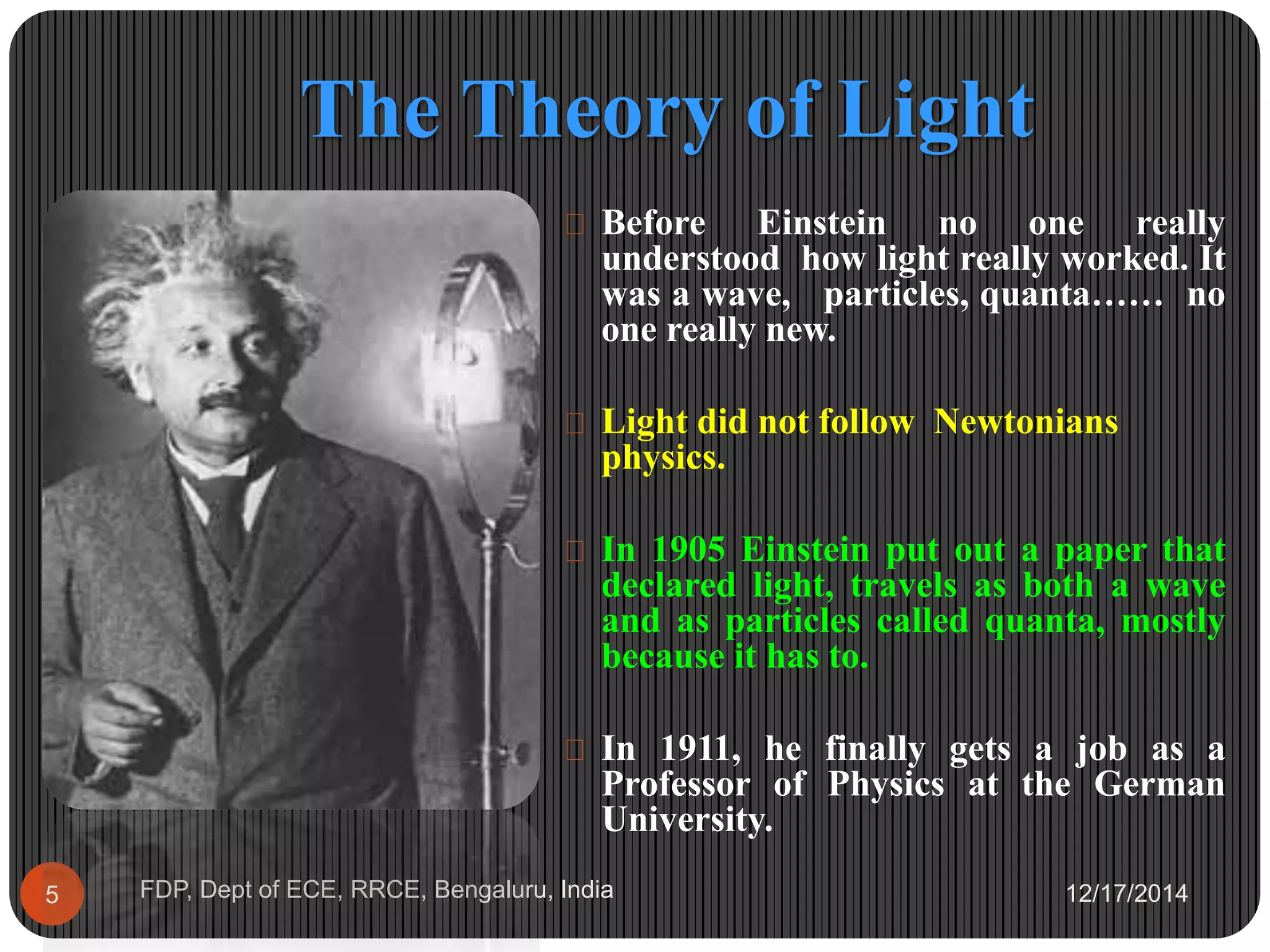
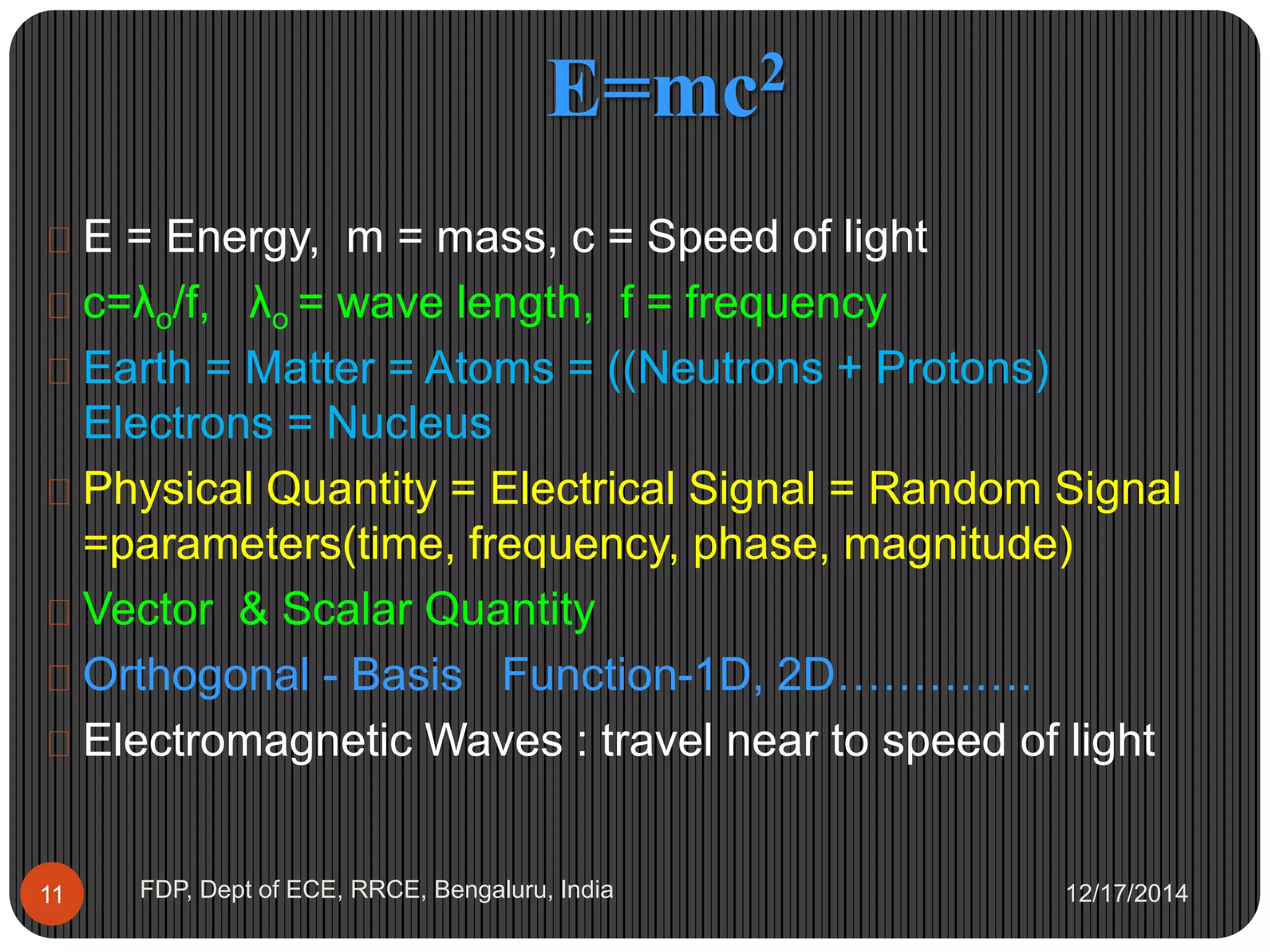
Albert Einstein was a German-born physicist who developed the theory of relativity and E=mc2. Some key points about Einstein include:
- He was born in Germany in 1879 and later worked in Switzerland and the United States, making important contributions to physics.
- His theories of special and general relativity revolutionized scientific understanding of space, time, mass, and energy.
- His mass-energy equivalence formula E=mc2 explained that even small amounts of mass could be converted into huge amounts of energy.
