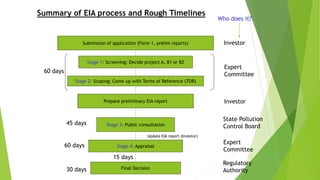
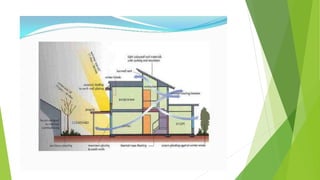
The document discusses Environmental Impact Assessment (EIA) processes, emphasizing their importance in assessing the environmental consequences of proposed projects while ensuring fairness, credibility, and sustainability. It outlines the history of EIA, its procedural stages in India, and introduces the concept of green buildings and green technologies aimed at reducing environmental impact. Additionally, it highlights the challenges and benefits of adopting sustainable practices in construction and energy generation.