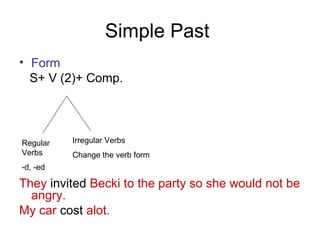
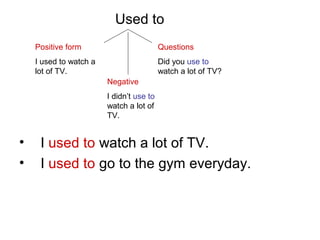
The document provides an overview of the simple past and past continuous tenses in English, detailing their forms, uses, and examples. It highlights how to construct questions and negatives for both tenses and discusses time clauses and contrasting past actions with present habits using 'used to' and 'would.' Additionally, it includes a freewriting activity and emphasizes the context of events and actions in the past.