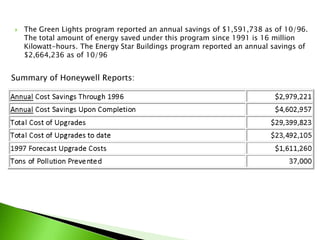
ISO 14000 introduces a self-regulatory approach to environmental management, aimed at transforming the traditional command-and-control methodology. It encompasses guidance and specification documents that outline standards for organizations committed to environmental stewardship, helping to enhance environmental performance while ensuring compliance. Market demand, regulatory pressures, and operational excellence drivers motivate businesses, such as Honeywell, to adopt these standards for sustainable practices and improved stakeholder relationships.