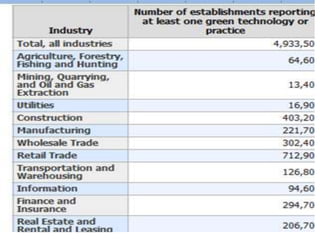
This document discusses green technology and its importance for sustainable development. It defines green technology as methods and materials that generate energy and non-toxic products in an environmentally friendly way. The objectives of green technology are sustainable development, eliminating waste, reusability, innovation, and feasibility. Key areas of green technology discussed include green chemistry, nanotechnology, buildings, IT, and energy from renewable sources like water, wind, and solar power. Major industries in India adopting green tech are also listed.