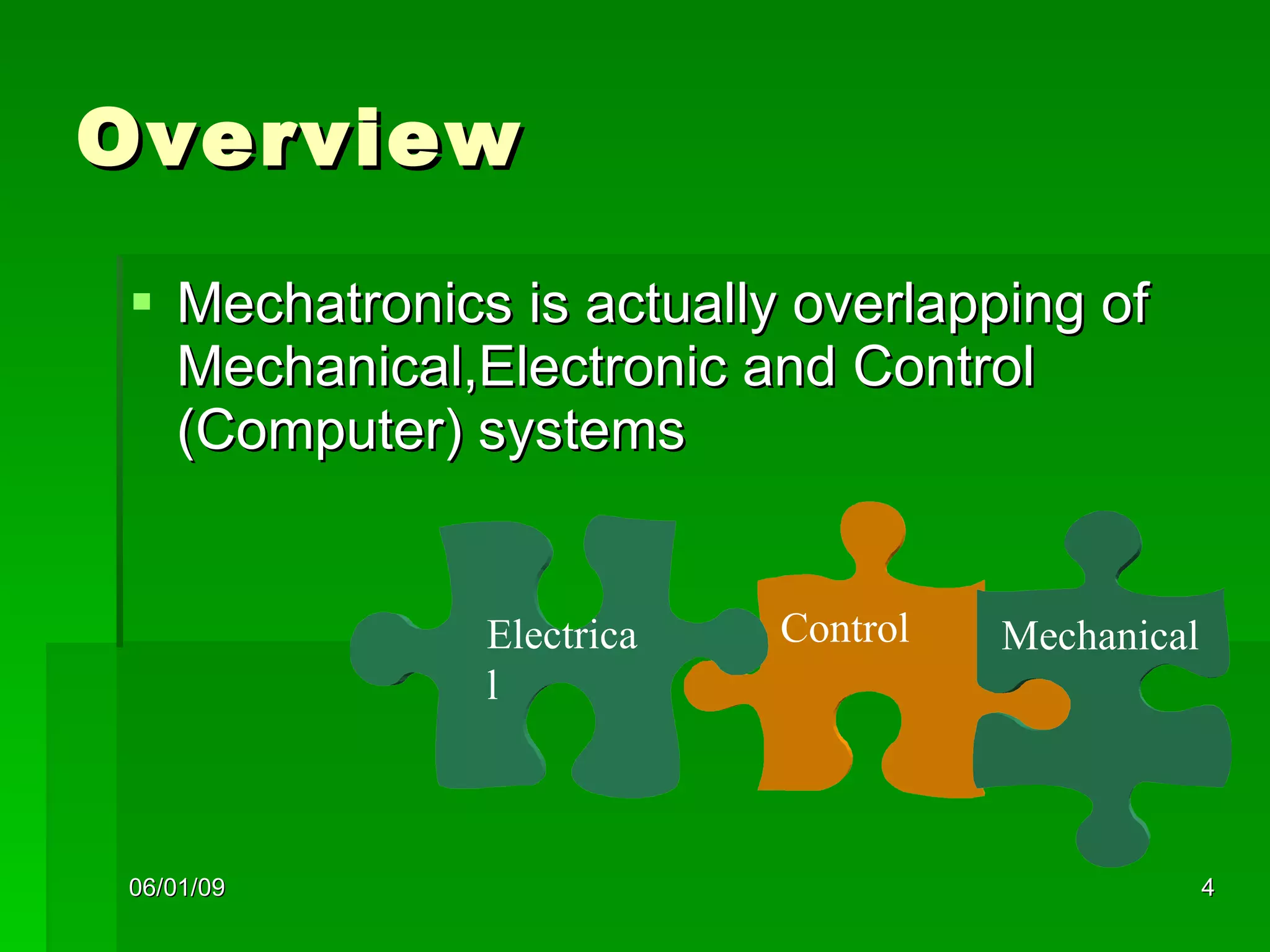
