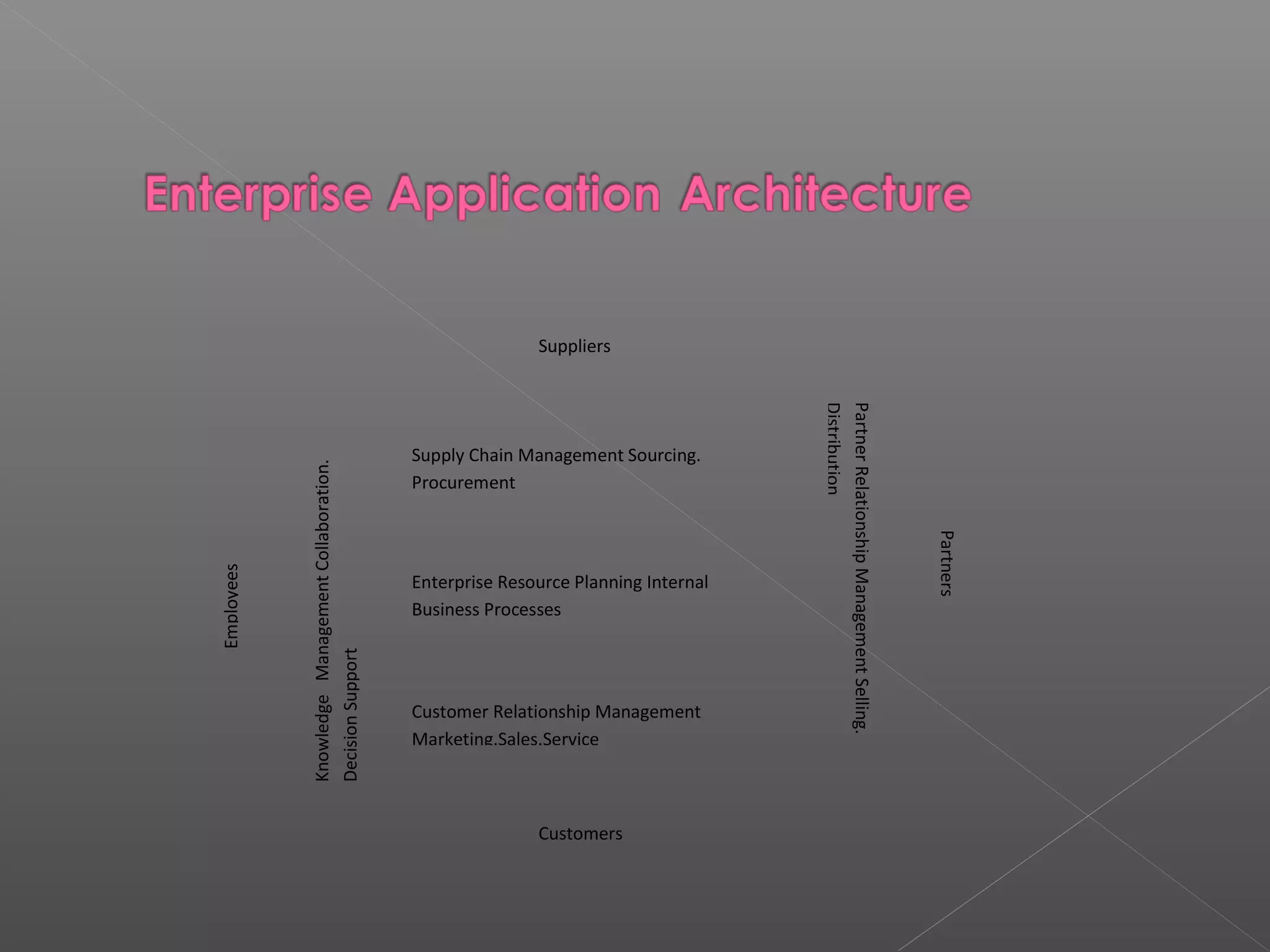
This document discusses various aspects of enterprise business systems including e-business, e-commerce, enterprise application architecture, enterprise application integration, transaction processing systems, and enterprise collaboration systems. It provides examples of how companies like Hilton Hotel Corp use integrated systems to improve business processes across the enterprise. The enterprise application architecture framework illustrates the interrelationships between cross-functional applications related to supply chain management, ERP, CRM, and other areas.