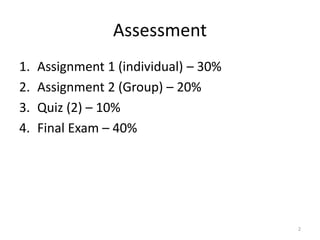
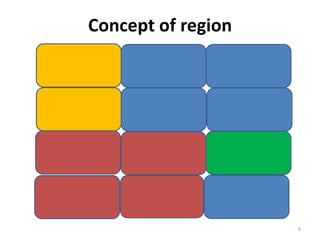
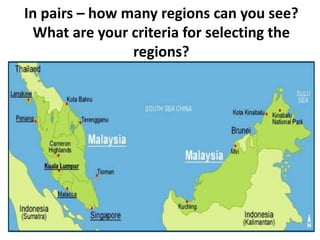
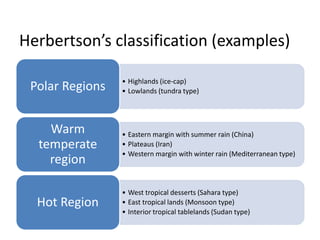
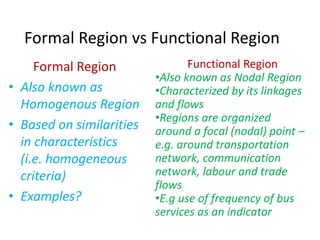
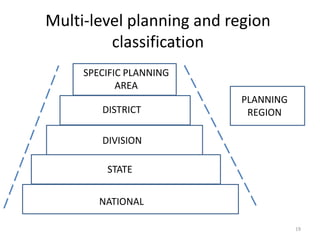
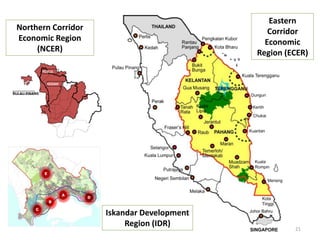
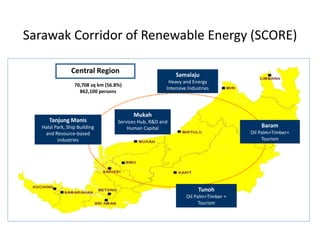
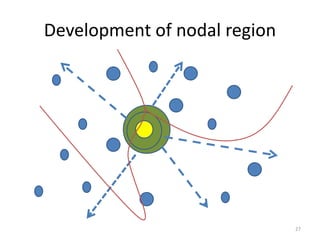
This document provides an overview of key concepts in regional planning. It defines a region as an area with specific boundaries and characteristics. Regions can be classified in different ways, such as formal, functional, and perceptual regions. Formal regions are based on physical similarities, while functional regions are organized around nodes and flows. The document also discusses techniques for delimiting regions and identifies different types of regions, such as economic development regions and activity regions. Finally, it explains the concepts of planning regions and regional planning, which involves coordinating resources and development across administrative boundaries.