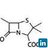
Reaction intermediates
- 1. Dr. Tanuja Nautiyal Department of Chemistry Sharda Public School Almora Radicals and Chemical Formulae
- 2. Radicals Ions How to write a chemical formula Radicals and Chemical Formulae
- 3. Radicals are atomic or molecular species with unpaired electrons which are capable of independent existence. Radicals
- 5. •The attacking reagents are classified into three types: Electrophiles •Positively charged or neutral species, which are deficient of electrons and can accept a pair of electrons are called electrophiles. These are also called electron loving (philic) species. •For example: H+, H3O+, Cl+, CH3 +, NO2 + (Positively charged)AlCl3, BF3, SO3 (Neutral) •Both Al and B act as electrophiles as they have total of six electrons i.e. two less than the octet, and so they try to complete their octets. These are also called as Lewis acids. Electrophile
- 6. •A nucleophile is a reagent containing an atom having unshared or lone pair of electrons. •As a nucleophile is electron rich it seeks electron deficient sites i.e., nucleus (nucleus loving). •According to Lewis concept of acids and bases, nucleophiles behave as Lewis bases. •For example: NH3, H2O, ROH, ROR (neutral) Nucleophiles
- 7. A free radical may be defined as an atom or group of atoms having an unpaired electron. Free radicals are produced during the homolytic fission of a covalent bond. Free Radical
- 8. Free radicals are very reactive as they have strong tendency to pair up their unpaired electron with another electron from wherever available. These pairs are very short lived and occur only as reaction intermediates during reactions. For example, dissociation of chlorine gas in the presence of ultra-violet light produces chlorine free radicals: Free Radical
- 9. The alkyl free radical may be obtained when free radical chlorine attacks methane. Free Radical
- 10. Free radicals may be classified as primary, secondary or tertiary depending upon whether one, two or three carbon atoms are attached to the carbon atom carrying the odd electron: Free Radical
- 11. The order of stability of alkyl free radicals is: CH3 <>o <>o <>o This order of stability can easily be explained on the basis of hyperconjugation. Larger the number of alkyl groups, attached to the carbon atom carrying the odd electron, greater is the delocalisation of the odd electron and hence more stable is the free radical. Accordingly, the tertiary free radical with three alkyl groups attached to the carbon atom carrying the odd electron is more stable than the secondary free radical containing two alkyl groups and so on. Stability of free radicals
- 12. The carbon atom in alkyl free radicals involves sp2 hybridization. Therefore, it has a planar structure. Three hybrid orbitals are used in the formation of three s-bonds with three H atoms or alkyl group. The unpaired electron is present in unhybridized p orbital. Structure of alkyl free radical Orbital structure of free radicals
- 13. Types of Radicals Acid radicals:-The acid radical is an anion left after removal of hydrogen atoms from an acid. Basic radicals:-The basic radical is the cation left after removal of OH or other alkaline group from the bases.
- 14. •An ion is a charged species in which an atom or a group of atoms possess a net electric charge. •The net electric charge of an ion can either be positive or negative. •Positively charged ions are called cations and negatively charged ions are called anions.
- 15. Cations are atoms that have lost an electron to become positively charged. The ions of all the metal elements are cations. If an atom loses one electron, then the cation formed has 1 unit positive charge. Examples:- Na+ , Zn2+, Mg2+, Al3+ etc.
- 16. A neutral lithium (Li) has 3 protons and 3 electrons, and it is missing an electron. Then we have 3 protons and 2 electrons. So lithium loses one electron to become a 1+cation.
- 18. Anions are atoms or groups of atoms that have gained electrons. Having more negatively charged electrons than positively charged protons, they are negatively charged. Most anions are composed from multiple atoms, and are called polyatomic ions. Examples:- Cl− , O2- , co3 2-, PO4 3- etc. ANIONS
- 19. A neutral chlorine Cl has 17 protons and 17 electrons, and it is gaining one electron. Then we have 17 protons and 18 electrons. So, chlorine gained one electron to become a 1- anion. ANIONS
- 20. ANIONS
- 21. Chemical formula of a compound is the symbolic representation of its atomic constituents. In other words, a chemical formula represents the composition of a molecule in terms of the symbols of the elements present in that molecule. To write the chemical formula of a compound, one should have prior knowledge of two things. 1.The symbols of the constituent elements. 2.The combining capacity of each atom constituting the compound
- 22. The combining power or the combining capacity of an atom or an element is called its valency. The number of atoms of other elements with which one atom of an element combines is decided by the valency of that element. For example, both hydrogen and chlorine have a valency of 1. Therefore, one atom of hydrogen reacts with one atom of chlorine to formone molecule of hydrogen chloride. The valency of an ion is equal to the charge on it.
- 23.
- 24. The valencies of some common ions are given in the following table. Name of ion Symbol Valency Name of ion Symbol Valency Aluminium Al3+ 3 Sulphite SO3 2- 2 Ammoniu m NH4 + 1 Bromide Br− 1 Calcium Ca2+ 2 Carbonate CO3 2- 2 Copper(II) Cu2+ 2 Chloride Cl− 1 Hydrogen H+ 1 Hydride H− 1 Iron(III) Fe3+ 3 Hydroxide OH− 1 Potassium K+ 1 Oxide O2− 2 Zinc Zn2+ 2 Sulphide S2− 2
- 25. STEPS TO WRITE A CHEMICAL FORMULA 1.Write the symbols of the elements which form a compound. If we have to write the formula of hydrogen sulphide. First write down the symbols of hydrogen and sulphur. Symbols: H S
- 26. 2. Below the symbol of each element, write down its valency. Symbols: H S Valencies: 1 2 STEPS TO WRITE A CHEMICAL FORMULA
- 27. 3.Finally cross-over the valencies of the combining atoms. This will give the required formula. Symbols: H S Valencies: 1 2 STEPS TO WRITE A CHEMICAL FORMULA
- 28. Formula of some compounds Chemical compounds Chemical Formula Silver chloride AgCl Aluminium nitrate Al(NO3)3 Barium chloride BaCl2 Calcium carbonate CaCO3 Potassium nitrate KNO3 Magnesium aluminate Mg(AlO2)2 Sodium carbonate Na2CO3
- 29. Dr. Tanuja Nautiyal Department of Chemistry Sharda Public School Almora Thank you