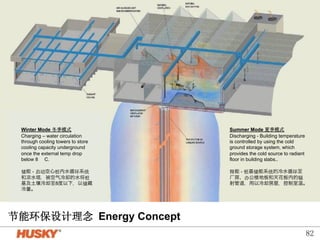
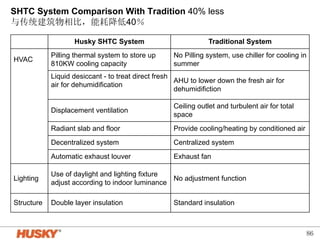
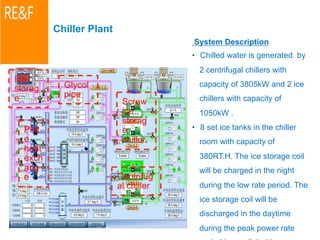
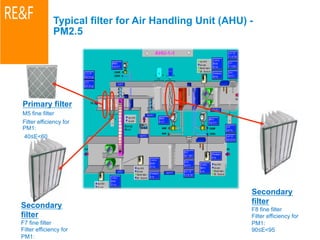
The document presents energy-saving and environmentally friendly design concepts implemented by Microsoft, focusing on efficient temperature control and resource management in building facilities. Systems mentioned include cold storage for temperature regulation, advanced HVAC systems, and innovative lighting solutions that maximize natural light. The integration of automation and sensor technologies enhances performance while minimizing energy waste, achieving a significant reduction in energy consumption compared to traditional systems.