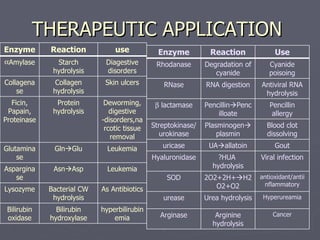
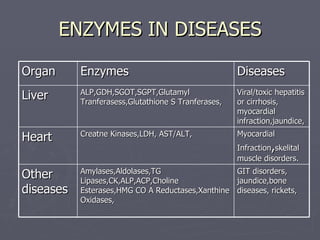
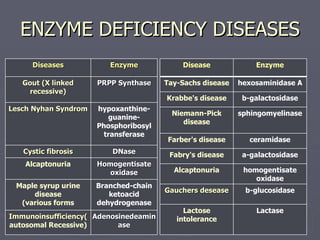
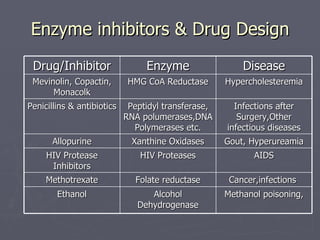
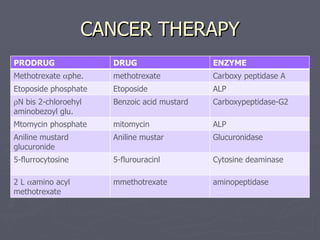
This document discusses various medical applications of enzymes including enzyme therapy for diseases of organs like the liver and kidney, enzyme deficiency diseases, and clinical diagnosis. It also describes the use of enzymes in disease treatment like amylase for digestive disorders and collagenase for skin ulcers. Specific enzymes are discussed in relation to diseases like asparaginase for leukemia and lysozyme as an antibiotic. The roles of enzymes in determining metabolites and diseases are also summarized briefly in 3 sentences or less.