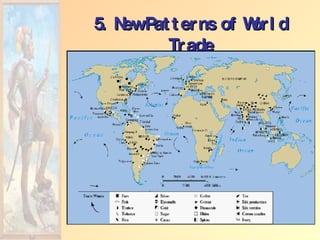
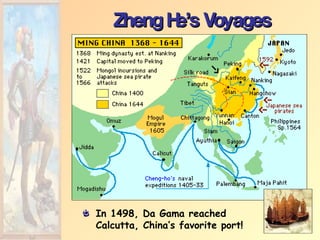
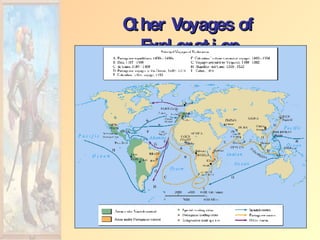
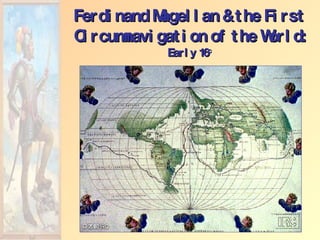
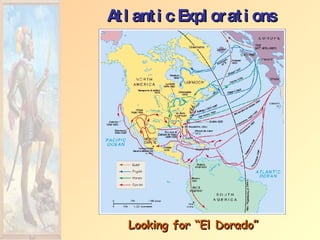
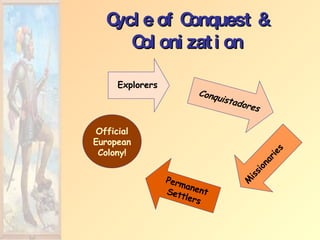
The document summarizes early European exploration and conquests from the 15th to 17th centuries. It discusses key explorers like Columbus, Magellan, and da Gama and their voyages that led to contact between Europe, Africa, Asia, and the Americas. It also outlines the establishment of European colonial empires in the Americas and their systems of administration, including the encomienda system and the influence of the Catholic Church. European expansion resulted in devastating impacts like disease epidemics among native populations and the transatlantic slave trade.





![New Maritime Technologies Hartman Astrolabe (1532) Better Maps [Portulan] Sextant Mariner’s Compass](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/european-exploration-and-colonization-119987558692008-3/85/European-Exploration-And-Colonization-6-320.jpg)




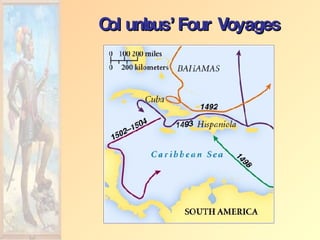
![Christofo Colon [1451-1506]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/european-exploration-and-colonization-119987558692008-3/85/European-Exploration-And-Colonization-12-320.jpg)






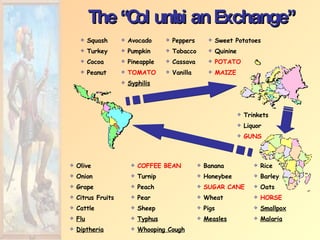
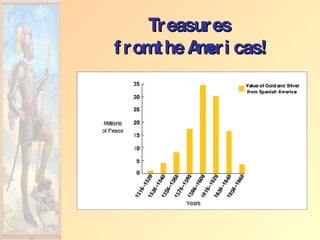
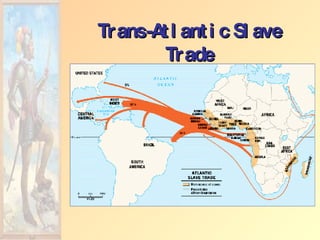




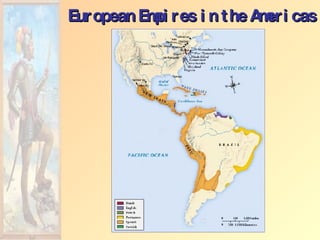
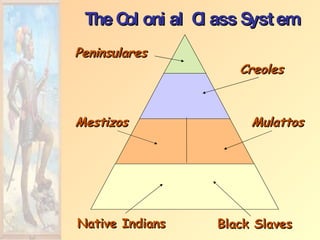


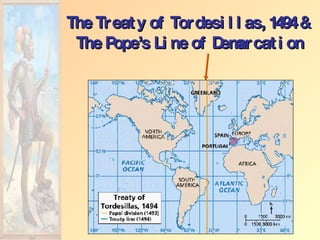


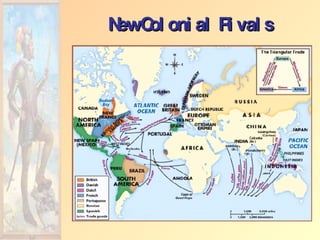
![Impact of European Expansion Native populations ravaged by disease. Influx of gold, and especially silver, into Europe created an inflationary economic climate. [ “Price Revolution” ] New products introduced across the continents [“Columbian Exchange”]. Deepened colonial rivalries.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/european-exploration-and-colonization-119987558692008-3/85/European-Exploration-And-Colonization-39-320.jpg)