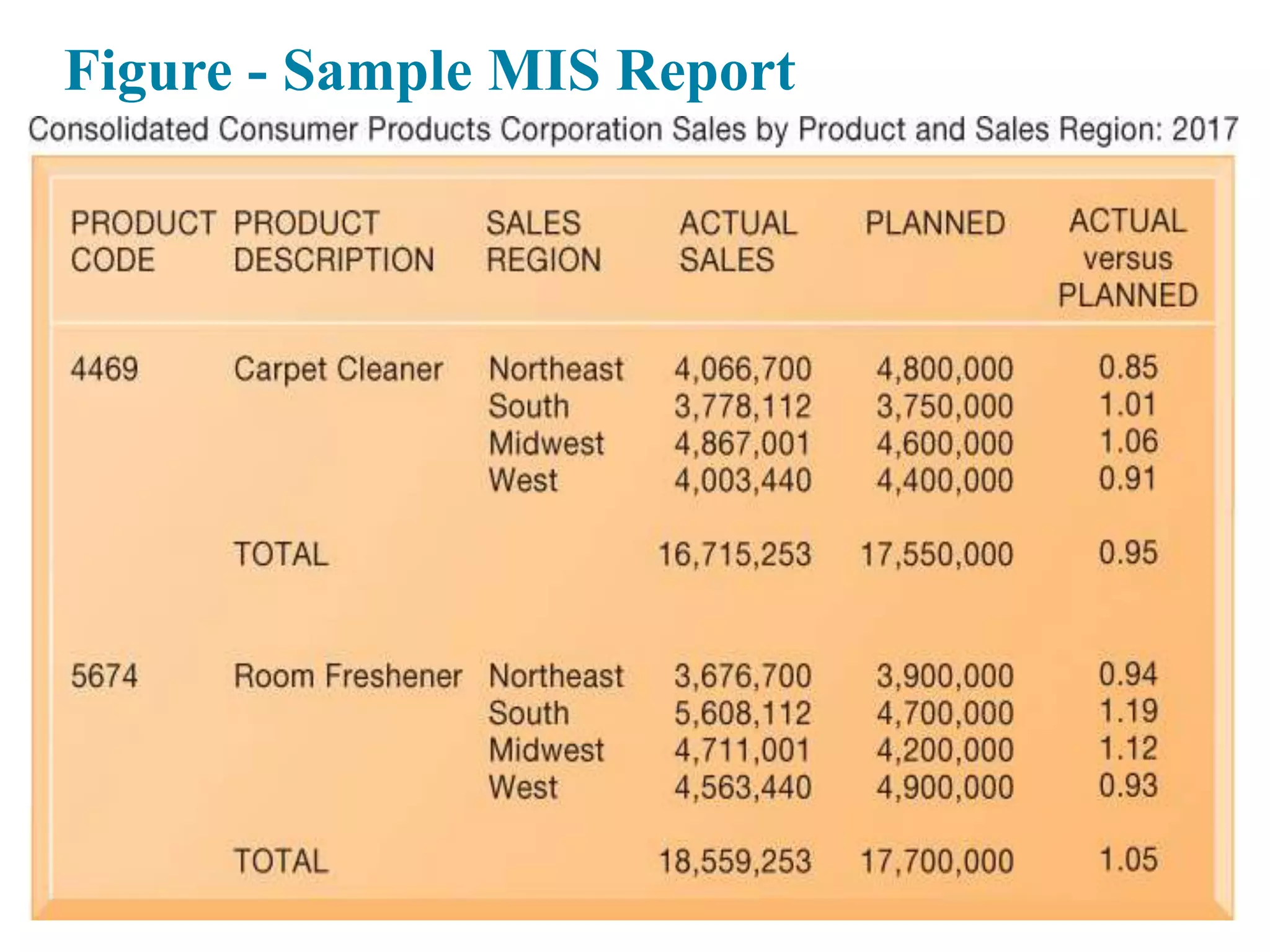
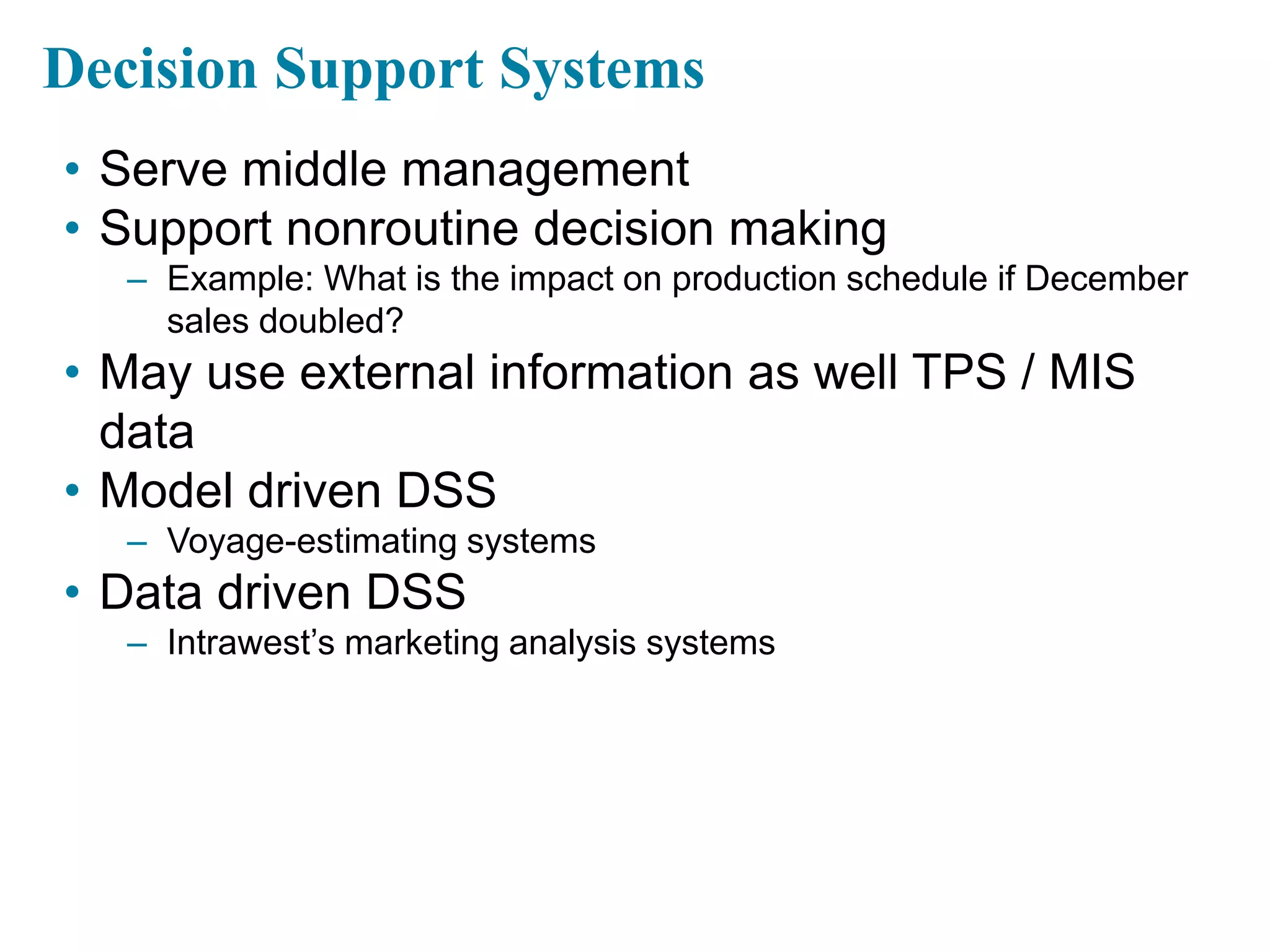
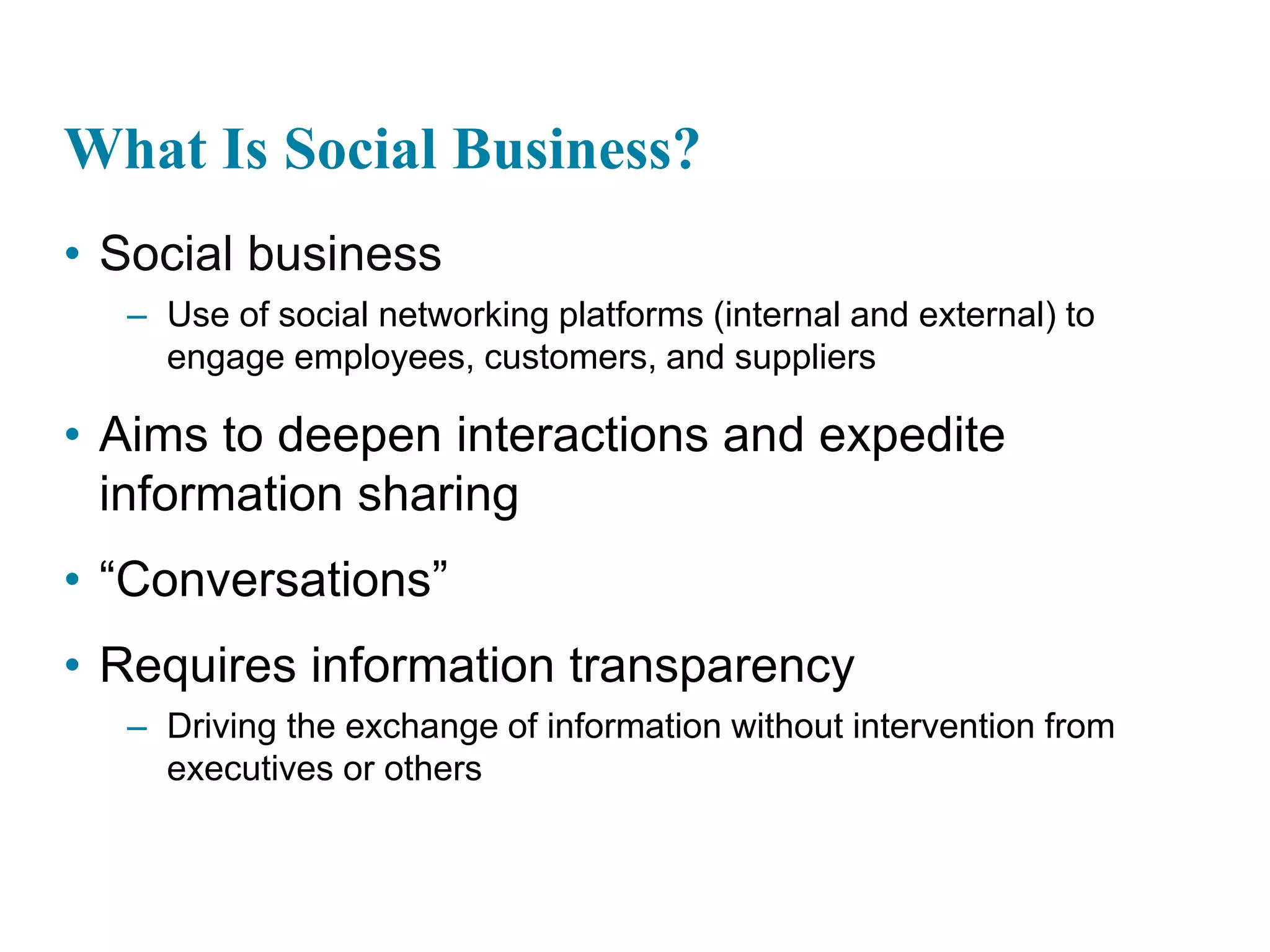
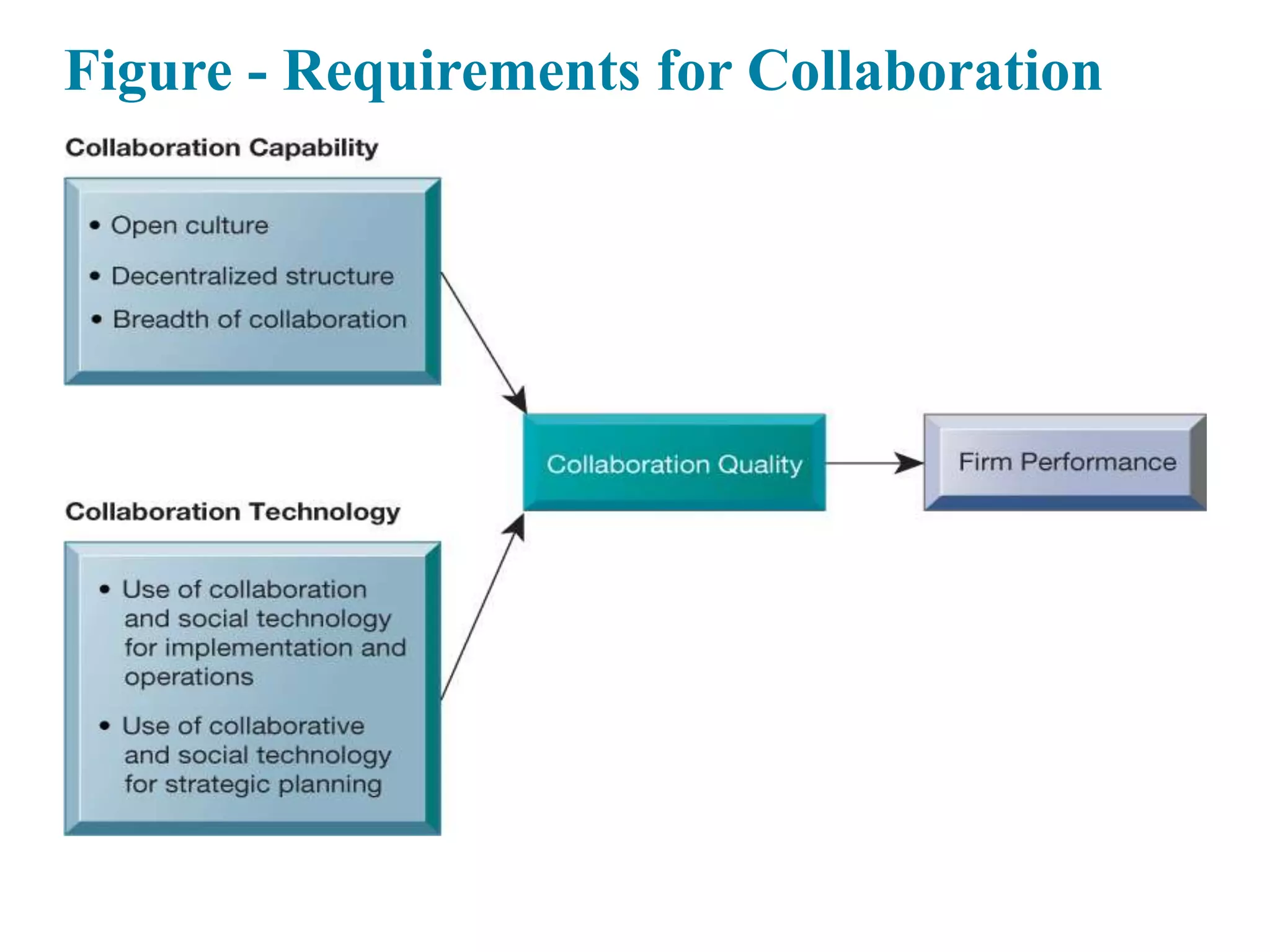
This document provides an overview of key concepts related to how businesses use information systems. It introduces topics like e-business, enterprise applications, collaboration tools, and the role of the information systems department. The learning objectives cover understanding business processes and how different systems serve management groups. Case studies on companies like Walmart, Cemex, and Greenwell Couture illustrate these concepts.