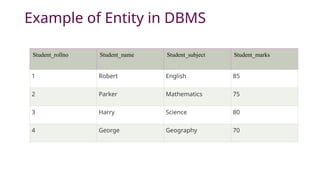
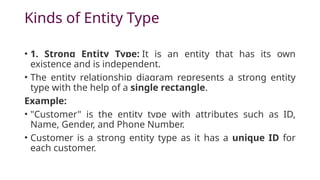
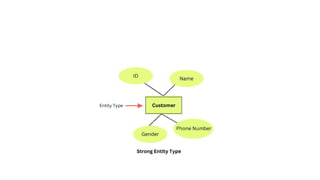
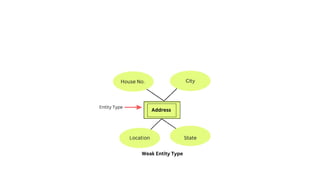
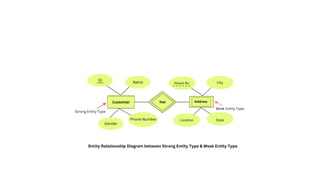
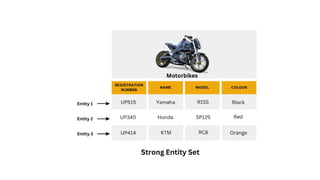
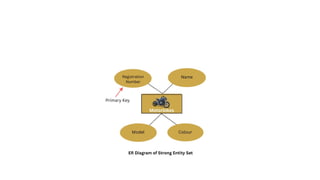
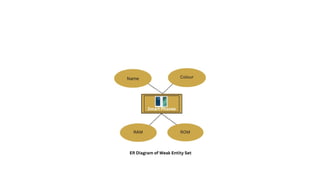
The document explains the concept of entities in database management systems (DBMS), defining them as identifiable objects that can be tangible, like a car, or intangible, like a bank account. It discusses the characteristics of entities, types of entities (strong and weak), and how they are represented in an entity-relationship diagram, including the relationship between strong and weak entities. Additionally, it describes entity sets and distinguishes between strong entity sets (with primary keys) and weak entity sets (without primary keys).