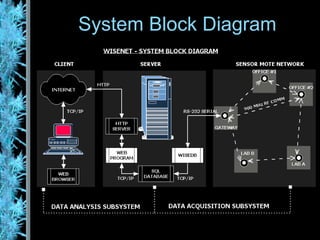
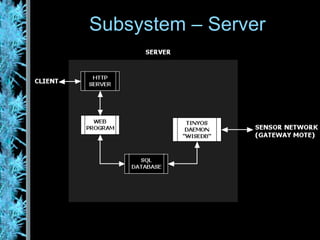
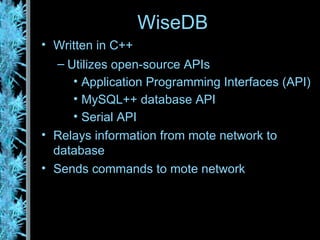
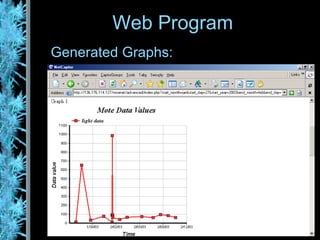
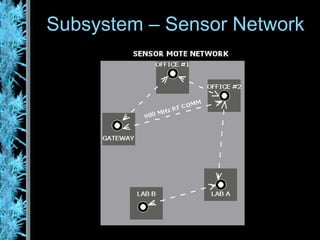
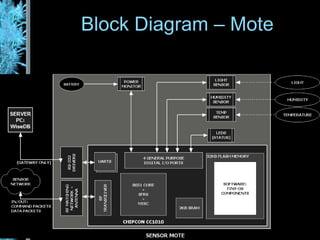
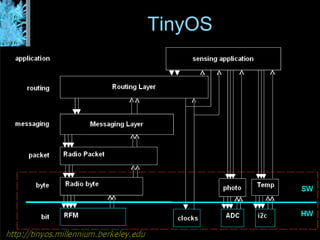
The document describes the Wisenet wireless sensor network project. The project aims to use wireless sensor nodes to monitor environmental factors like temperature and humidity in office buildings. The network uses off-the-shelf components like TinyOS, MySQL database, and PHP web interface. The network architecture includes wireless sensor nodes that form self-organizing networks, a server to collect sensor data and power the web interface, and a standard web browser for users to access reports. The system is currently a prototype but aims to expand the network and further develop the software and applications.