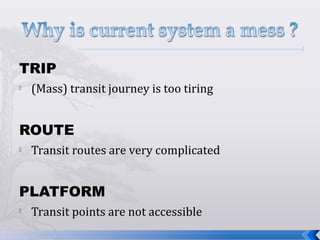
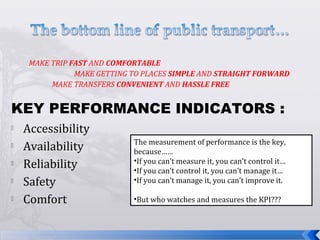
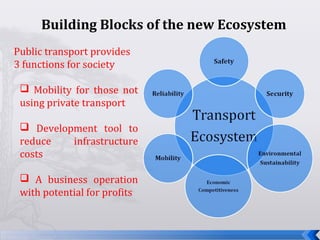
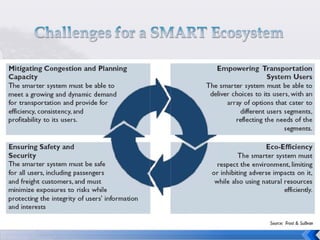
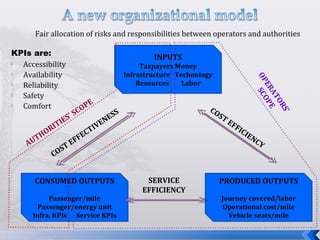
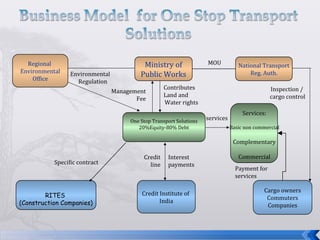
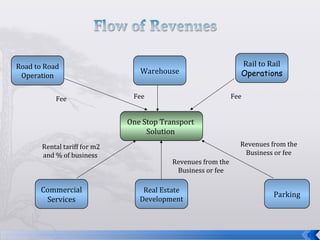
This document summarizes an operations strategy case presentation on improving public transportation ecosystems. The presentation addresses issues with current public transportation such as inconvenient trips, complicated routes, and inaccessible transfer points. It advocates for a centralized authority to oversee transportation as a strategic task and to establish standards, regulations and enforcement. Key elements of the new ecosystem proposed include integrated transportation modes, unified access through technology, and re-engineering infrastructure for scalability. Performance would be measured based on key indicators like accessibility, availability, reliability, safety and comfort.