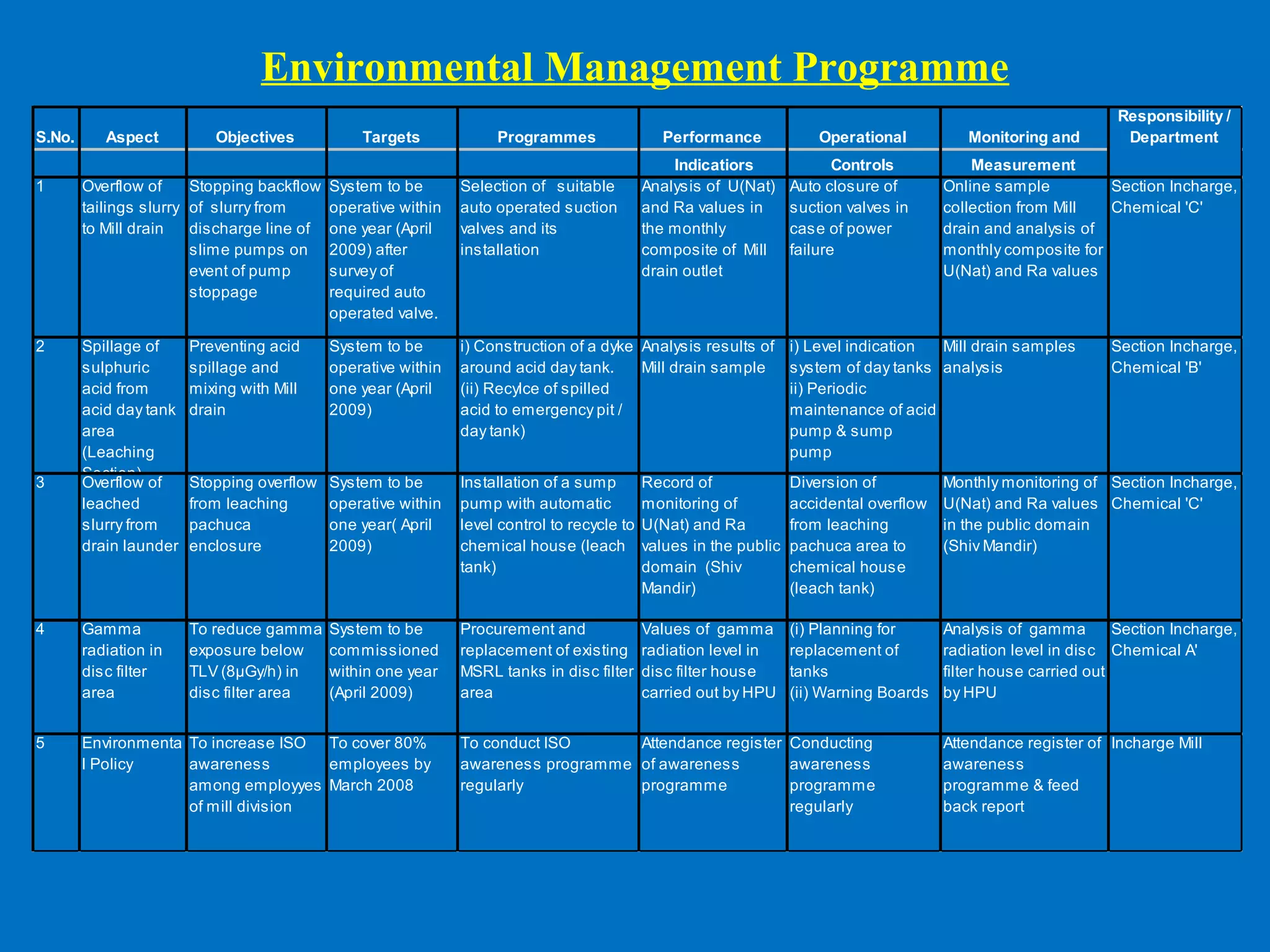
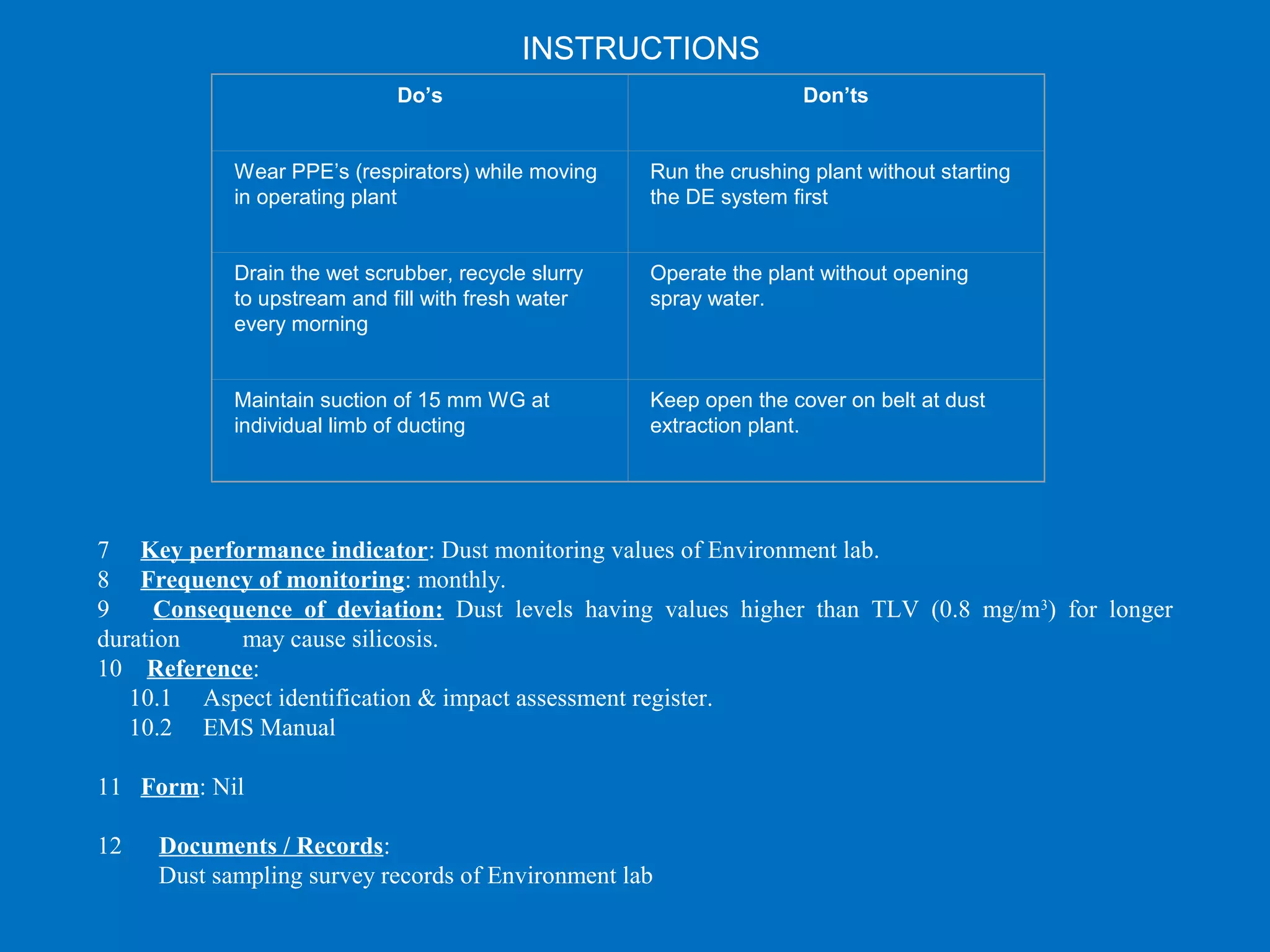
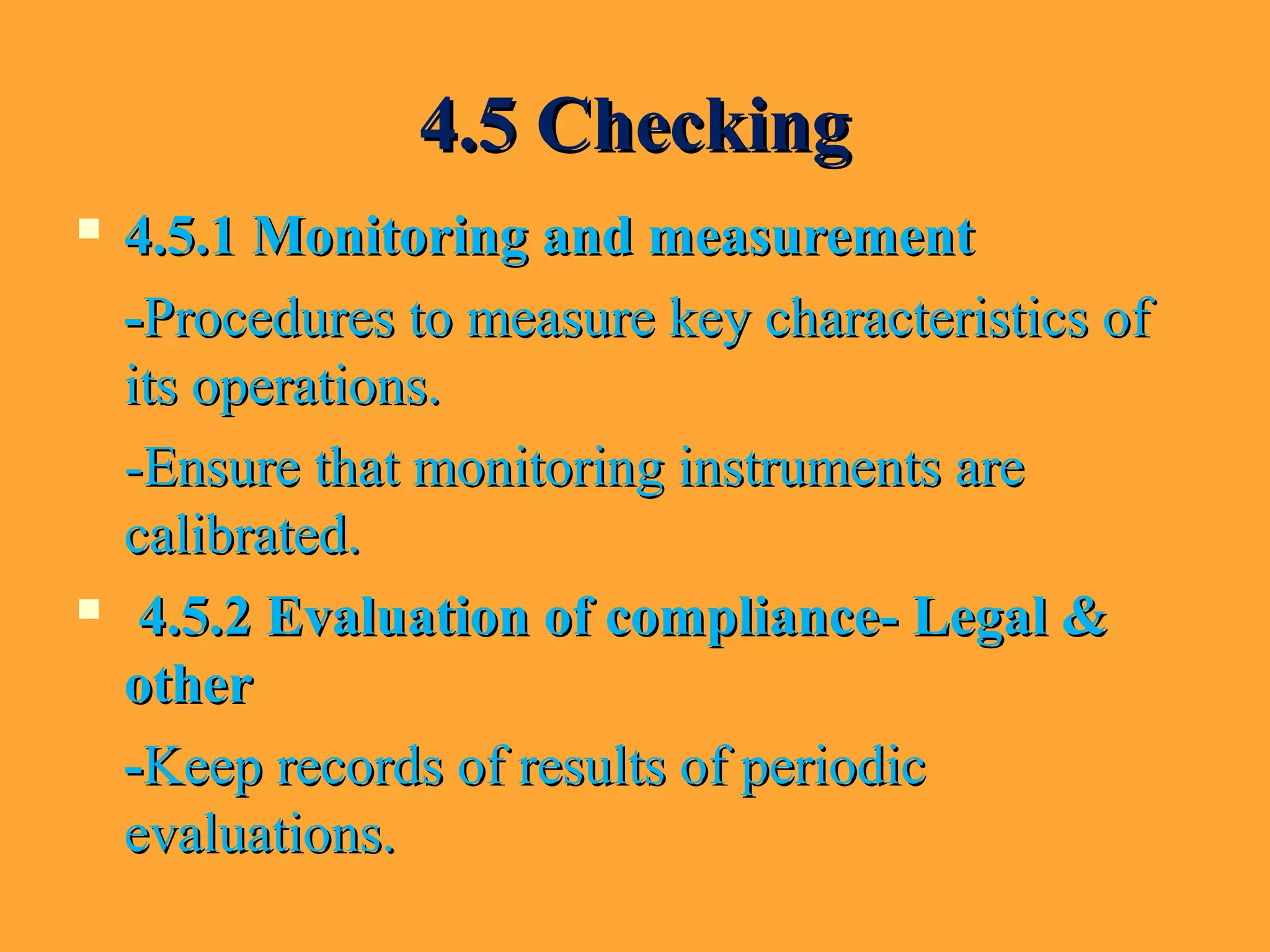
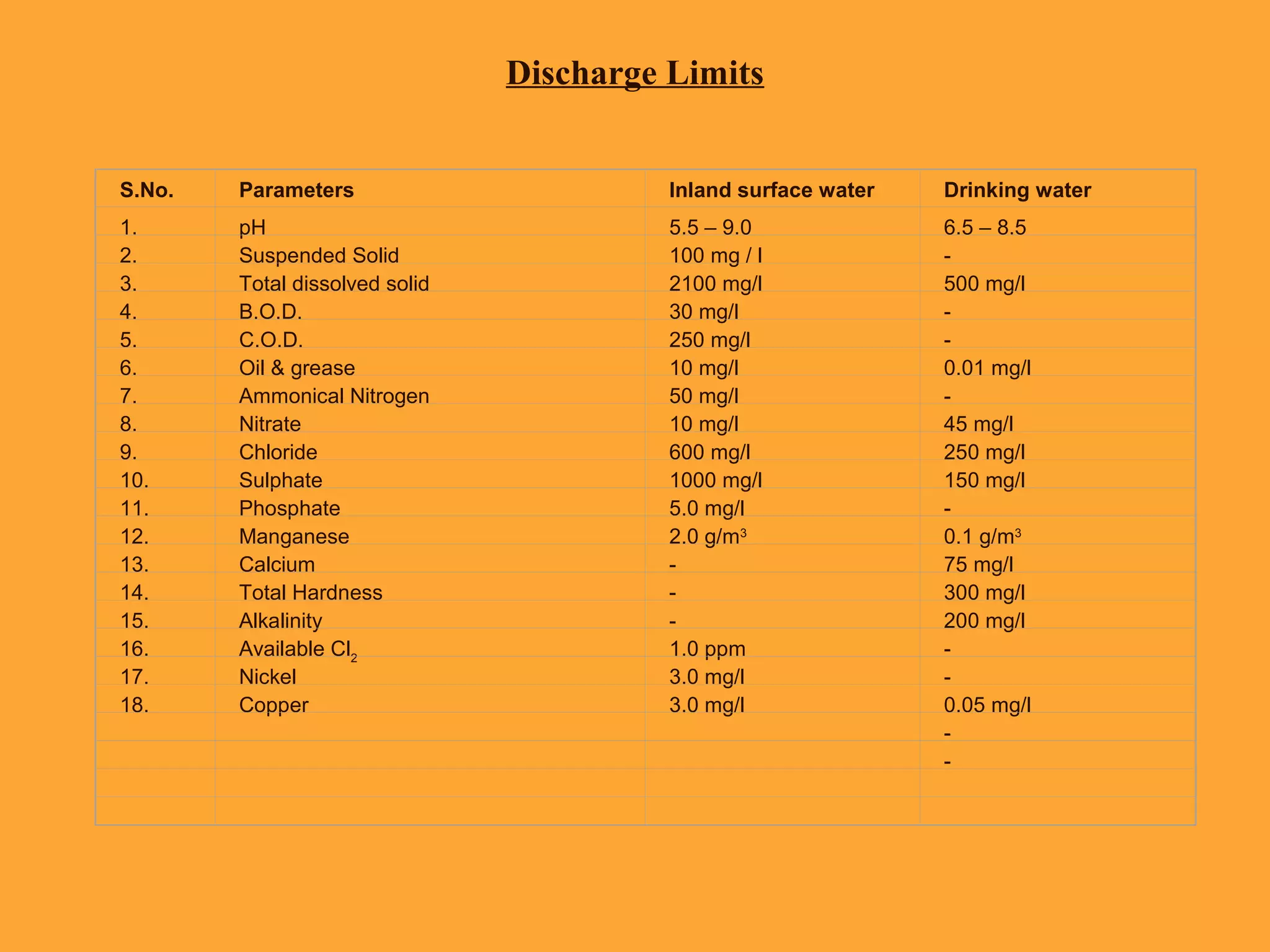
The document provides an overview of ISO, particularly focusing on ISO 14001:2004, which is an international standard for environmental management systems. It outlines requirements for organizations to manage their environmental responsibilities, including monitoring and improving environmental performance through defined policies, objectives, and compliance with legal regulations. Additionally, it includes guidance on the roles, resources, and operational controls necessary for successful implementation of an environmental management system.