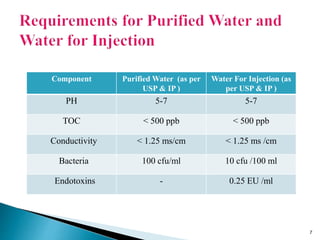
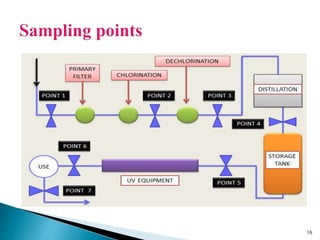
This presentation discusses the validation of water systems used in pharmaceutical manufacturing. It covers the need for high quality water and purification systems, as well as the various qualification activities involved in validating such systems, including design qualification, installation qualification, operational qualification, and performance qualification. The presentation provides details on regulatory requirements and specifications for purified water and water for injection. It emphasizes that validation is necessary to ensure water systems consistently produce water meeting quality standards to avoid contamination of pharmaceutical products.