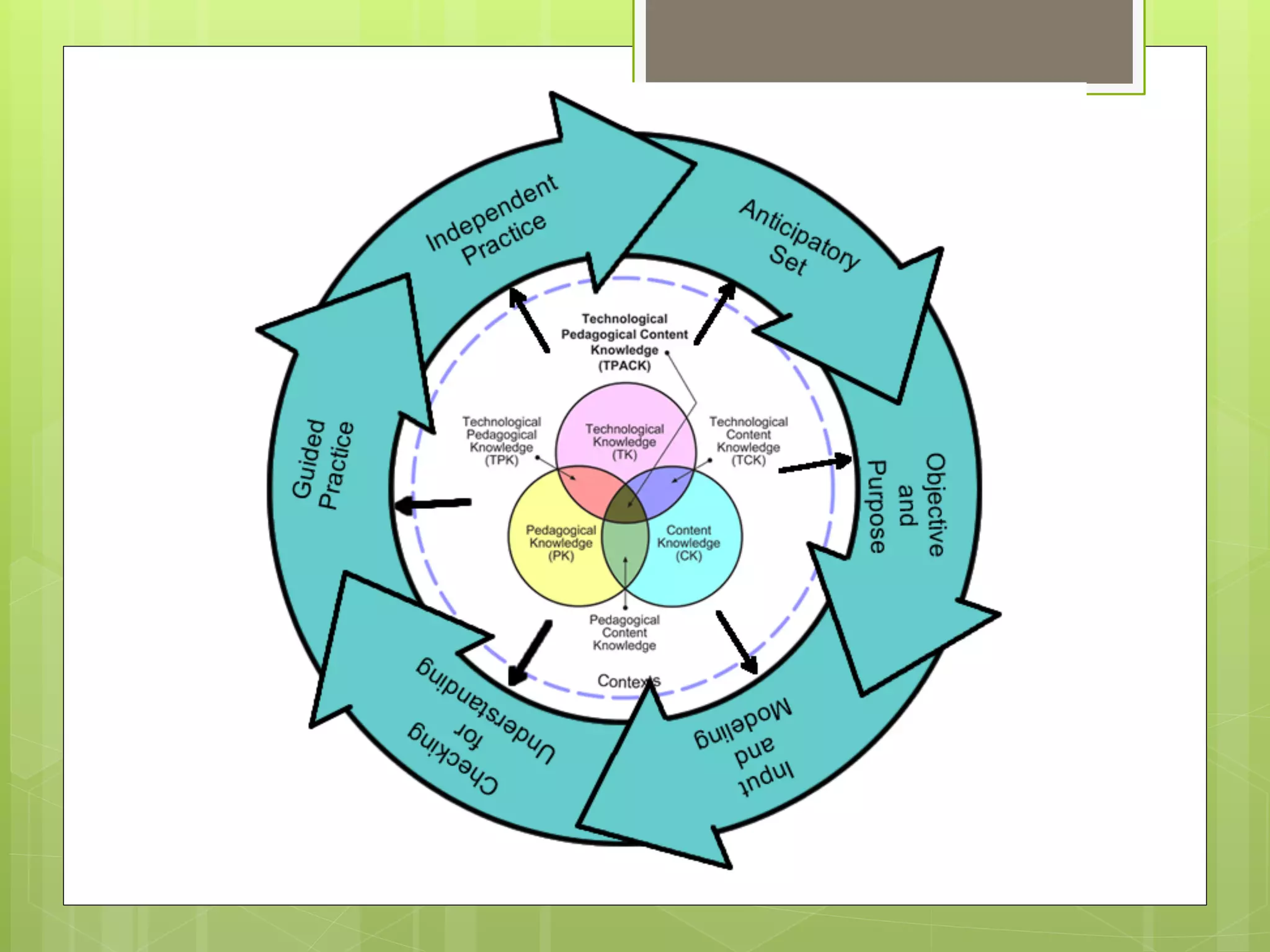
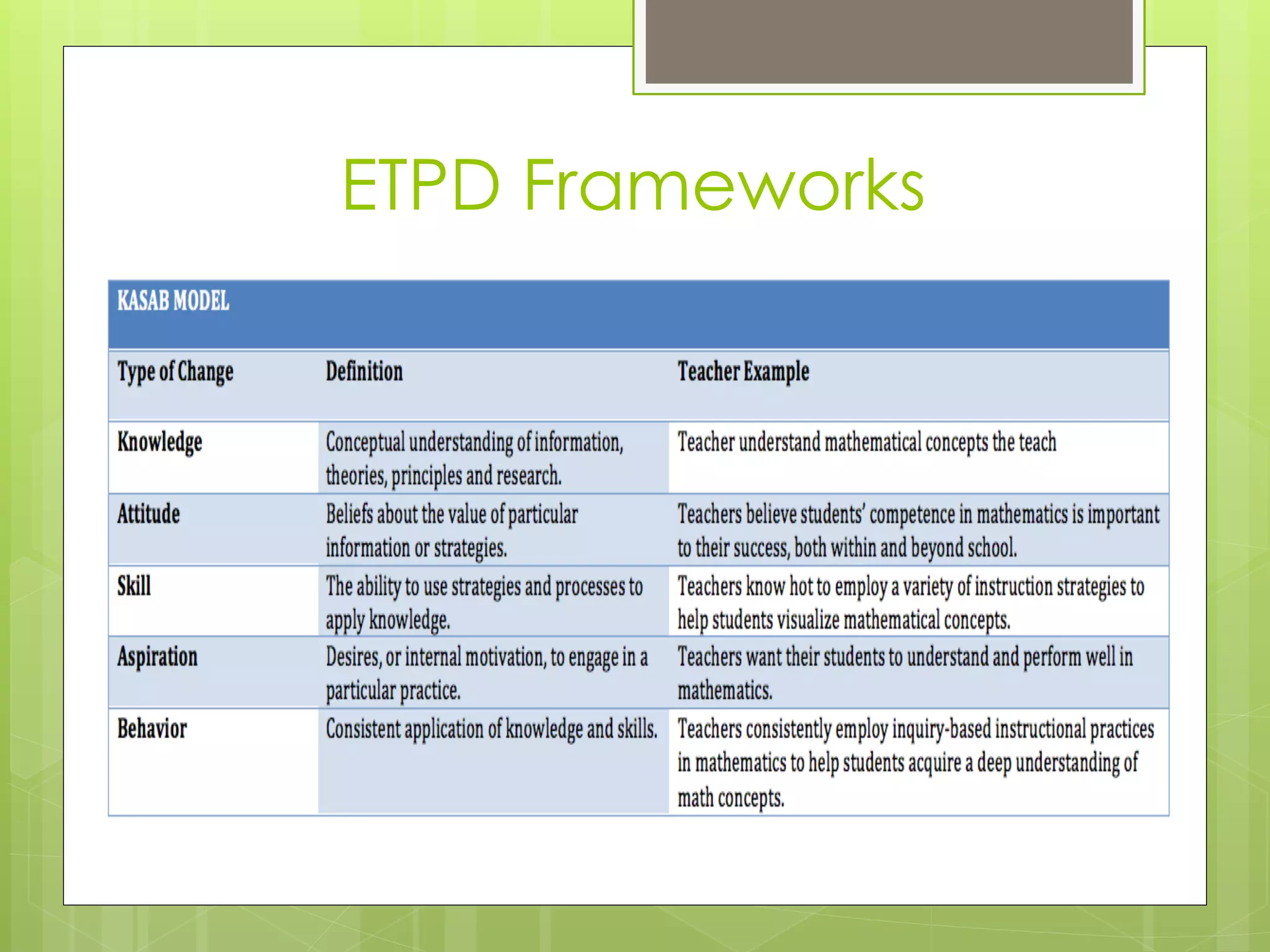
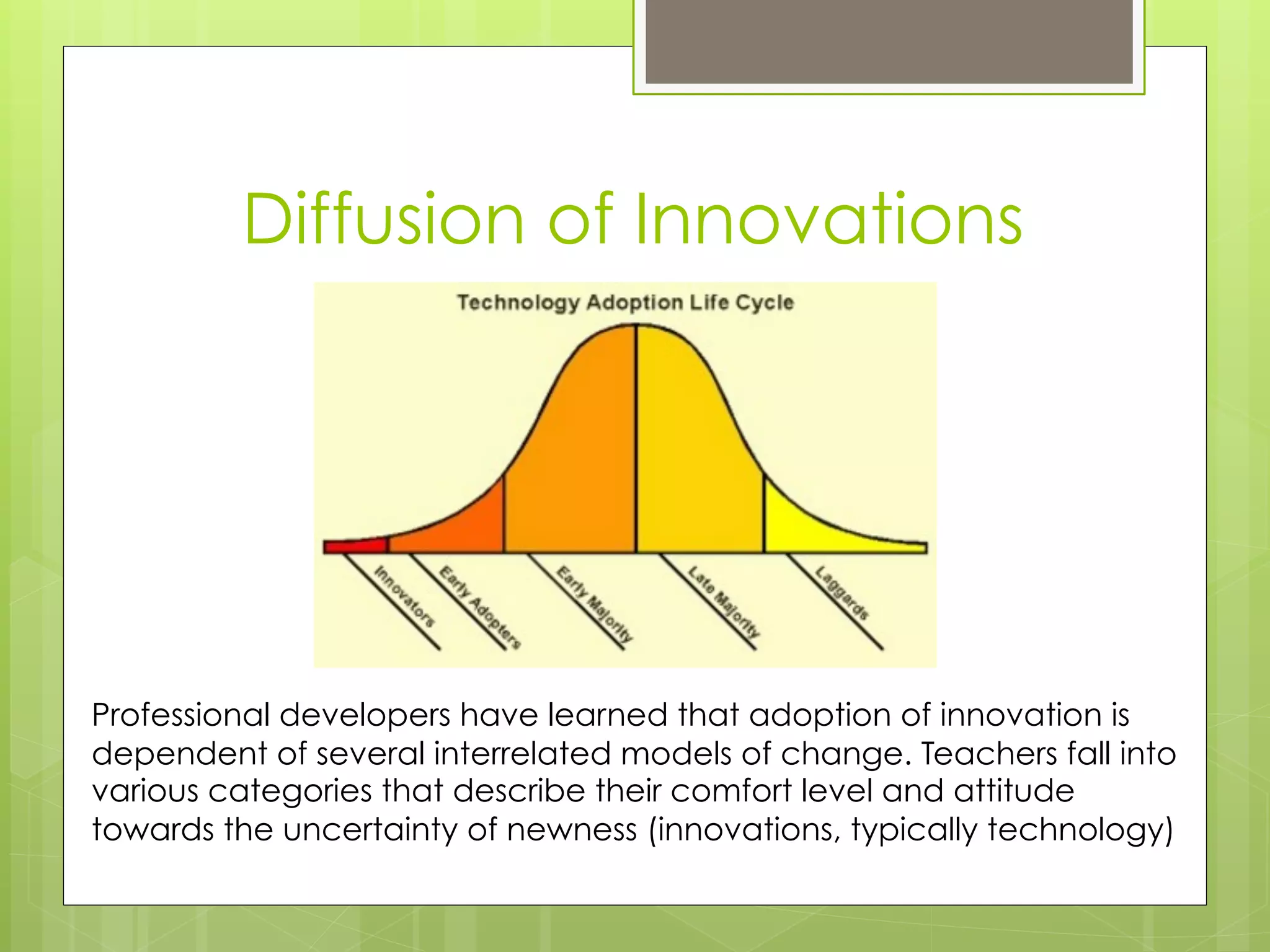
This document summarizes best practices and frameworks for effective professional development (PD). It notes that while mentoring, peer coaching, hands-on activities, and other strategies show promise, the field has not agreed on what makes PD truly effective. The document discusses frameworks like TPACK that emphasize teachers understanding content, pedagogy and technology, and knowing when each is appropriate. It also contrasts linear one-time PD with cyclical PD that incorporates reflection, collaboration, observation and ongoing evaluation. Finally, it questions how to ensure high fidelity of PD implementation and encourage adoption of innovations.