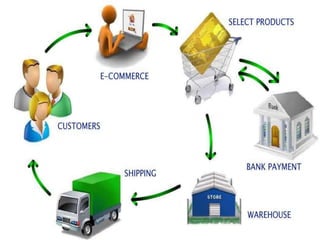
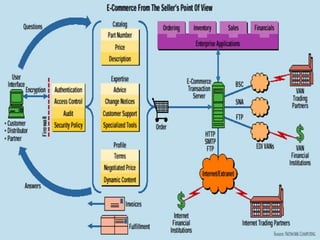
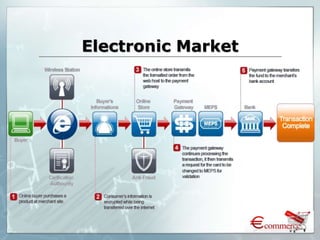
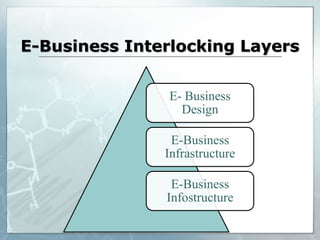
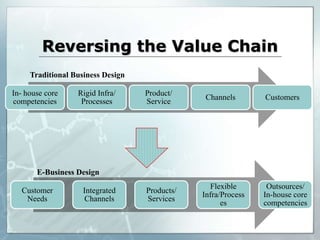
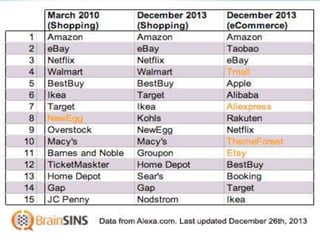
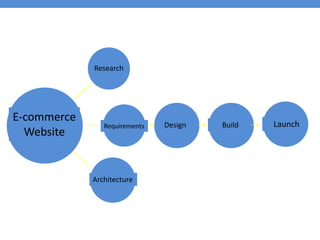
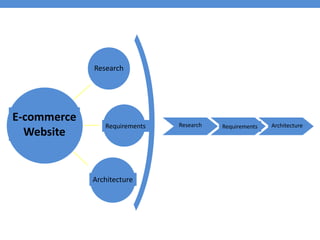
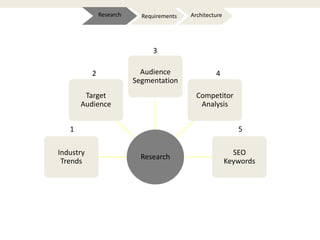
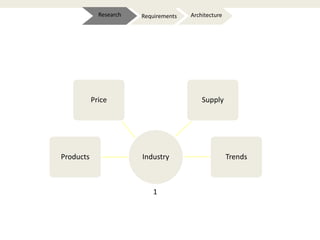
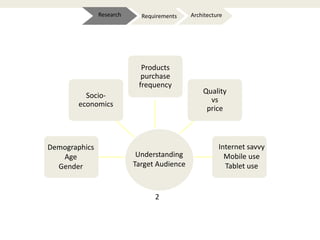
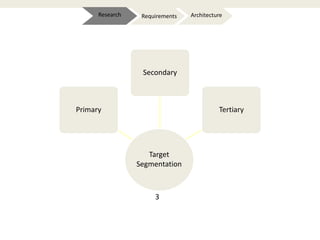
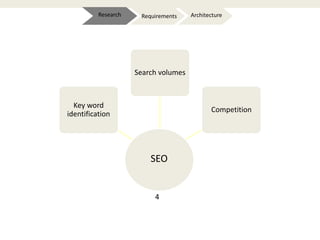
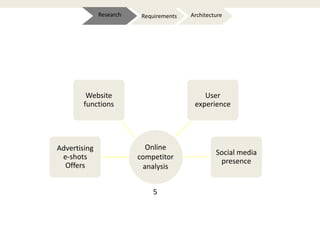
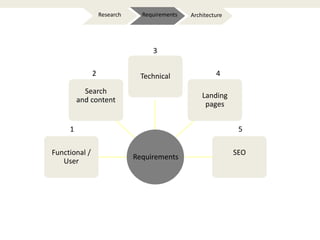
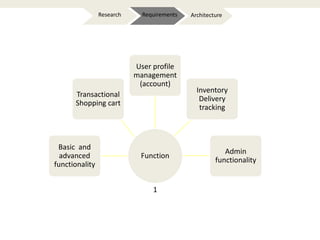
The document provides an introduction to e-business and e-commerce. It discusses key concepts such as the definition of e-commerce, unique features of e-commerce including ubiquity and interactivity. It also outlines major types of e-commerce like B2B, B2C, B2G. Advantages of e-commerce include 24/7 access and global reach. The document concludes with discussing opportunities for different industries and challenges for adopting e-commerce in India.