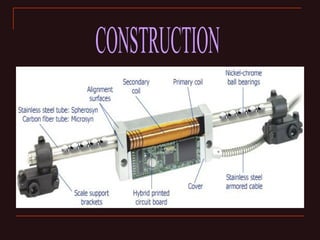
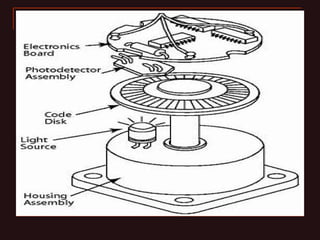
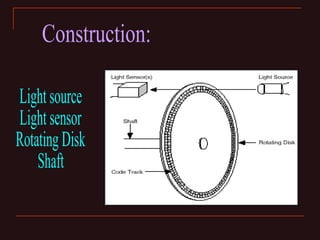
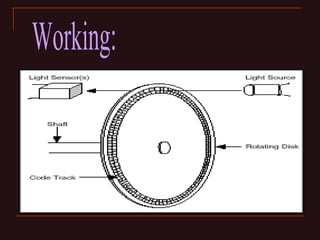
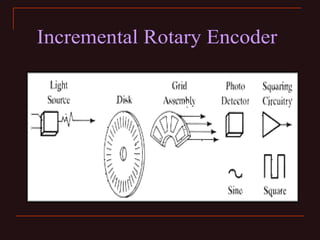
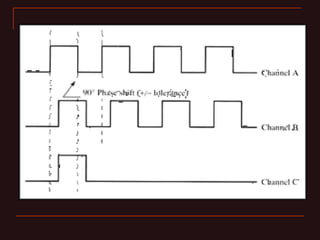
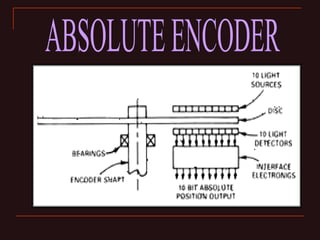
The document discusses different types of encoders, including linear encoders, optical encoders, and rotary encoders. It describes the basic principles and components of encoders. It provides details on the construction, working, types, specifications, and applications of linear encoders, optical encoders, and rotary encoders. The presentation aims to educate engineers on the fundamentals of encoders.