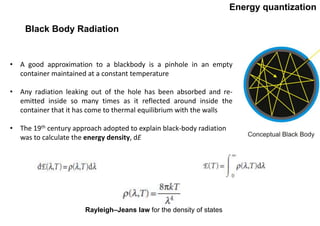
Quantum theory replaced classical mechanics in describing the motion of small particles like electrons. It introduced the concept of energy quantization, where energy can only be absorbed or emitted in discrete packets called quanta. This helped explain phenomena like blackbody radiation, heat capacities of solids, and atomic/molecular spectra that classical mechanics could not. Max Planck proposed quantizing energy to avoid the "ultraviolet catastrophe" where classical physics predicted infinite radiation from hot objects. Einstein further applied the idea to explain heat capacities at low temperatures. Spectroscopy also showed radiation absorbed/emitted at discrete frequencies, supporting energy quantization.