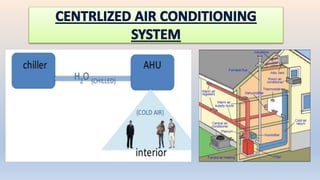
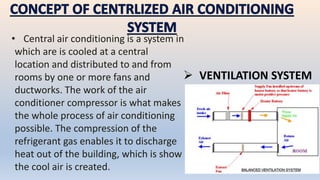
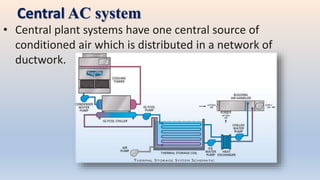
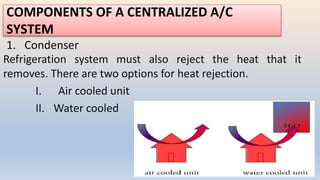
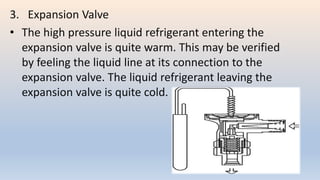
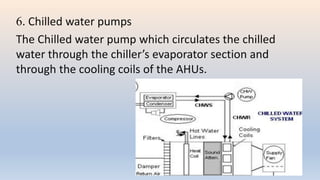
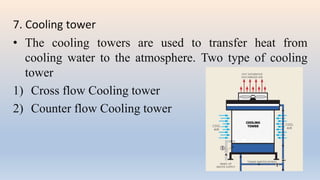
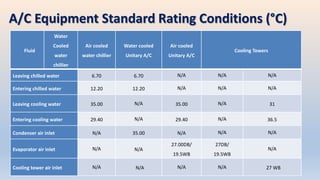
The document discusses building services systems in Sri Lanka, focusing primarily on air conditioning systems, which are essential for creating comfortable and safe environments for occupants. It details different types of air conditioning units, including room, package, and central systems, and explains their components and design parameters. Additionally, it addresses energy-efficient design practices and the implementation of codes for energy-efficient buildings in Sri Lanka.