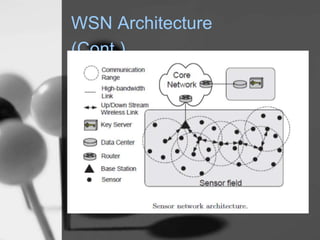
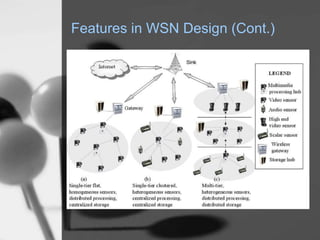
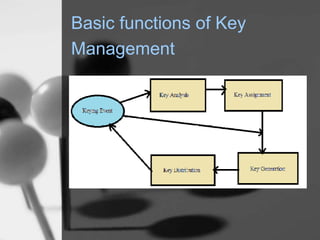
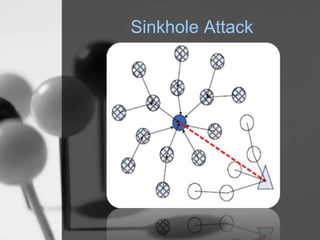
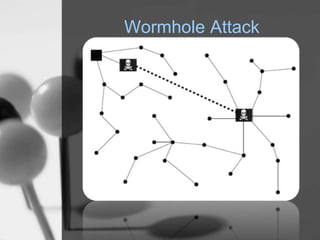
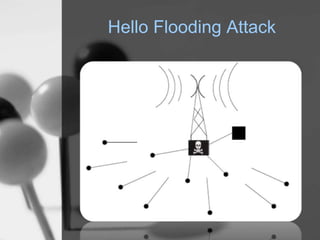
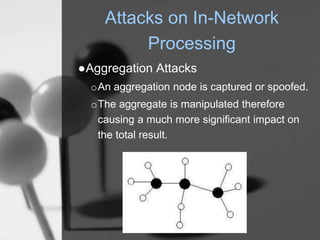
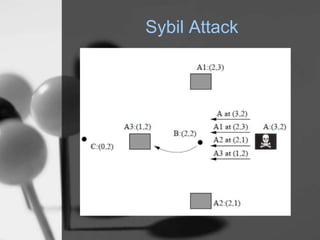
Wireless sensor networks (WSN) are networks of distributed autonomous sensors that monitor environmental or physical conditions. A WSN consists of sensor nodes that collect data and transmit it wirelessly to gateways or base stations. Key components of sensor nodes include processors, transceivers, memory, power sources, and sensors. The design of WSNs aims to minimize node size, power consumption, and maximize diversity, robustness, security, connectivity, and scalability. Common routing protocols for WSNs include flat, hierarchical, location-based, and QoS-based protocols. Security challenges in WSNs include physical tampering, jamming, spoofing, and Sybil attacks. Defenses utilize techniques like encryption, authentication,