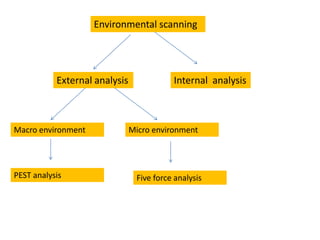
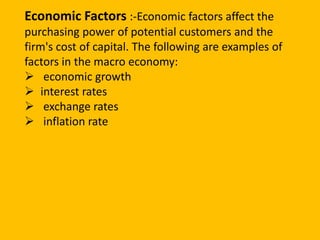
Environmental scanning is the process of gathering, analyzing, and sharing information about a company's external environment for strategic purposes. There are three types of environmental scanning: ad-hoc scanning for crises, regular scheduled scanning, and continuous scanning. Environmental scanning examines both the macro environment including political, economic, social, and technological factors (PEST analysis), as well as the micro environment including competitors, customers, and a company's internal environment. Environmental scanning helps managers predict future market conditions to make strategic decisions.