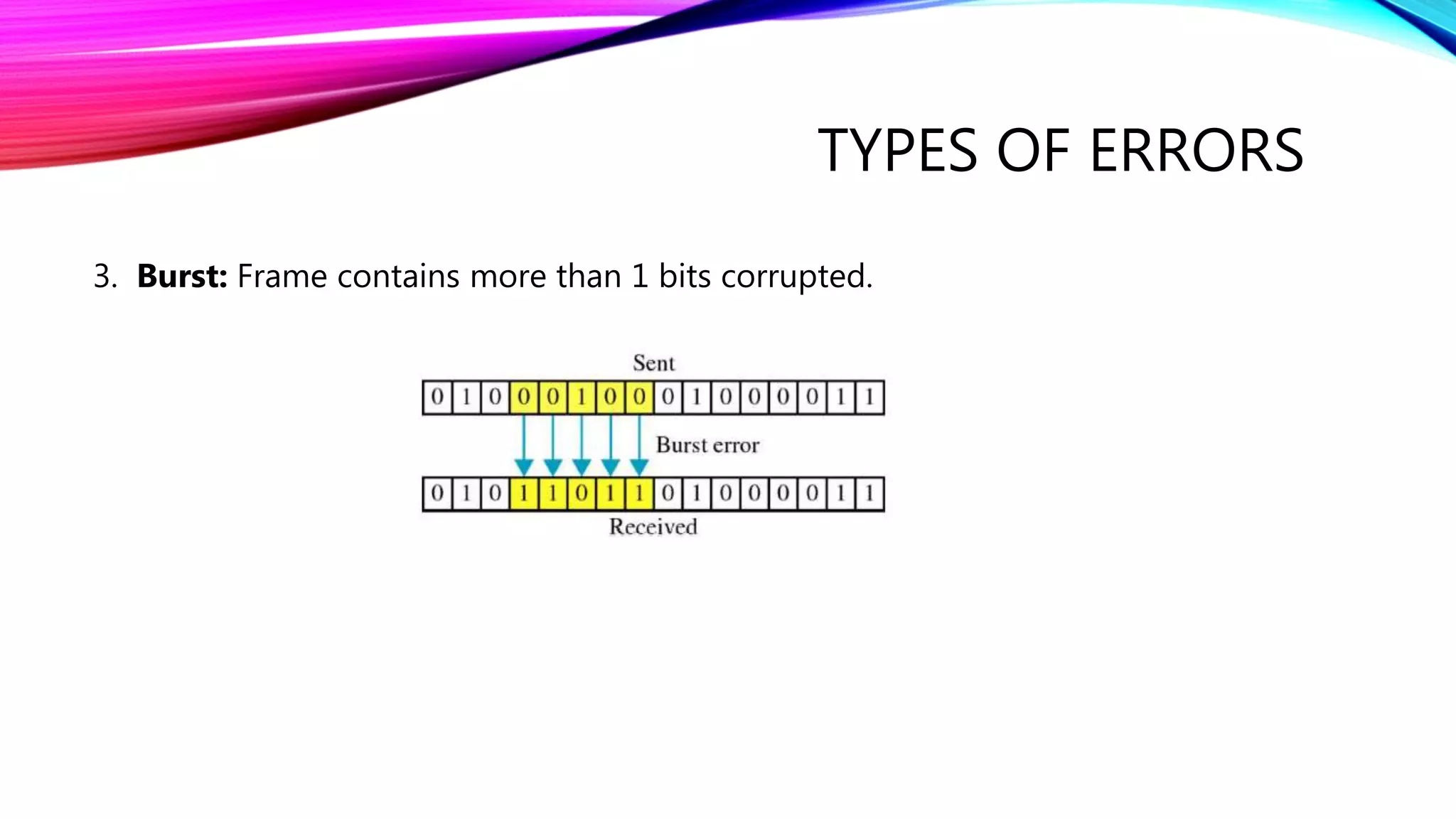
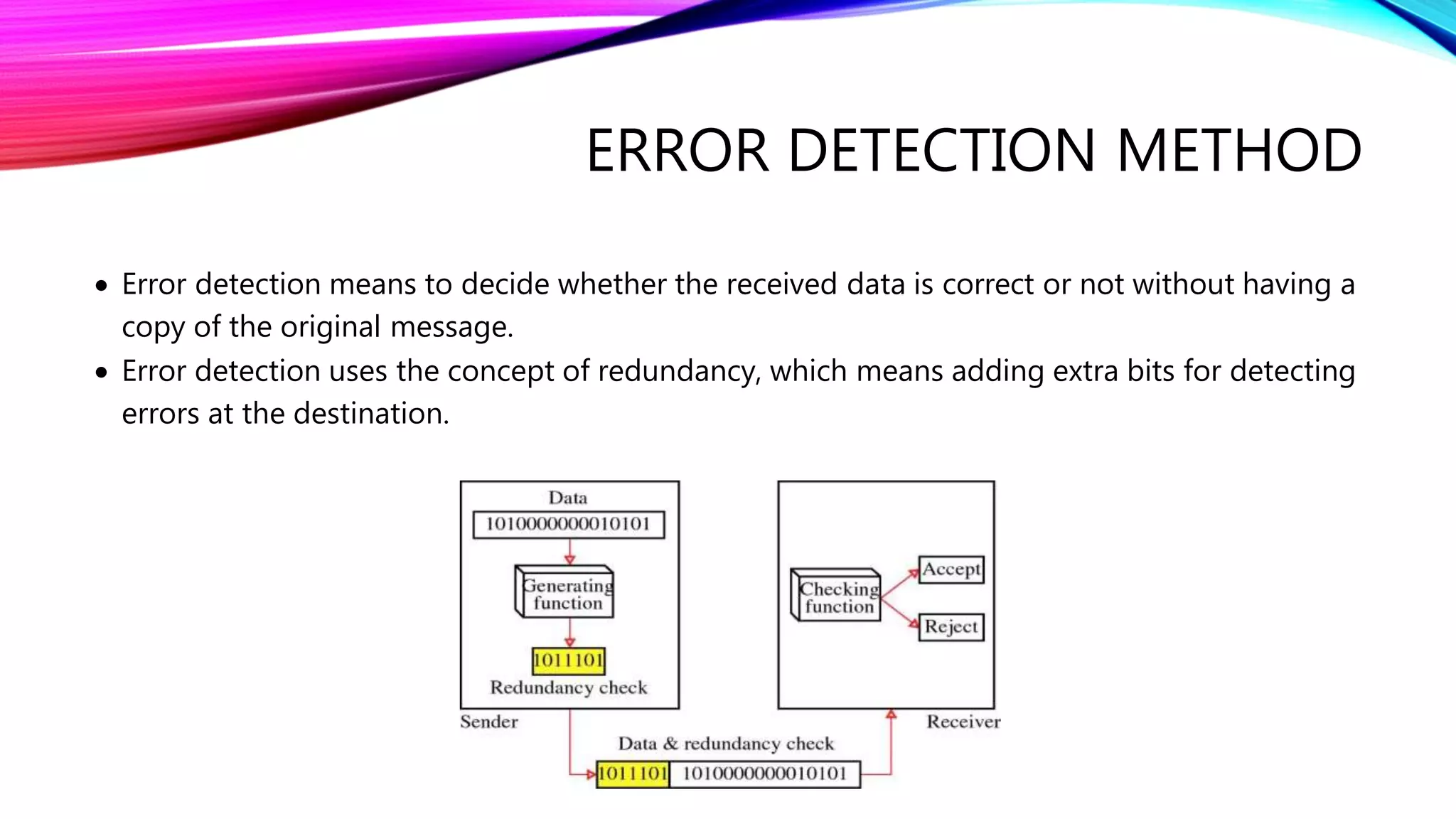
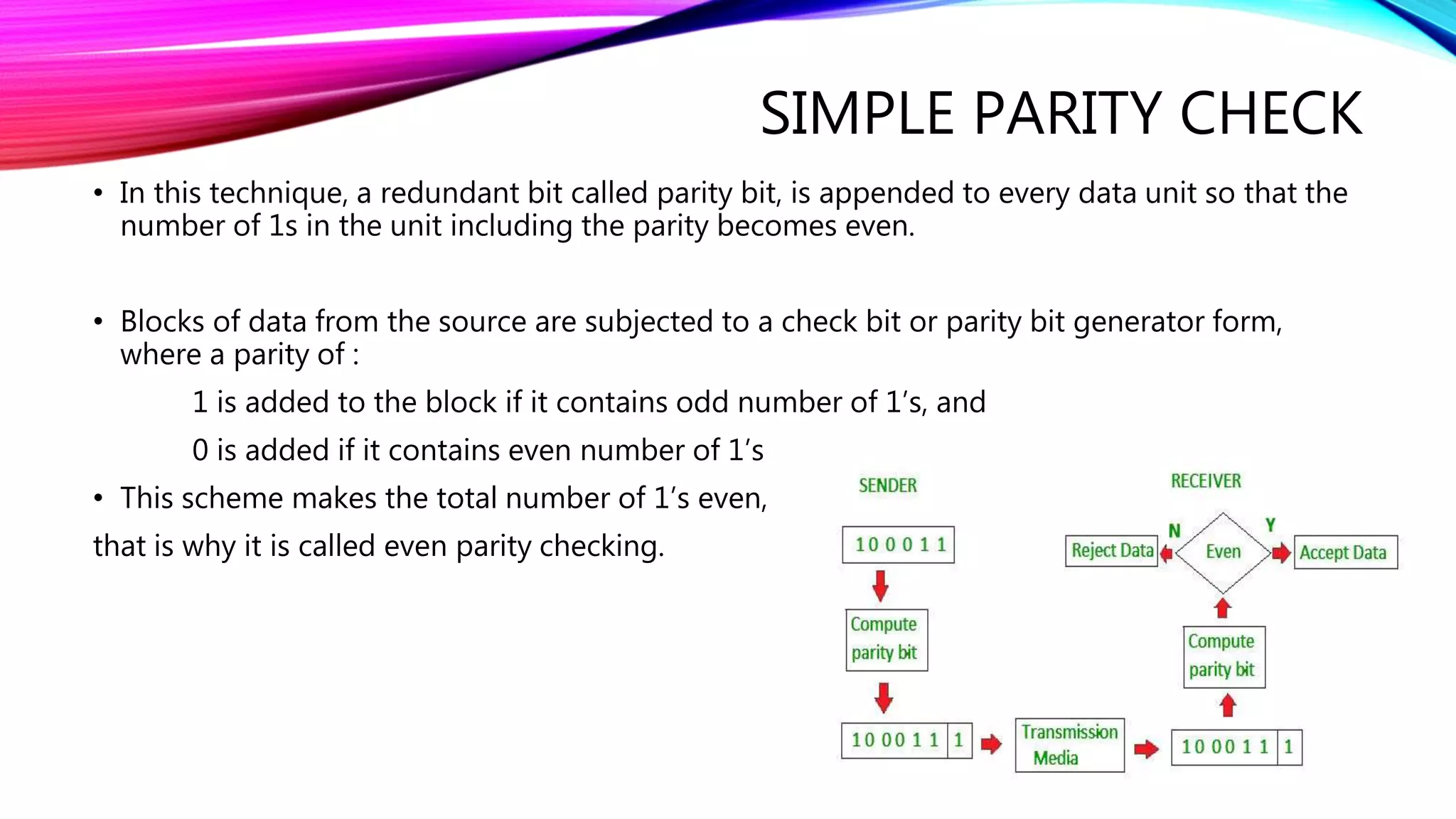
