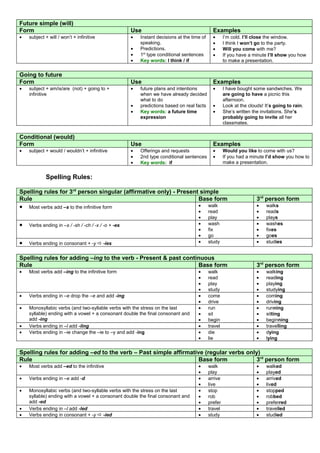
This document provides information on tense forms and usage in English, including:
- The present simple, present continuous, past simple, past continuous, present perfect, future with will, future with going to, and conditional tenses.
- Examples of each tense's form and common uses.
- Spelling rules for the third person singular in the present simple, adding -ing, and adding -ed to regular verbs.