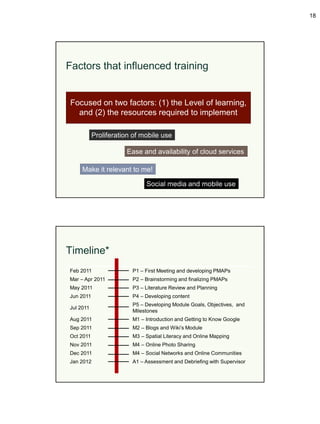
The document describes the development of a staff training program at the National Institutes of Health (NIH) Library called RATECH (Research Assistant Technology Challenge) to improve staff competencies with emerging technologies like mobile devices, social media, and Web 2.0 tools. The library conducted a needs assessment, developed a curriculum and timeline, implemented training modules, and evaluated the program's effectiveness through surveys and discussions. Key lessons learned included the importance of planning, making training relevant, and addressing varying levels of engagement among staff.





















![27
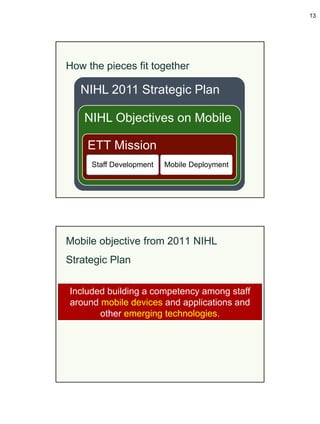
Lessons learned [1]
• How do we encourage the discovery of new services and
applications.
• Evaluating staff competencies with their devices.
• Time to develop & conduct the trainings.
• Determine how to evaluate? What to evaluate?
Lessons learned: [1]
• Planning and establishing goals at the outset are
essential.
• Distribution of work: be prepared for a lot of hand-holding
to get people up to speed.
• Jumping through government-specific TOS jargon/policies
(iTunes, 3G, repurposing the BlackBerry devices).](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/locra2012final-120823133833-phpapp02/85/Developing-Staff-Competencies-in-Emerging-Technologies-27-320.jpg)
![28
Lessons learned: [2]
• Squeezing in time here and there to focus on this entire
initiative does not work very well.
• Make what you are doing relevant. You cannot make
people excited about something.
• Innovation is hard. Even if you have the support of
leadership, implementing something new is not easy.
Lessons learned: [3]
• Just because you are invested in learning new and
innovative things you cannot expect everyone to be super
engaged.
• We had to become innovative in figuring out ways to
encourage staff without explicitly providing instructions.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/locra2012final-120823133833-phpapp02/85/Developing-Staff-Competencies-in-Emerging-Technologies-28-320.jpg)