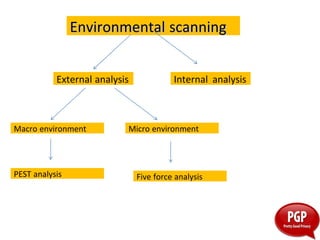
This document discusses environmental scanning, which is the process of gathering, analyzing, and sharing information for strategic purposes. There are three types of environmental scanning: ad-hoc, regular, and continuous. Environmental scanning examines both external and internal factors. Externally, it analyzes the macro environment using the PEST framework of political, economic, social, and technological factors. It also analyzes the micro environment using Porter's five forces model of new entrants, substitutes, buyer power, supplier power, and industry rivalry. Internally, environmental scanning analyzes the company's internal environment. The document concludes that environmental scanning is useful for revealing current market conditions and helping managers predict future conditions to make strategic decisions.