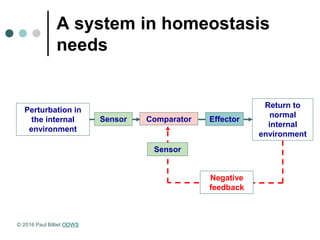
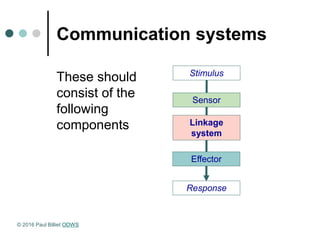
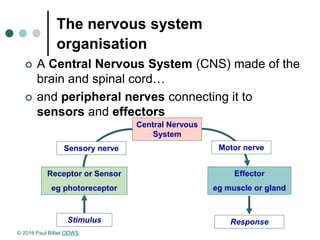
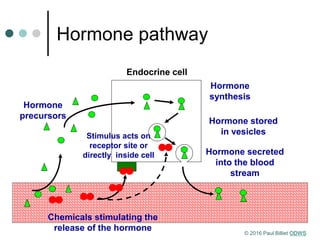
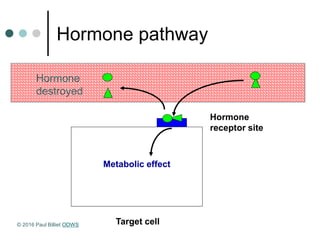
Homeostasis refers to the maintenance of a steady state in the body despite changes in the external environment. A system in homeostasis requires sensors to detect changes, a comparator to set a reference point, and effectors to bring the system back to the reference point using negative feedback. There are two main communication systems - the endocrine system uses hormones transported via blood, and the nervous system uses nerve impulses transmitted via neurons. Both systems help regulate homeostasis.