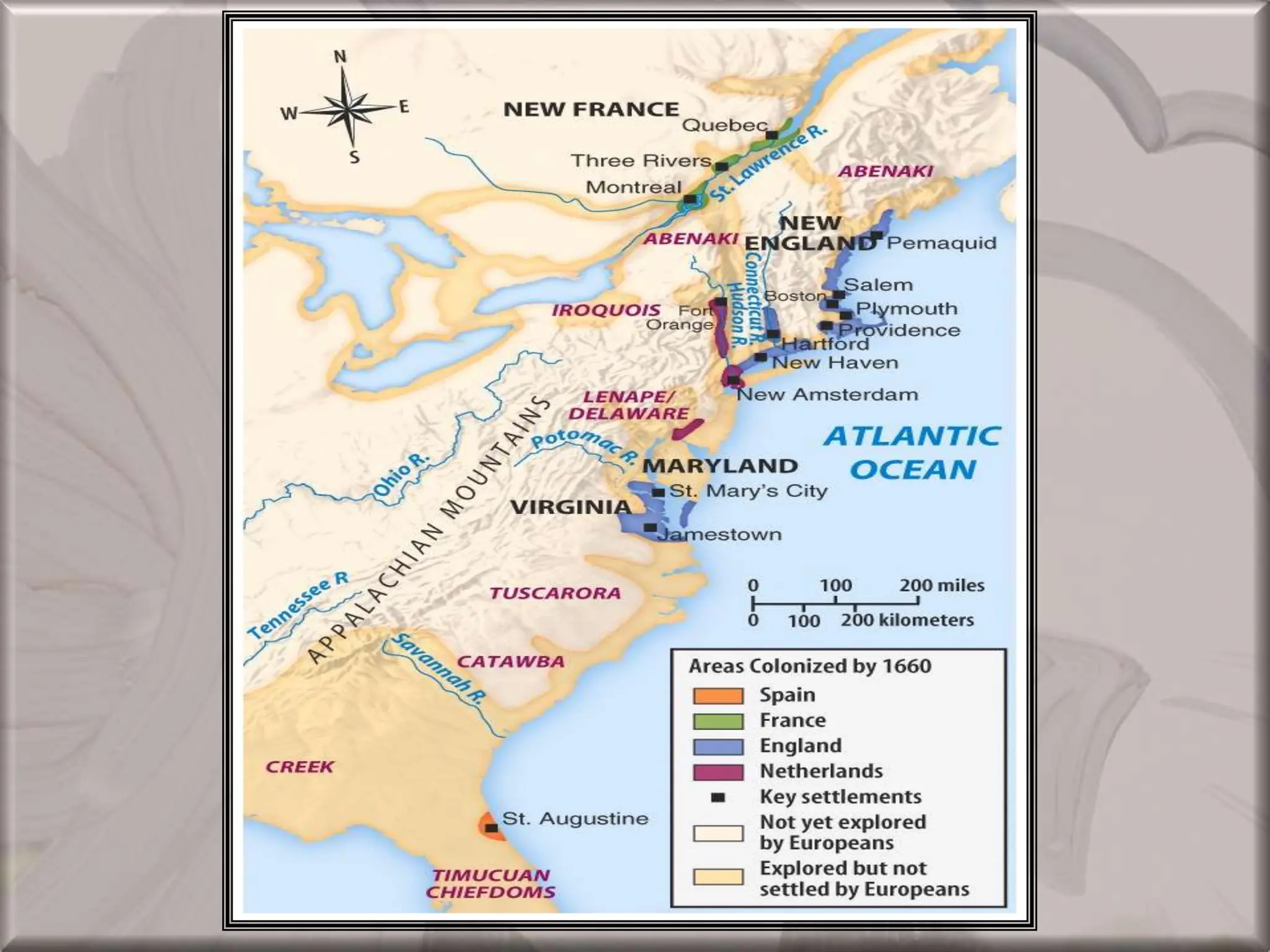
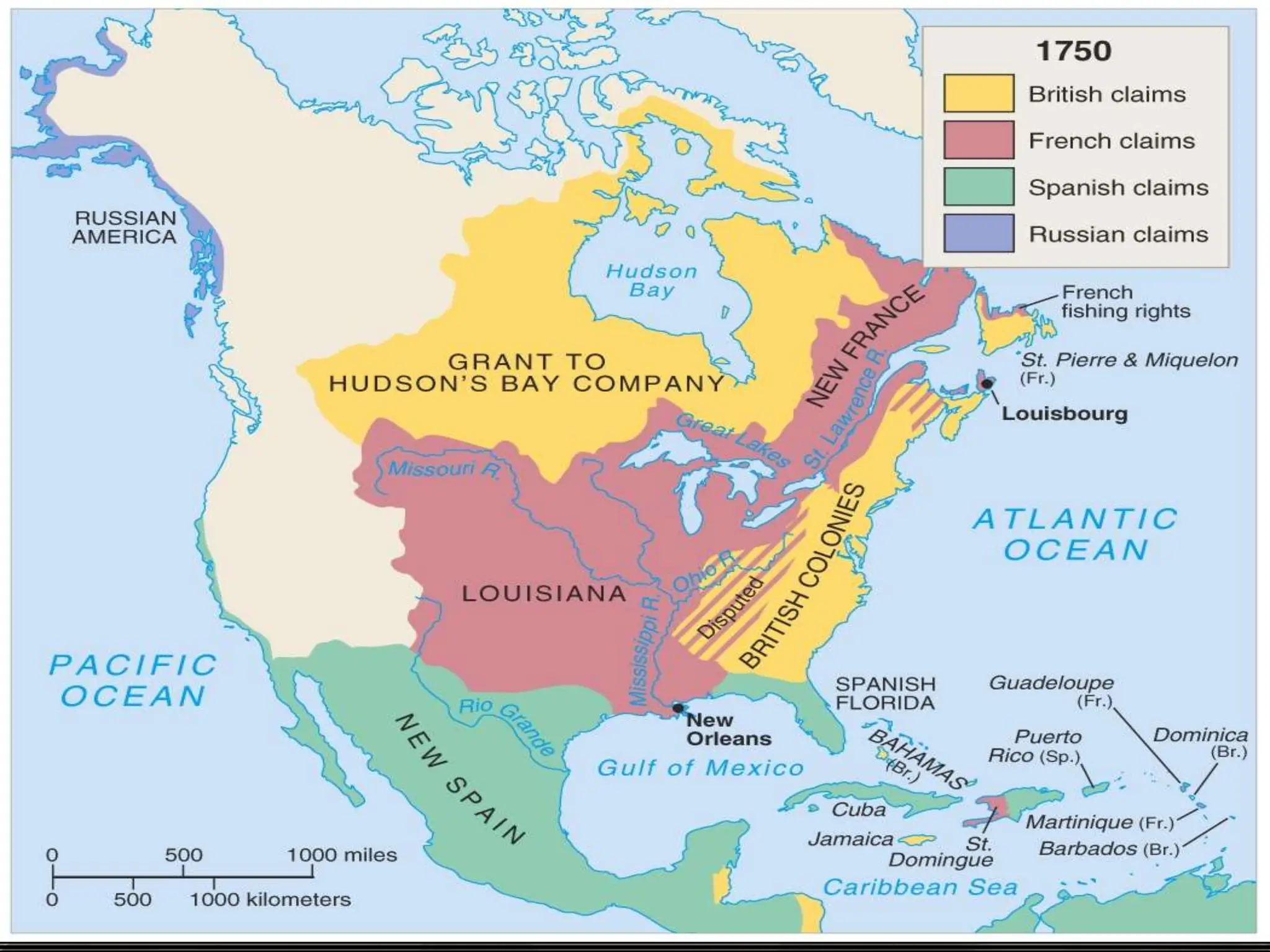
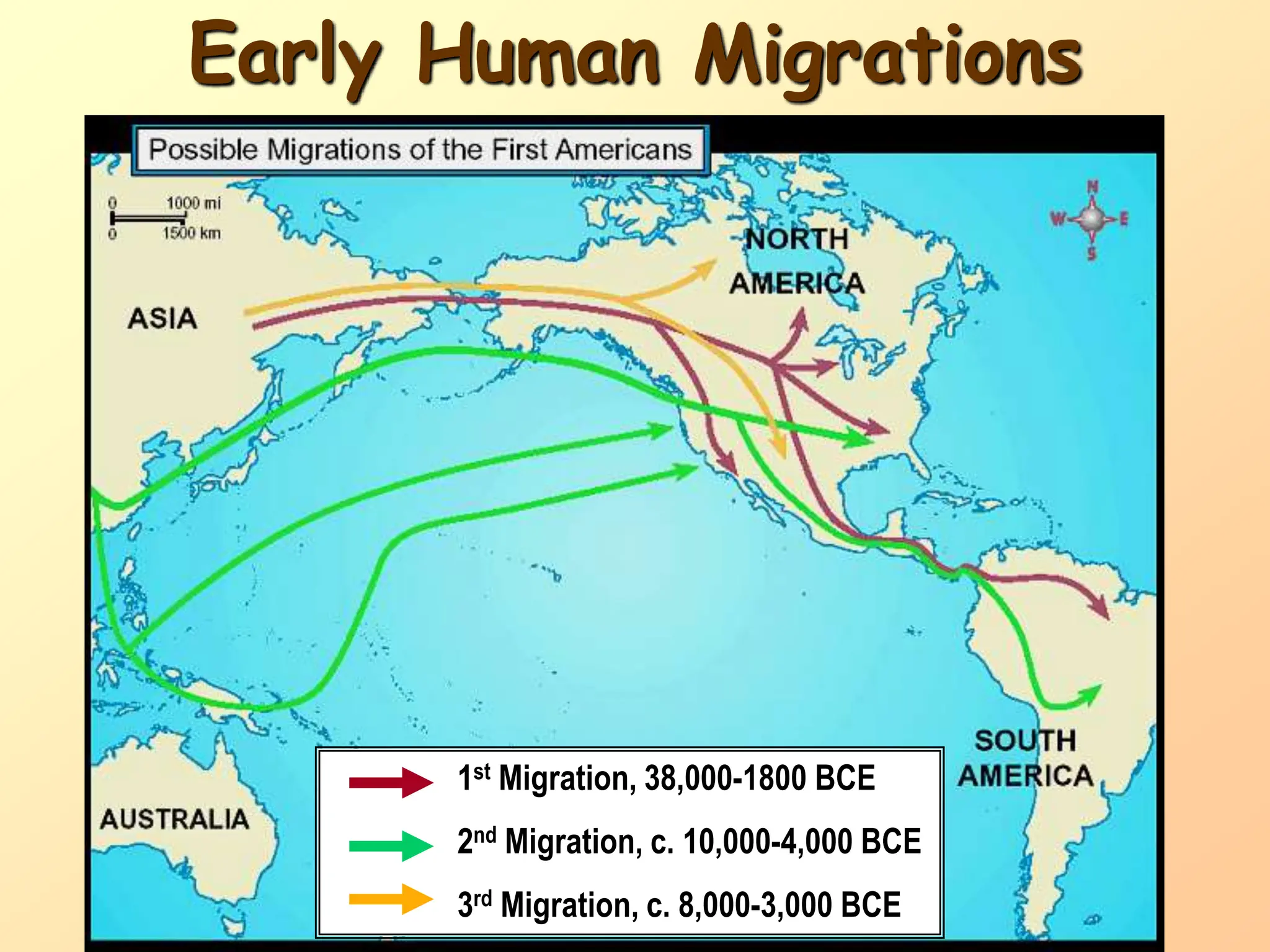
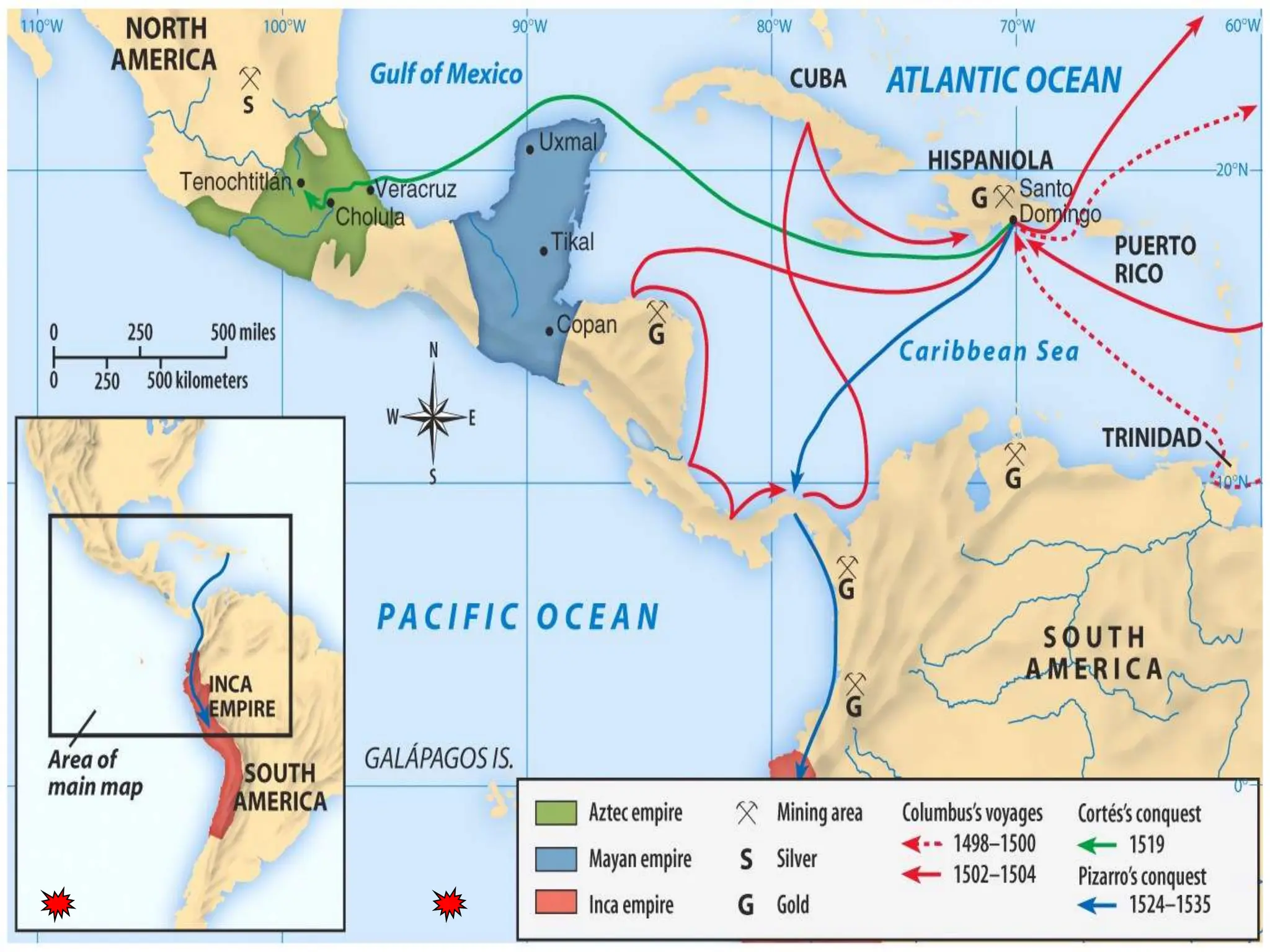
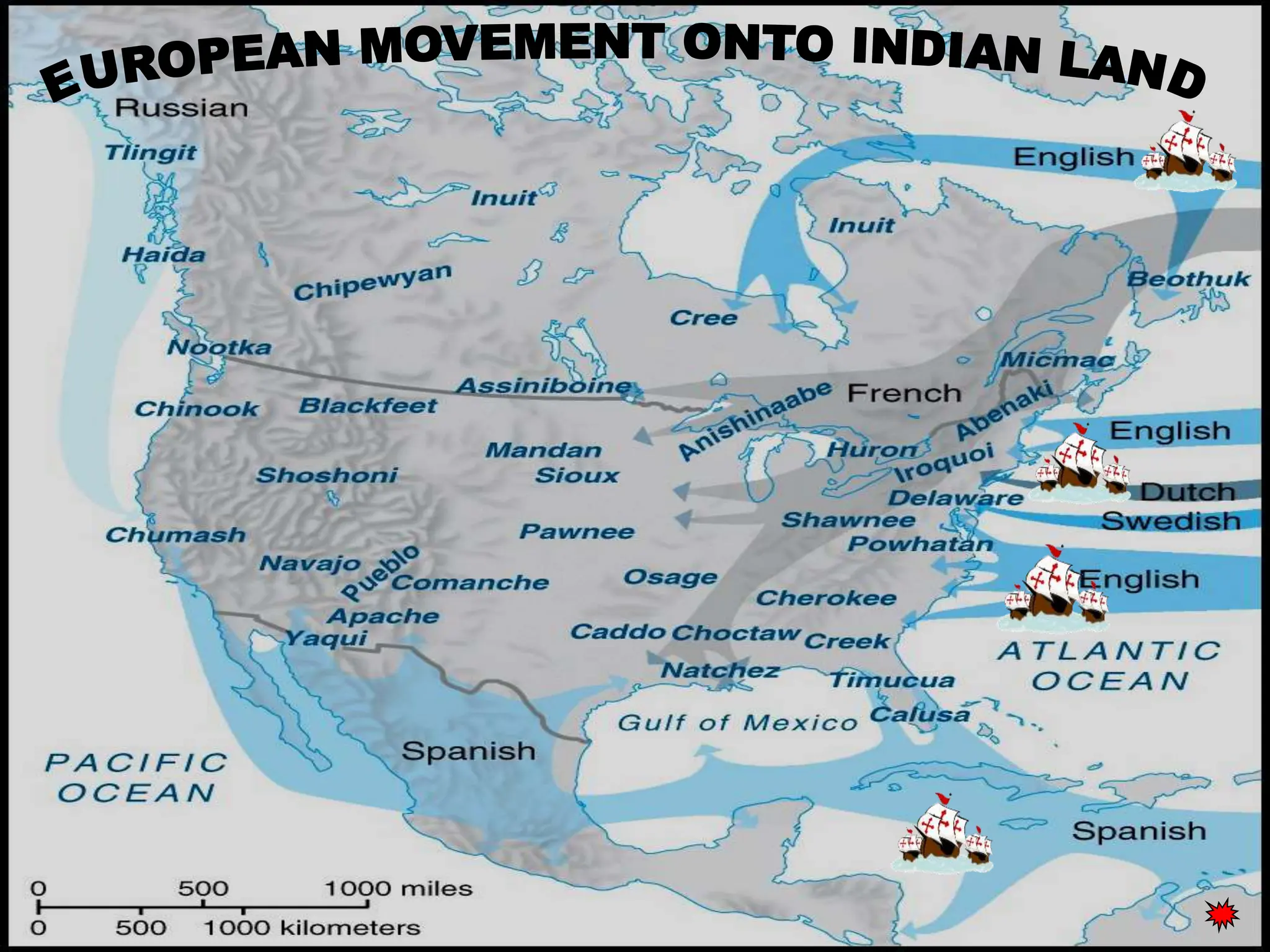
The document discusses the migration of the first Americans from Asia across the Bering Strait during the Ice Age and the subsequent European exploration and colonization of the Americas. It outlines the motivations for European exploration, such as the search for new trade routes, wealth, and the spread of Christianity, as well as the major European powers involved, including Spain, France, and Portugal. Additionally, it details the impact of these interactions on Native American populations and the establishment of colonial systems.








![New Maritime Technologies
Hartman Astrolabe
(1532)
Better Maps
[Portulan]
Sextant
Mariner’s Compass](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/01discoveryandsettlementofanewworld-240508153330-baa96b3b/75/01_Discovery_and_Settlement_of_a_New_World-ppt-12-2048.jpg)