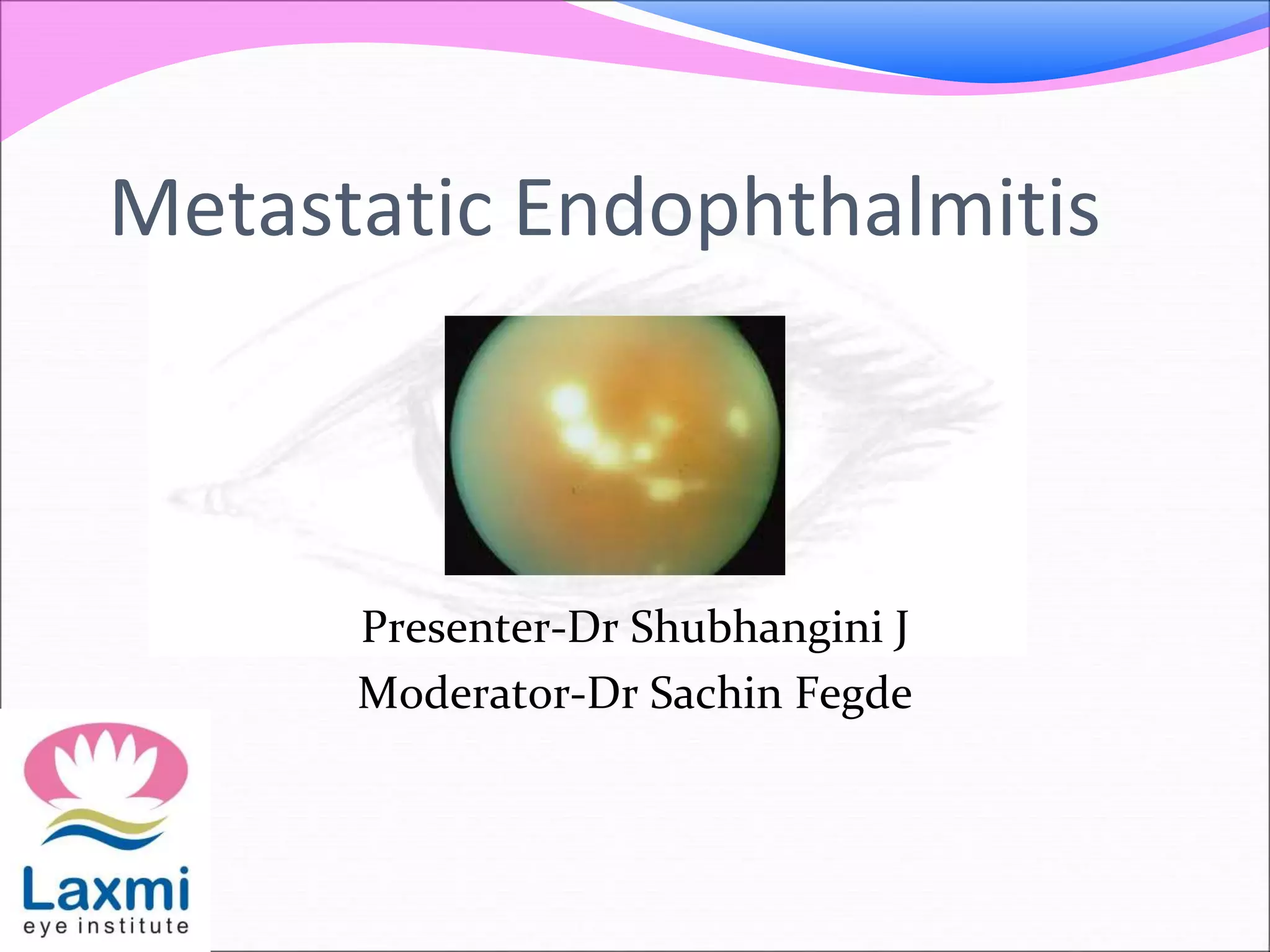
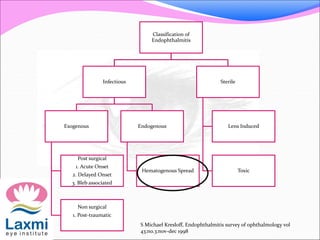
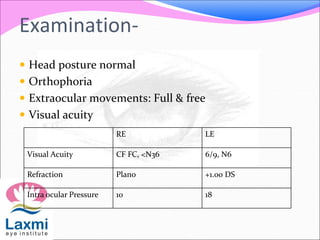
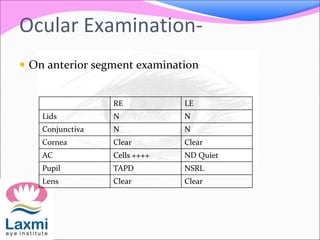
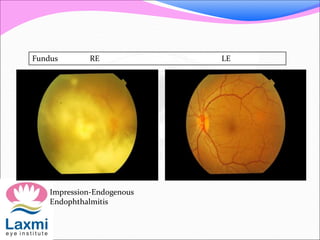
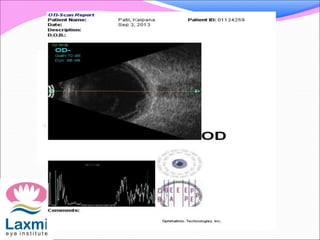
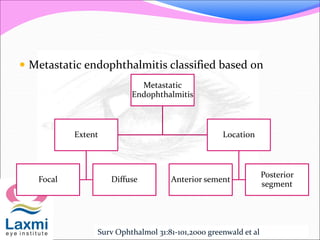
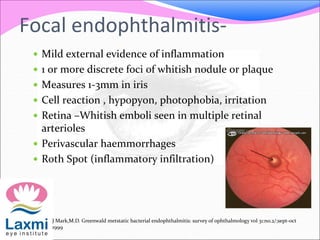
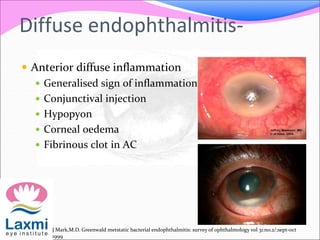
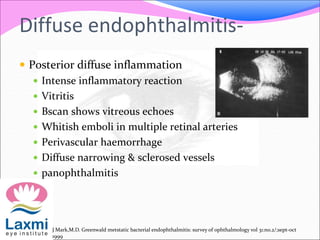
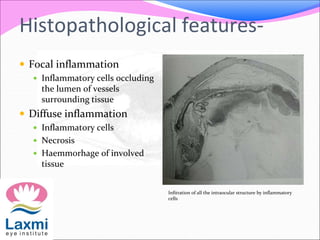
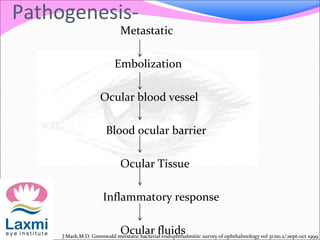
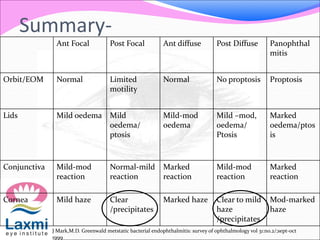
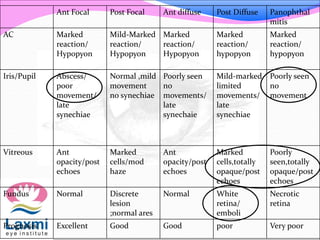
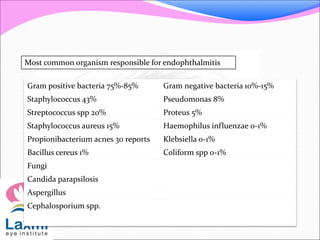
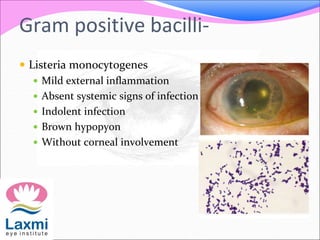
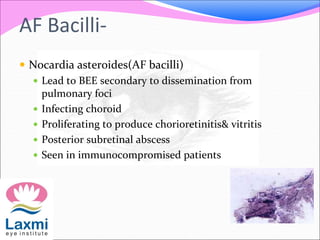
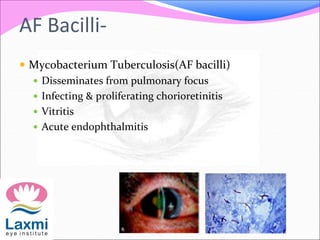
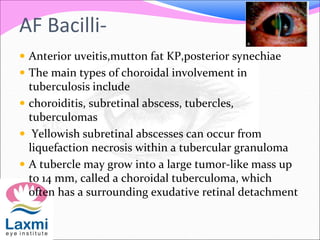
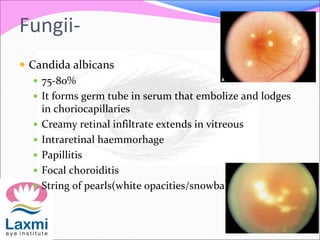