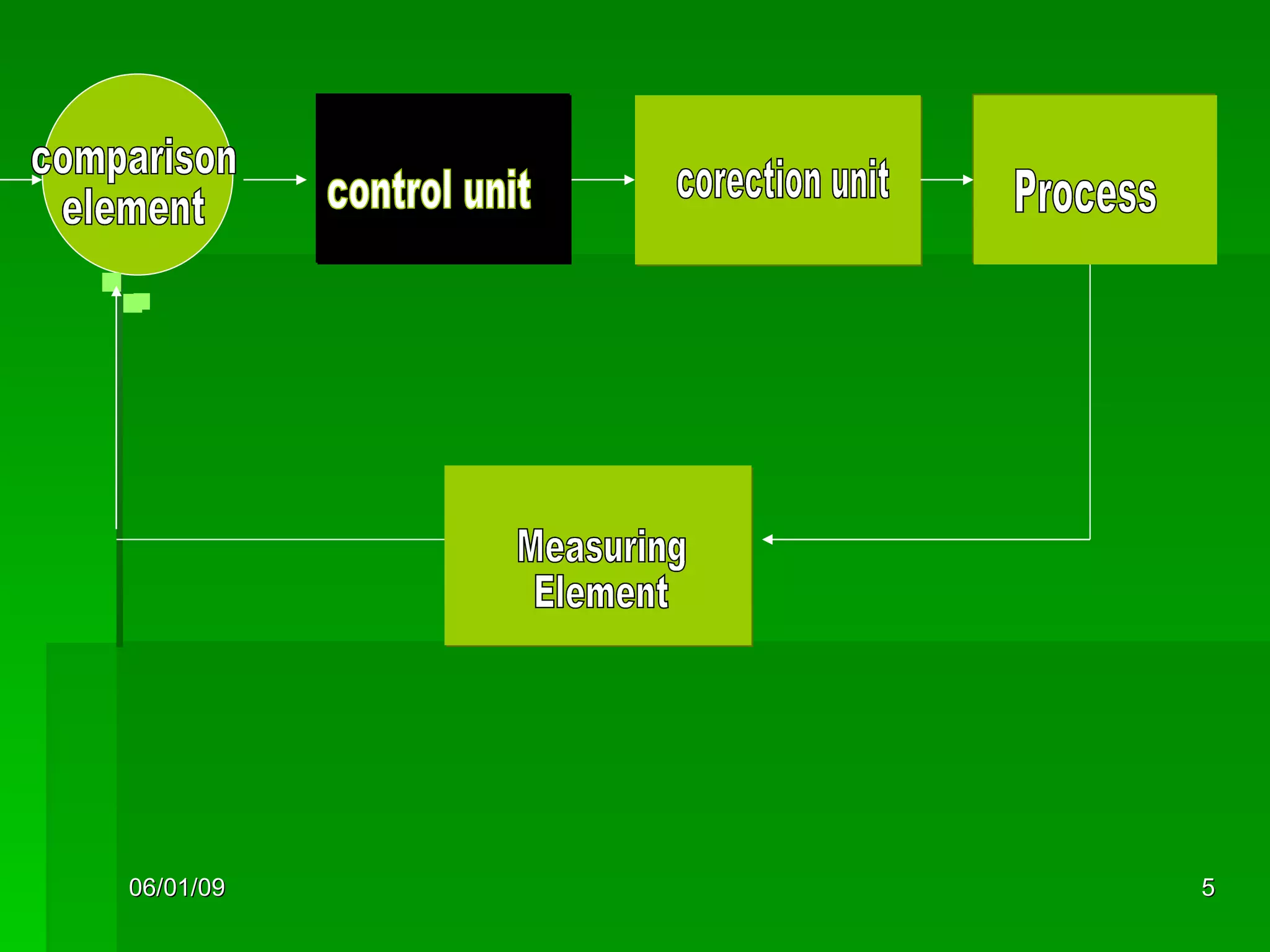
