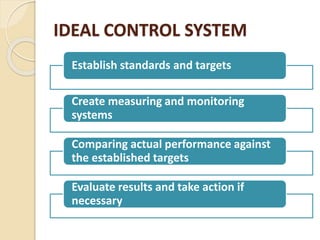
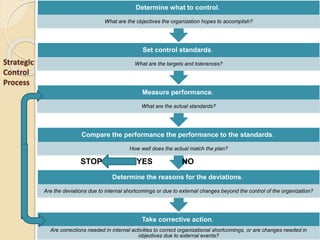
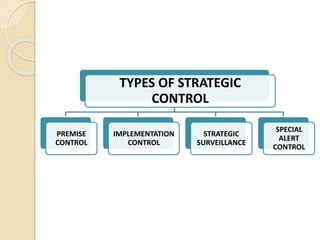
Strategic control involves tracking a strategy as it is implemented, detecting problems or changes, and making adjustments. It has several purposes, including helping achieve goals by monitoring and evaluating the strategic management process. There are different types of strategic control, including premise control to test assumptions, implementation control to monitor plans, strategic surveillance for broad monitoring, and special alert control for rapid response to unexpected events. Strategic control is meant to continually assess changes and their impact on an organization's strategy.