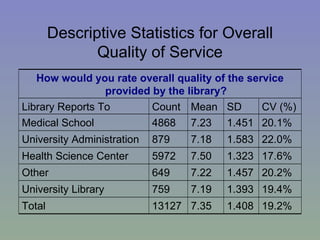
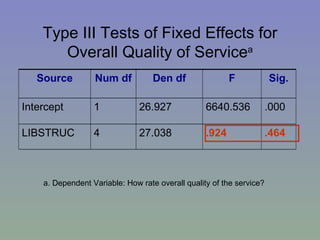
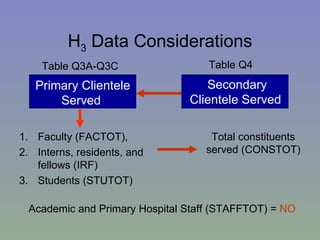
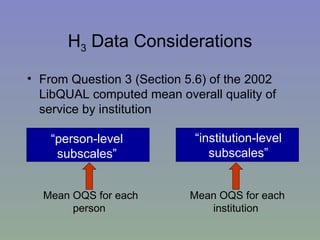
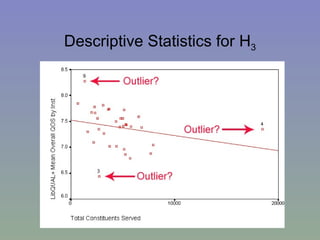
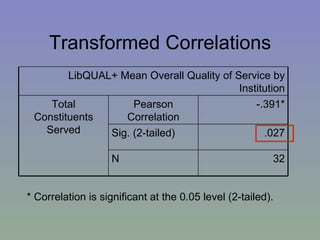
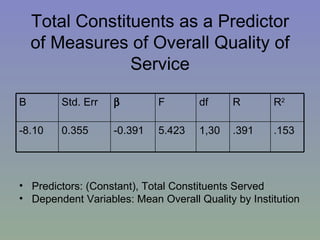
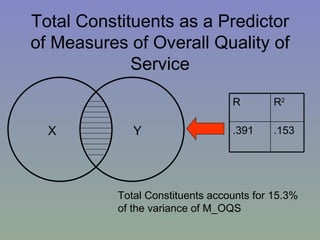
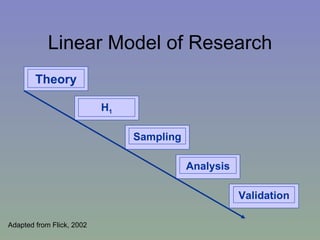
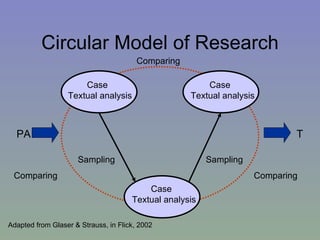
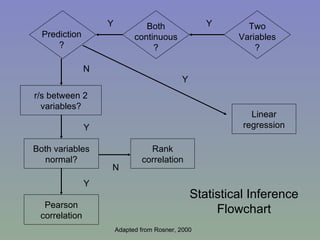
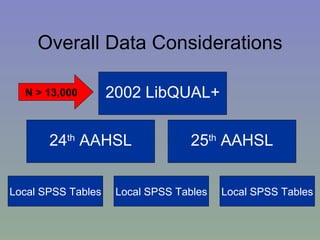
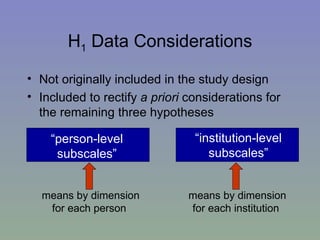
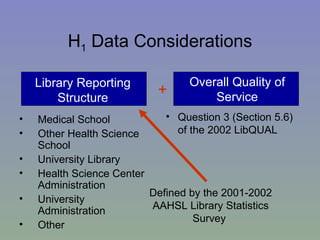
The document outlines a mixed-model approach to assessment in academic libraries, emphasizing the need to create a culture of assessment to enhance service quality and meet customer expectations. It discusses statistical analysis methods used to evaluate library service quality, including the impact of reporting structures and the number of constituents served on satisfaction ratings. The findings from various surveys, including LibQUAL+, are used to support the hypotheses related to quality of service and institutional characteristics.












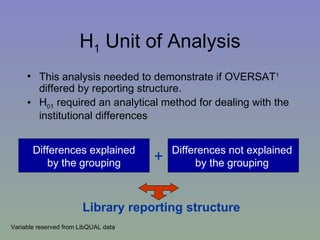
![H 1 Unit of Analysis A Linear Mixed Model (LMM) allowed me to control for fixed and random effects OVERSAT [DV] = LIBSTRUC [IV1] + INSTID(LIBSTRUC) [IV2] Fixed-effects Random-effects](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2004mla-100406101444-phpapp01/85/E-p-owering-Your-Institution-26-320.jpg)