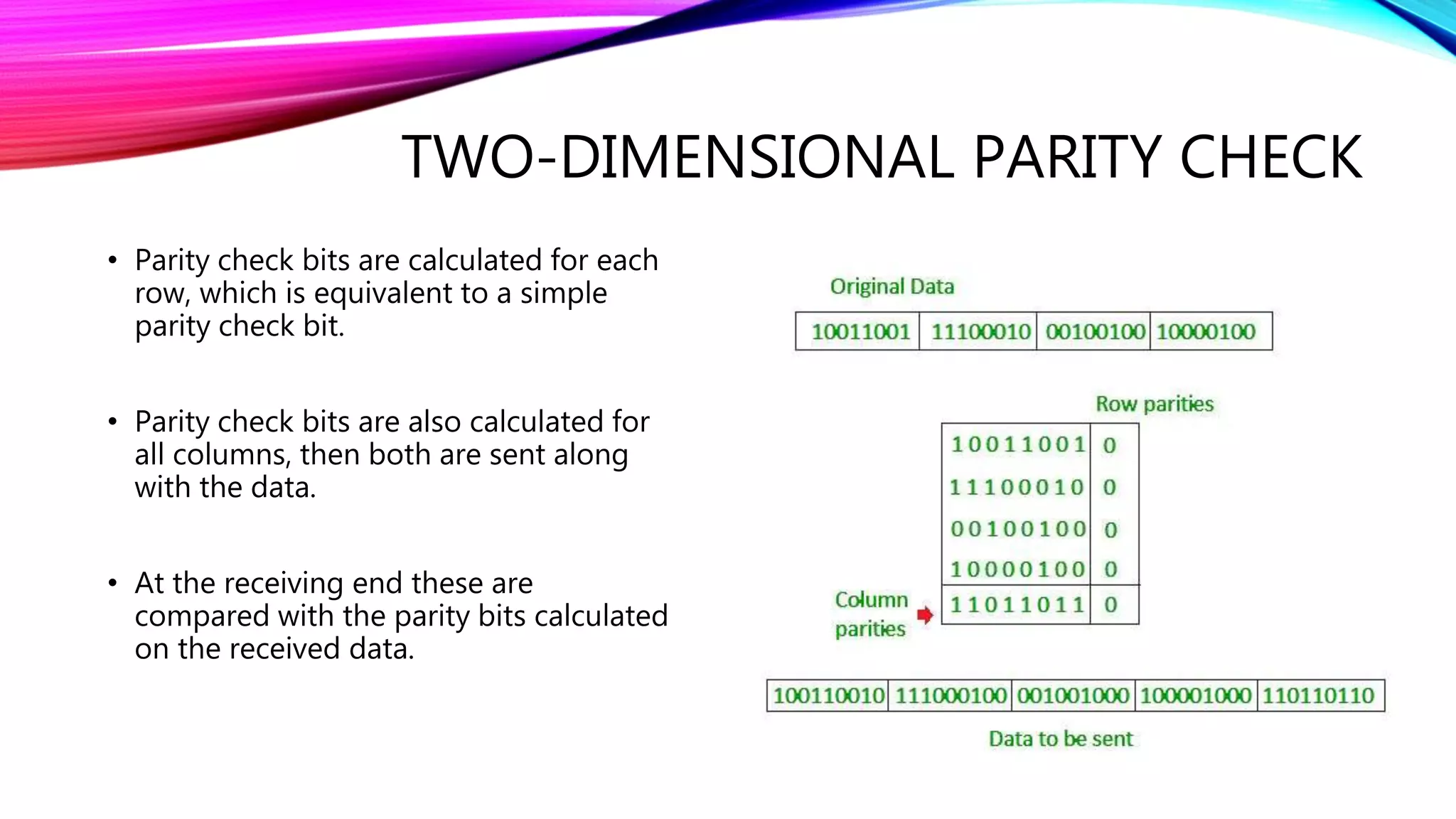
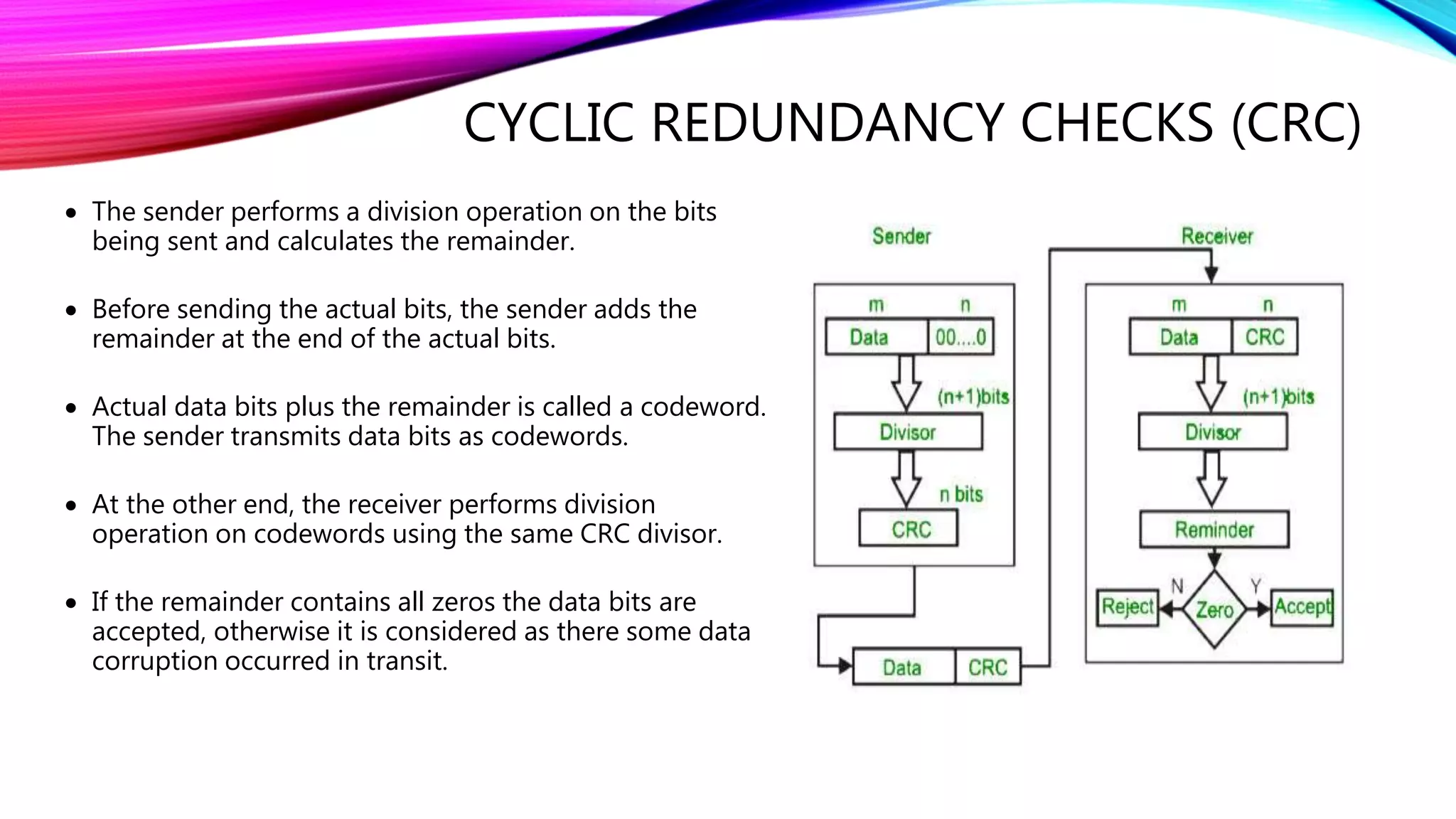
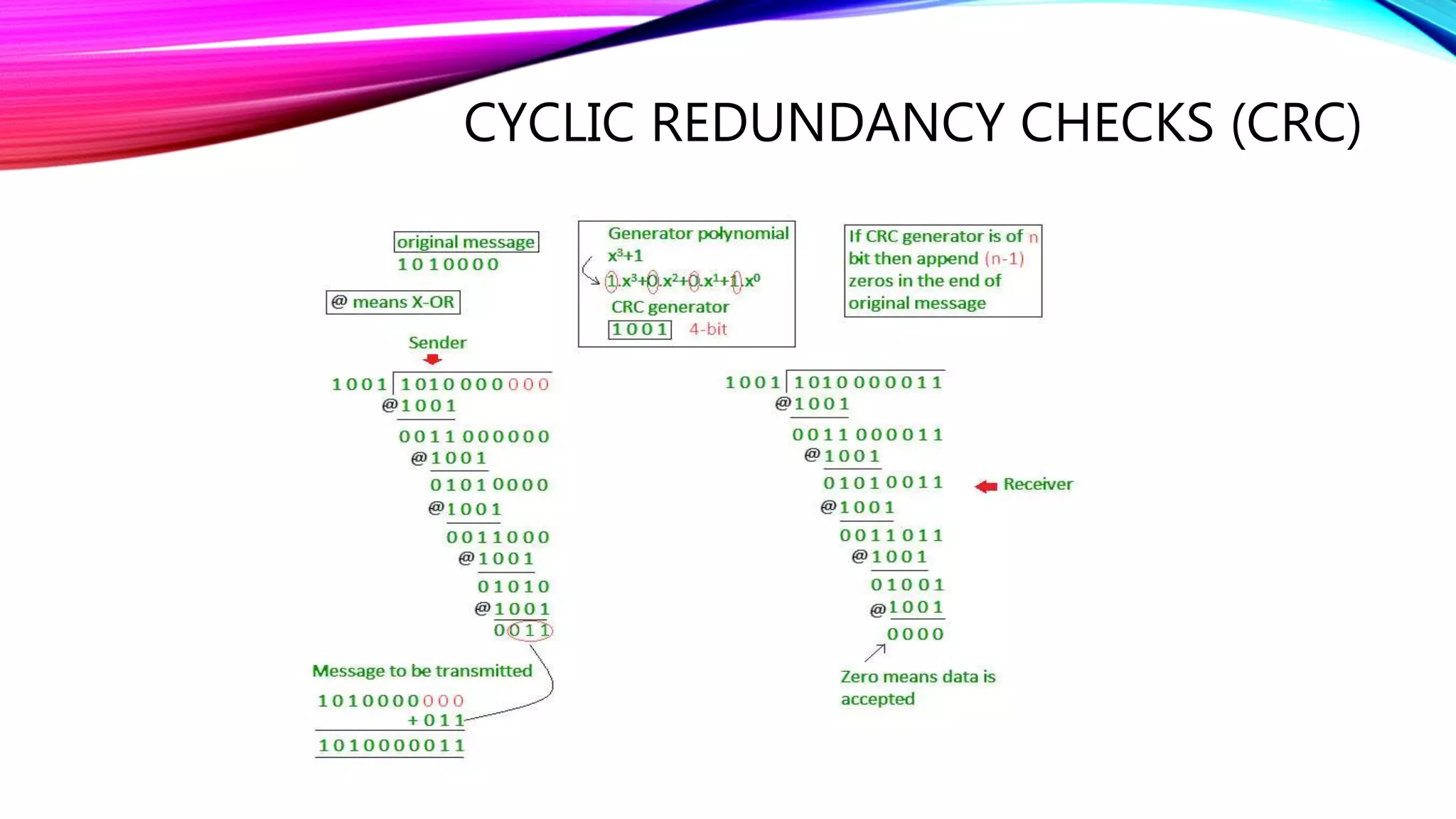
The document discusses error detection and correction techniques essential for reliable communication, covering various types of errors such as single bit, multiple bit, and burst errors. It details several methods, including simple parity checks, two-dimensional parity checks, checksums, and cyclic redundancy checks (CRC), highlighting their mechanisms and performance in detecting errors during data transmission. CRC is emphasized as the most effective and simple method, utilizing polynomial division to ensure data integrity.