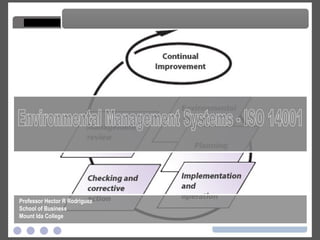
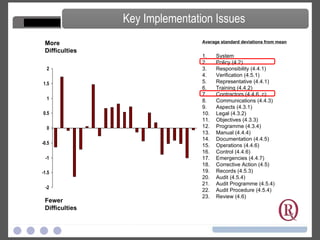
The document discusses ISO 14001 environmental management systems. It provides an overview of what an EMS is, how it was created by the International Organization for Standardization, and the key elements required by ISO 14001 certification including environmental policy, planning, implementation, checking and corrective action, and management review. Benefits of an EMS include more reliable environmental performance and compliance as well as opportunities for improvement and cost reduction.