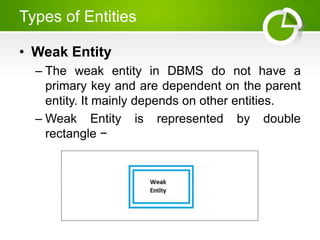
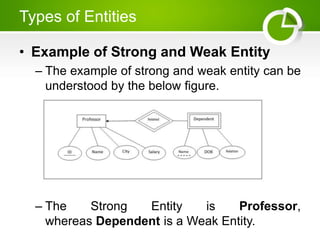
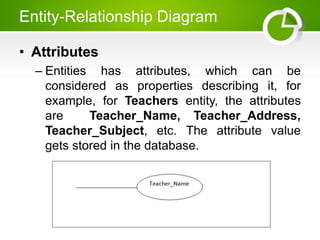
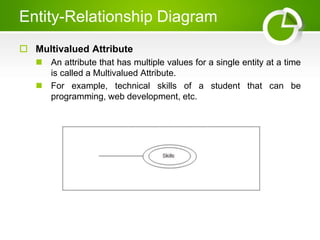
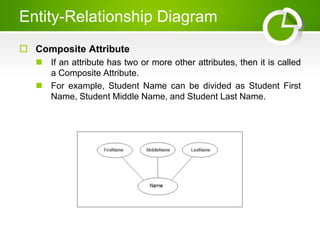
The document presents an overview of the Entity-Relationship (E-R) Model, a logical representation of data used to describe the elements and relationships within an organization, introduced by Peter Chen in 1976. It details major components such as entities, attributes, and relationships, distinguishing between strong and weak entities, and discussing various types of attributes. Additionally, it highlights advantages like conceptual simplicity and effective communication for database design.