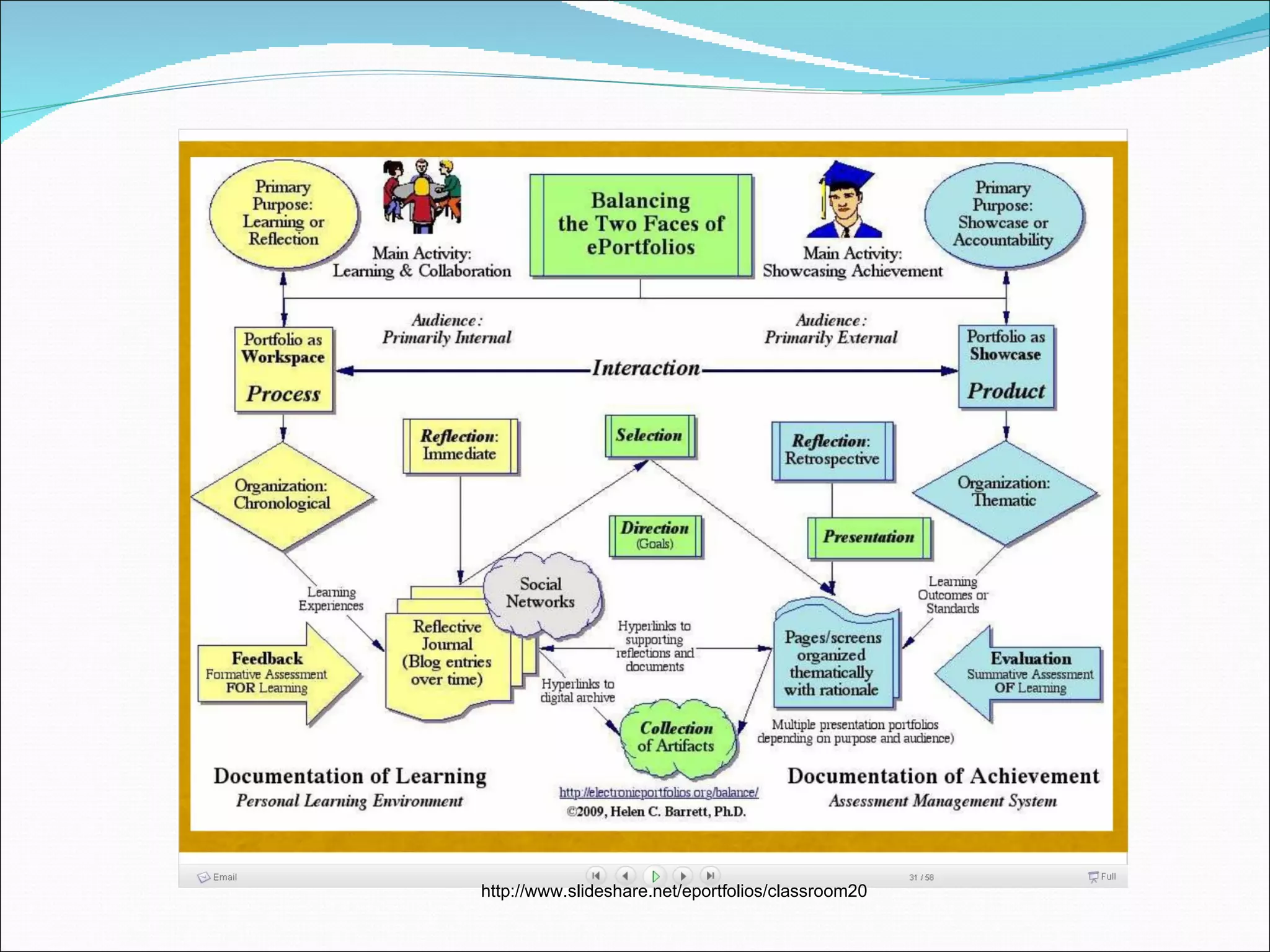
This document discusses the use of ePortfolios for student assessment. It defines an ePortfolio as a digital collection of student work and artifacts that can be used to track student growth over time. The document outlines various purposes and advantages of ePortfolios, such as enabling flexible assessment of skills, facilitating student self-assessment and reflection, and allowing teachers to easily access student work. It also notes some potential disadvantages, such as the need for technology skills and the time required to implement ePortfolios.