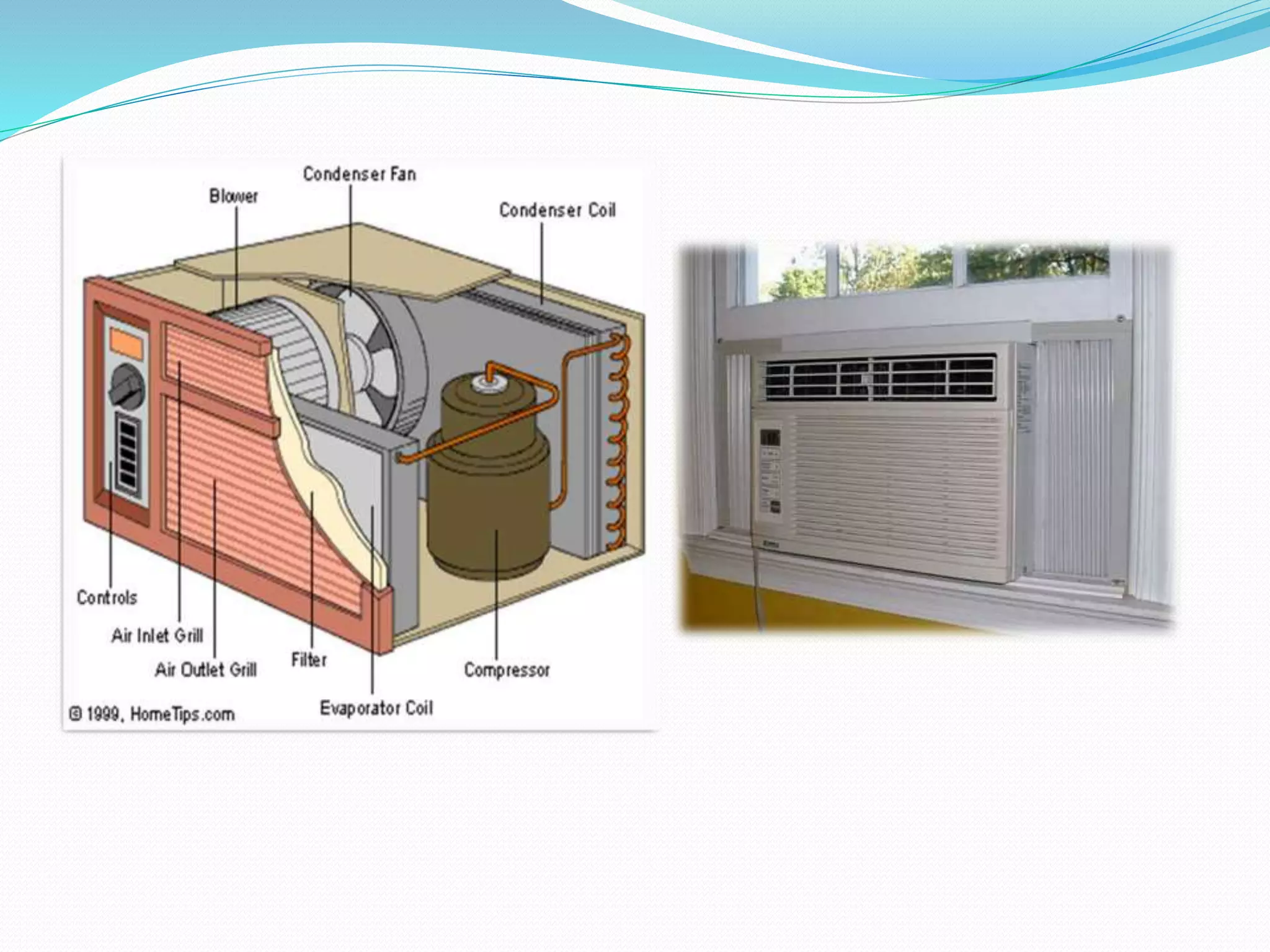
The document provides an overview of HVAC and refrigeration systems, detailing basic components, functions, and different air conditioning configurations. It explains the principles of heat transfer, types of air conditioning systems, and their applications in various environments. The goals of HVAC systems include maintaining comfort, ensuring good air quality, and promoting energy efficiency while addressing environmental concerns.