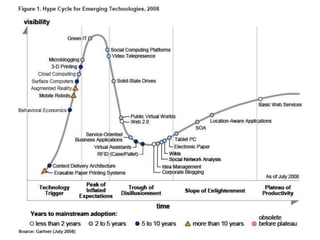
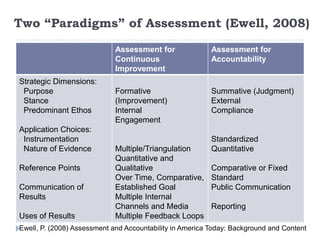
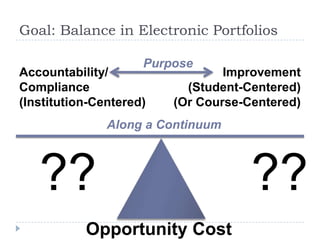
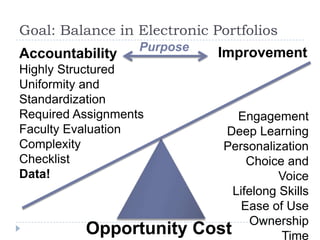
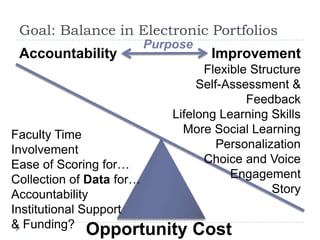
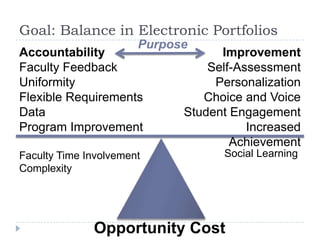
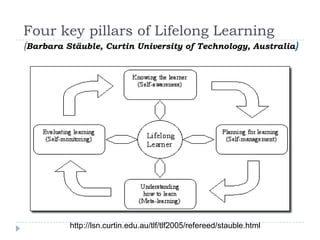
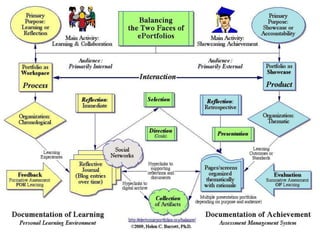
This document discusses balancing the purposes of e-portfolios between student-centered and institution-centered uses. It addresses implementing e-portfolios to support student learning and reflection as well as for evaluation and accountability. The document also discusses using e-portfolios to support lifelong learning through reflection, self-awareness, planning and evaluating learning. Different types of e-portfolio implementations and tools are presented to meet varied purposes.











![What is a Portfolio in Education?A portfolio is a purposeful collection of student work that exhibits the student's efforts, progress and achievements in one or more areas[over time]. (Northwest Evaluation Association, 1990)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/wakeforest0410-100408064010-phpapp01/85/Wake-Forest0410-15-320.jpg)
















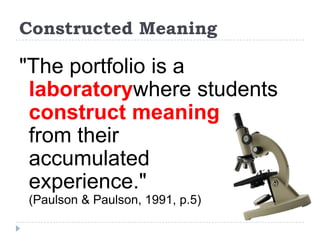


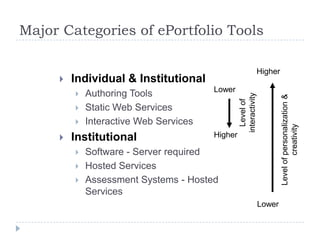
![Categories of E-Portfolio SoftwareCreated as part of my study of different online tools:http://electronicportfolios.org/categories.html“Not just tools for telling[presentation]but more tools for talking![conversation]”- Julie Hughes, University of WolverhamptonConversation transforms!](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/wakeforest0410-100408064010-phpapp01/85/Wake-Forest0410-39-320.jpg)