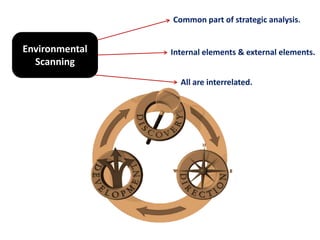
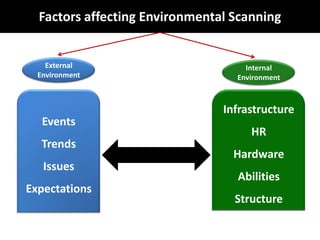
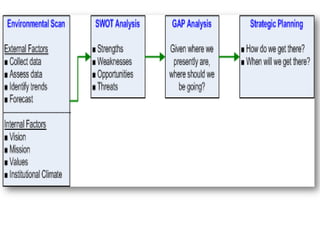
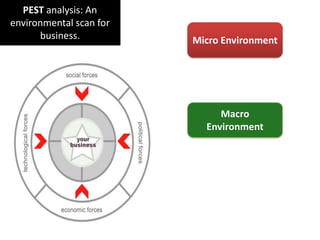
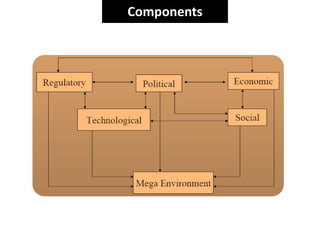
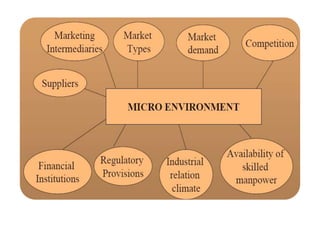
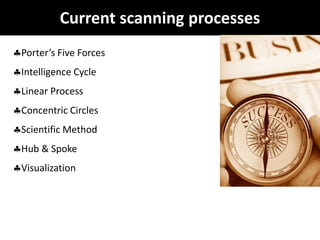
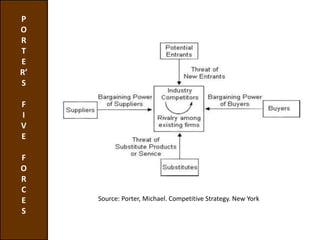
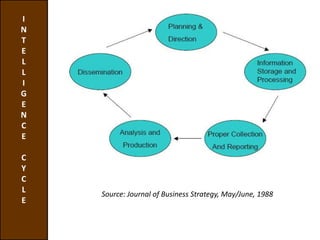
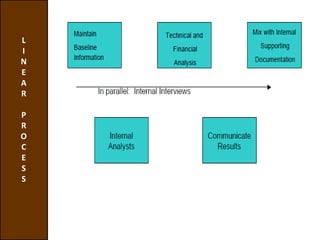
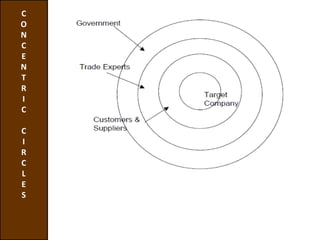
Environmental scanning, introduced by Francis Aguilar, involves gathering and analyzing information about a company's competitive environment for strategic decision-making. It helps organizations identify opportunities, anticipate problems, gauge customer needs, and enhances strategic planning. Various approaches to scanning include systematic, ad-hoc, and processed information gathering methods.