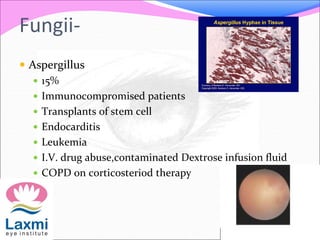
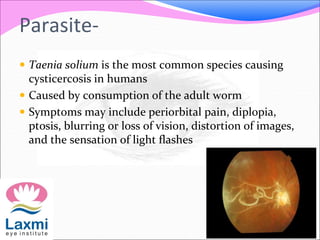
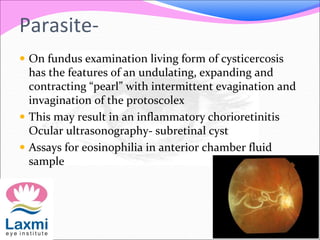
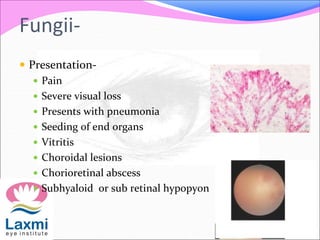
This document discusses metastatic endophthalmitis, which is inflammation of the eye resulting from a distant infection elsewhere in the body. It can be classified as focal or diffuse depending on the extent and location of inflammation in the anterior or posterior segment of the eye. Common predisposing factors include immunocompromise and intravenous drug use. Bacteria such as staphylococci and streptococci are frequent causes, as well as fungi like Candida. Evaluation may involve blood and imaging tests to identify the source of infection. Treatment involves antibiotics, vitrectomy, and sometimes silicone oil implantation.