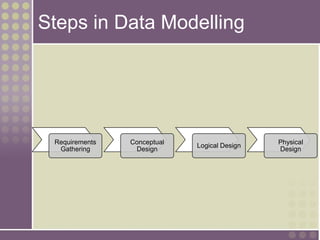
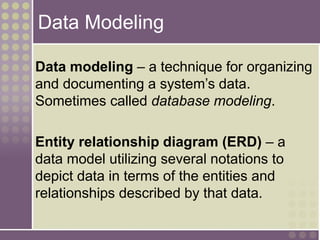
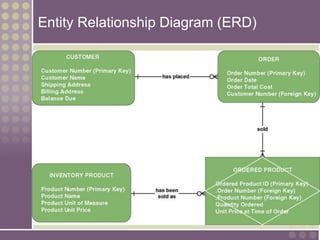
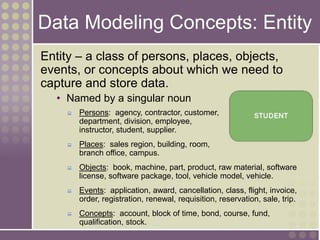
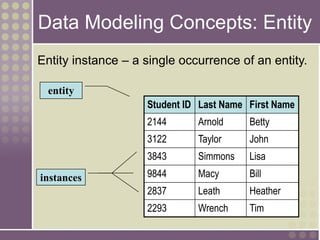
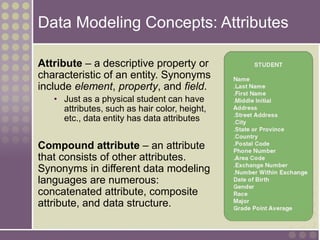
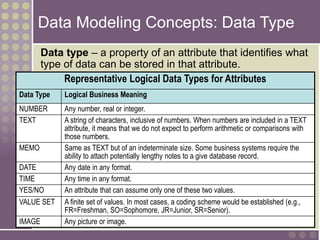
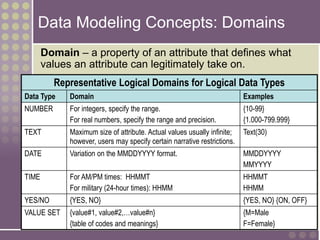
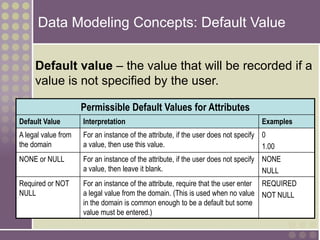
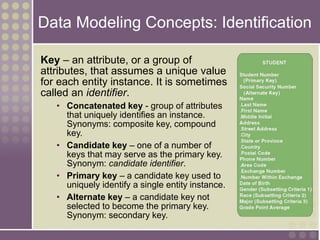
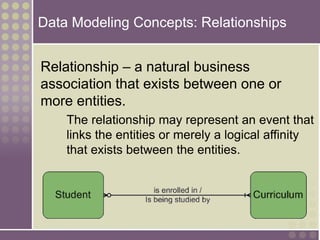
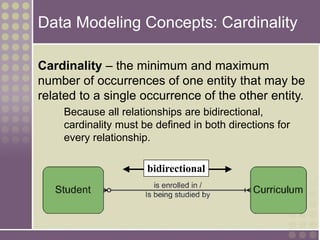
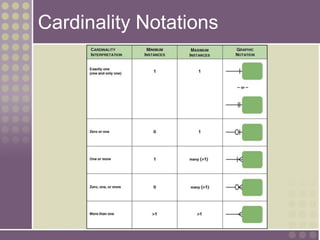
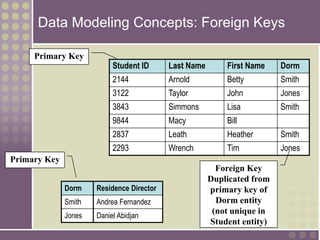
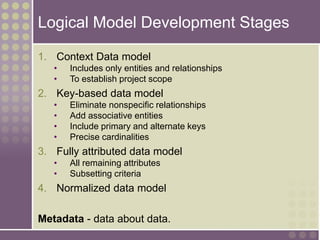
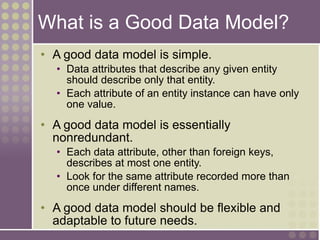
The document discusses the process of data modeling which includes gathering requirements, conceptual design, logical design, and physical design. It defines key concepts in data modeling such as entities, attributes, domains, relationships, cardinality, and foreign keys. The stages of logical data model development are outlined as context data model, key-based data model, fully attributed data model, and normalized data model. Characteristics of a good data model are that it is simple, nonredundant, and flexible to future needs.