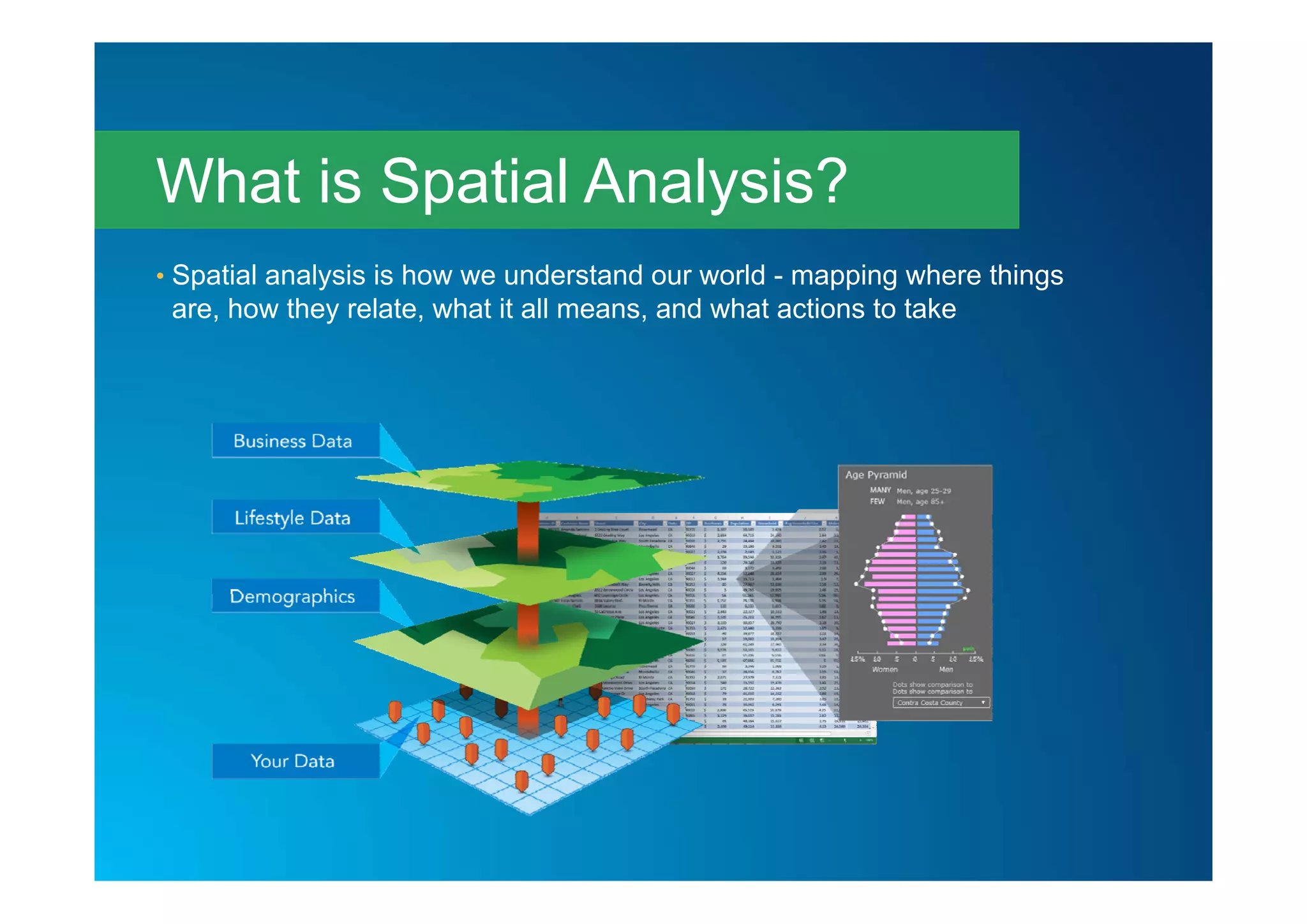
This document summarizes a presentation on spatial analysis given at the Esri UK Annual Conference in 2015. Spatial analysis involves understanding where things are located, measuring their size, shape and distribution, determining how places relate to each other, finding optimal locations, detecting patterns, and making predictions. The presentation categorized spatial analysis techniques and provided examples of how they can be used to gain insight, make more informed decisions, and achieve objectives like reducing costs and increasing efficiency. It concluded by listing common business benefits of spatial analysis and directing attendees to case studies on the Esri UK website.