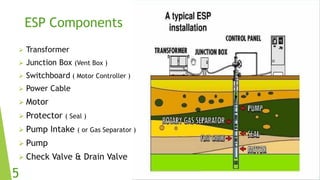
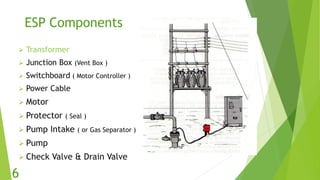
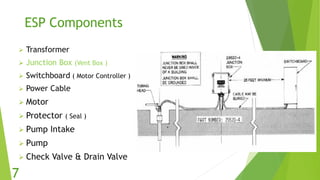
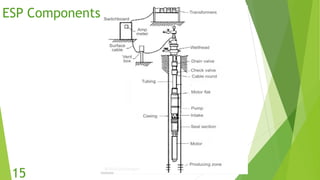
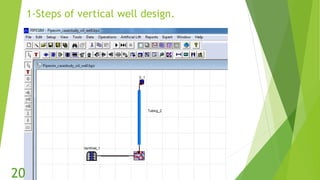
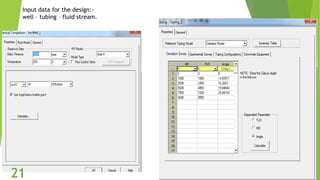
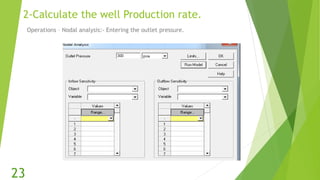
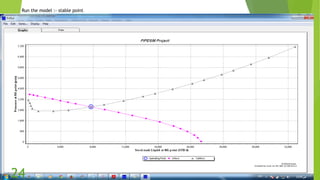
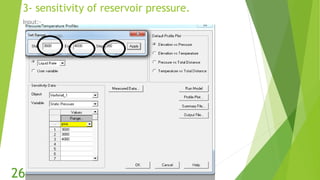
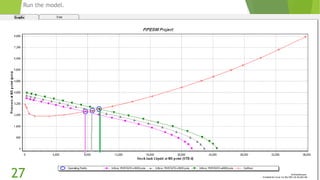
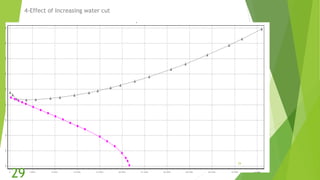
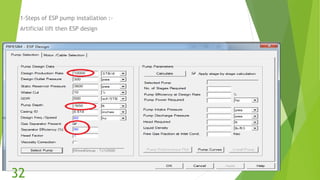
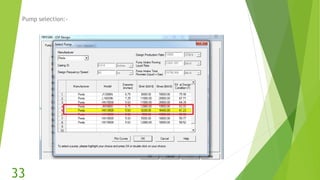
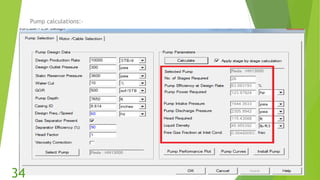
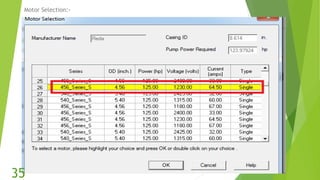
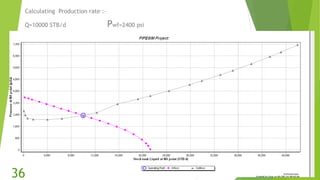
The document presents an overview of electric submersible pumps (ESP), detailing their operating principles, components, advantages, and disadvantages. It also covers the application of ESP pumps in well production, including the design, installation, and performance assessment through a case study using Pipesim software. Key components include a transformer, motor, and various valves, while the advantages include high production rates and environmental benefits, contrasting with the disadvantages of expenses and efficiency drops.