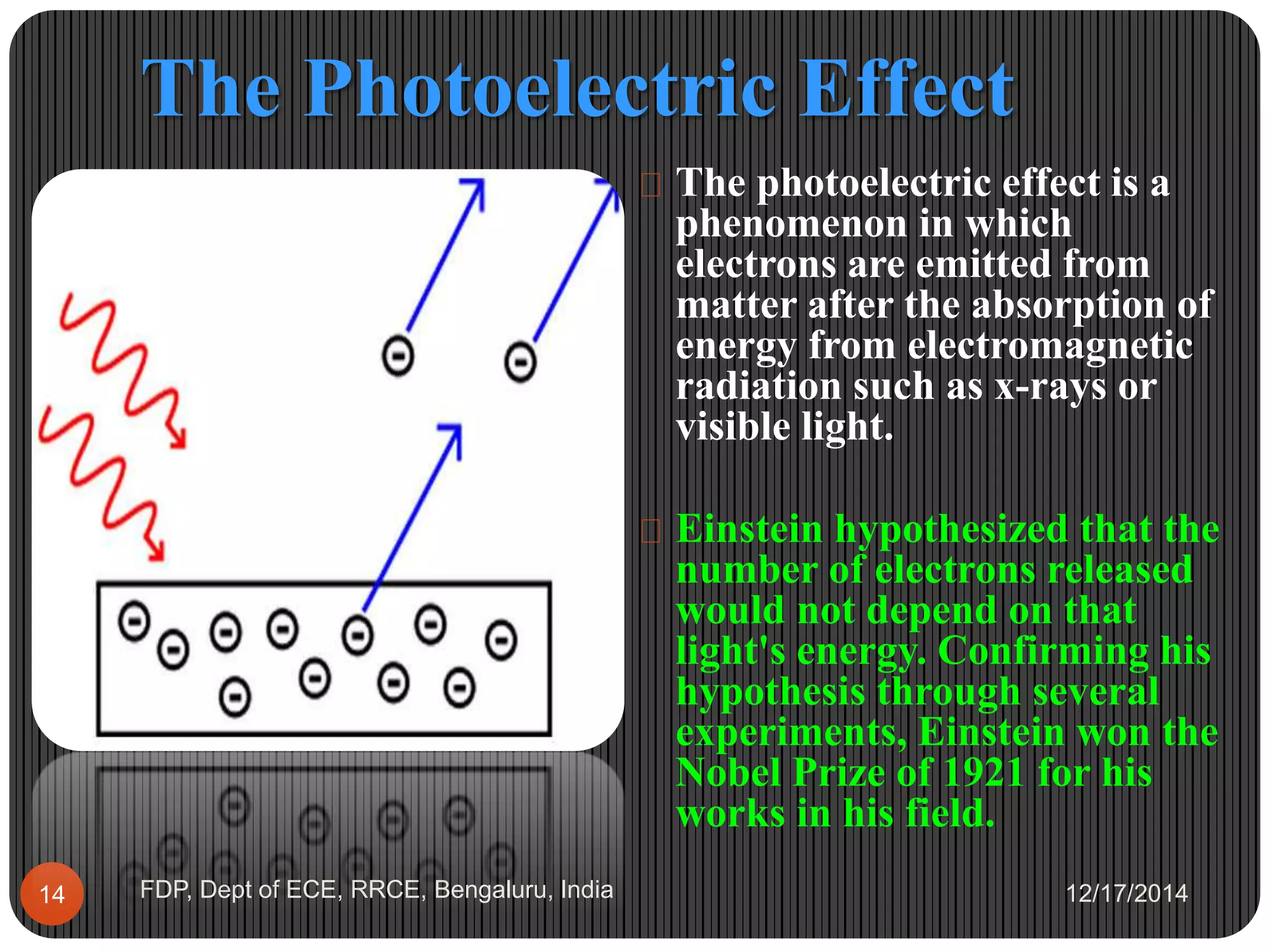
- Einstein received the 1921 Nobel Prize in Physics for his explanation of the photoelectric effect, which supported the theory of light quanta.
- His work was important to understanding atomic structure and the development of