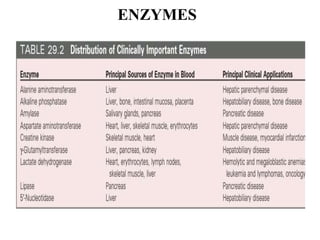
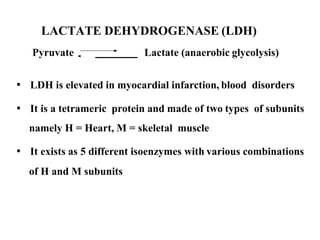
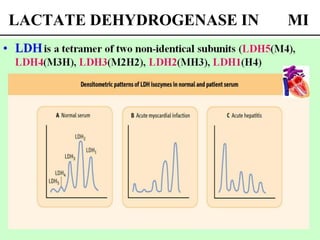
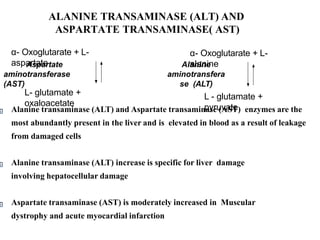
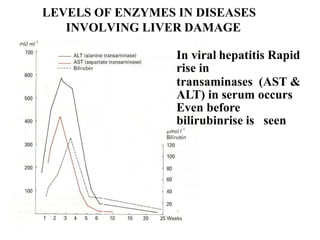
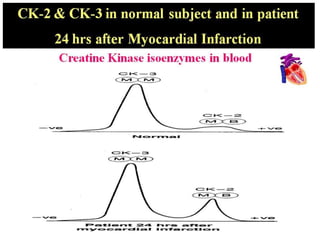
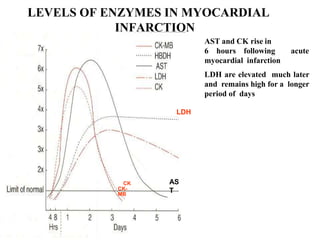
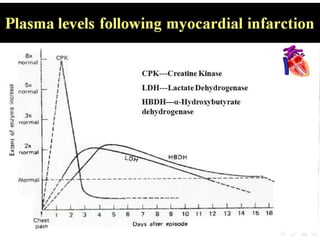
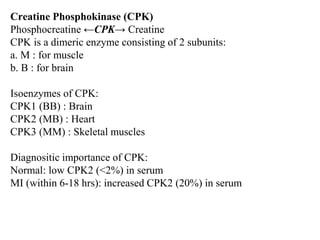
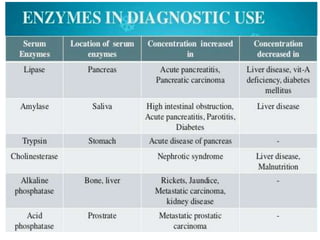
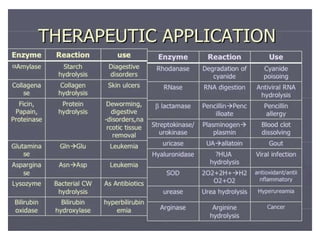
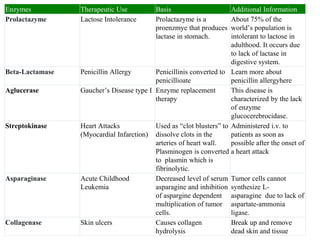
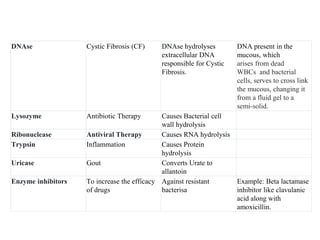
Enzymes are measured in body fluids to detect tissue damage or abnormalities. Key enzymes include aminotransferases for liver function, creatine kinase for heart disease, and amylase and lipase for pancreatic function. Isoenzymes are tissue-specific enzyme variants that can provide clues about the site of pathology, such as increased LDH1 in myocardial infarction. Enzyme levels are important biomarkers for diagnosing and monitoring many conditions.