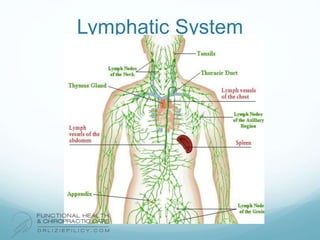
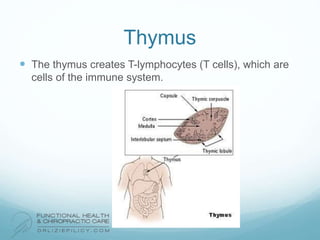
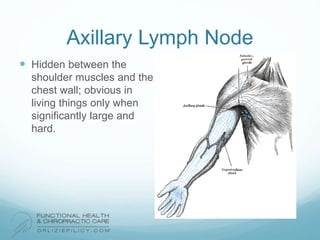
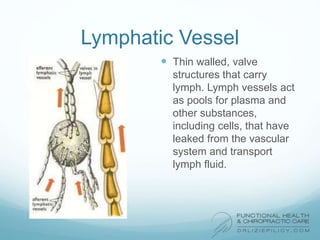
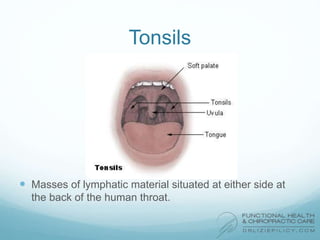
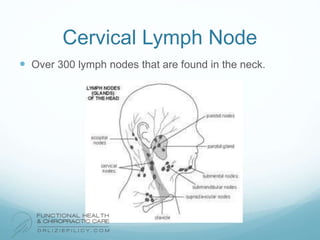
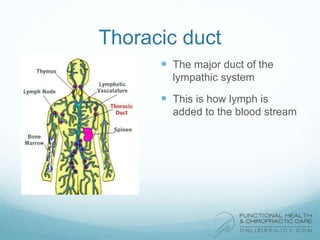
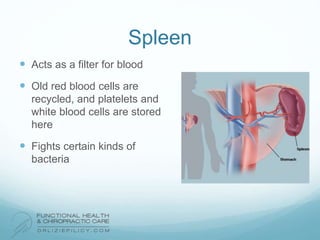
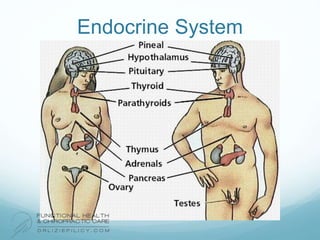
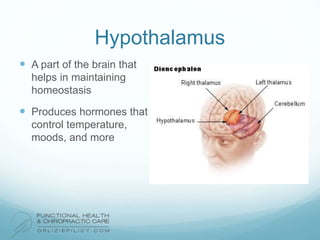
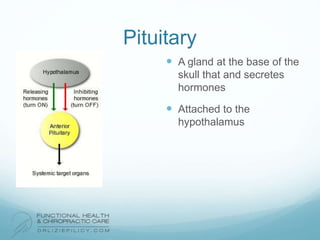
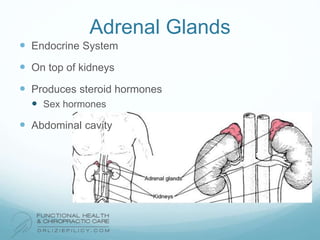
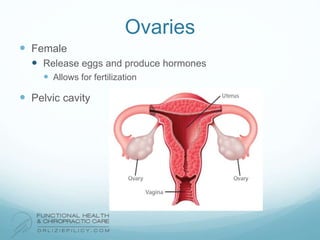
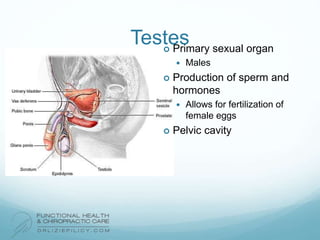
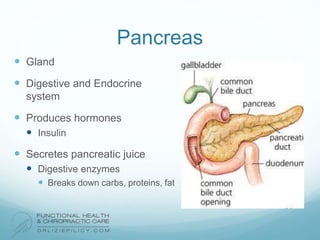
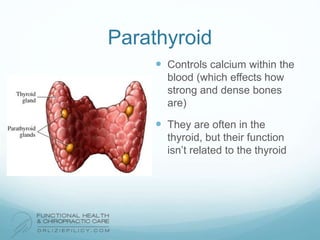
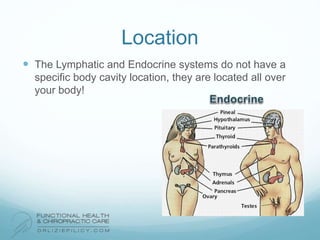
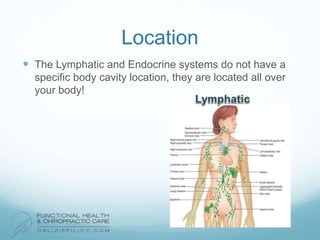
The lymphatic system aids the immune system by removing waste and toxins. It also absorbs and transports fats and fat-soluble vitamins. Key parts of the lymphatic system include lymph nodes, vessels, the thymus, spleen, tonsils, and more. The endocrine system regulates important bodily functions through hormones. Key glands are the hypothalamus, pituitary, thyroid, adrenals, ovaries, testes, pancreas, and parathyroids. Both systems do not have a single location but are found throughout the body.