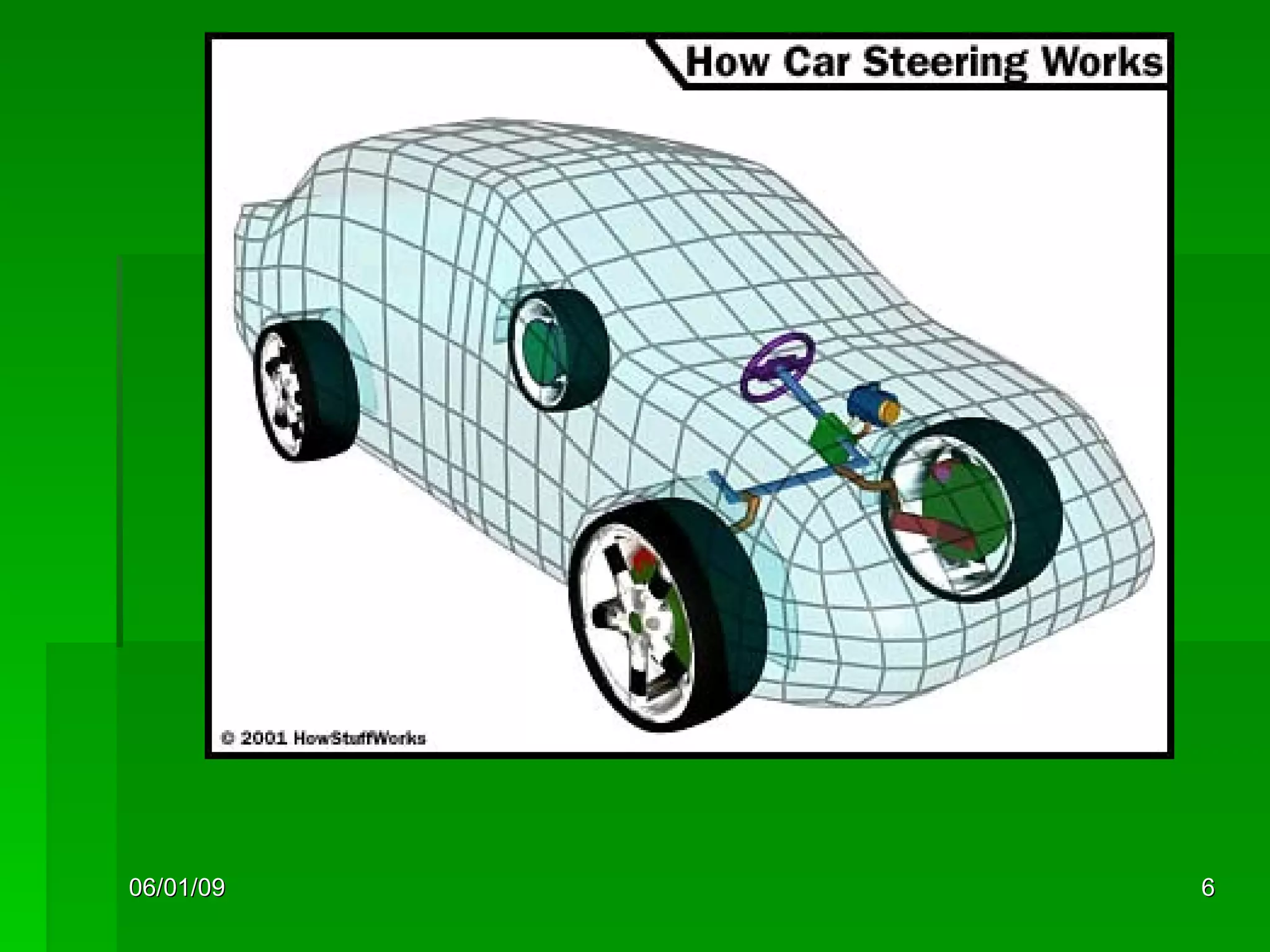
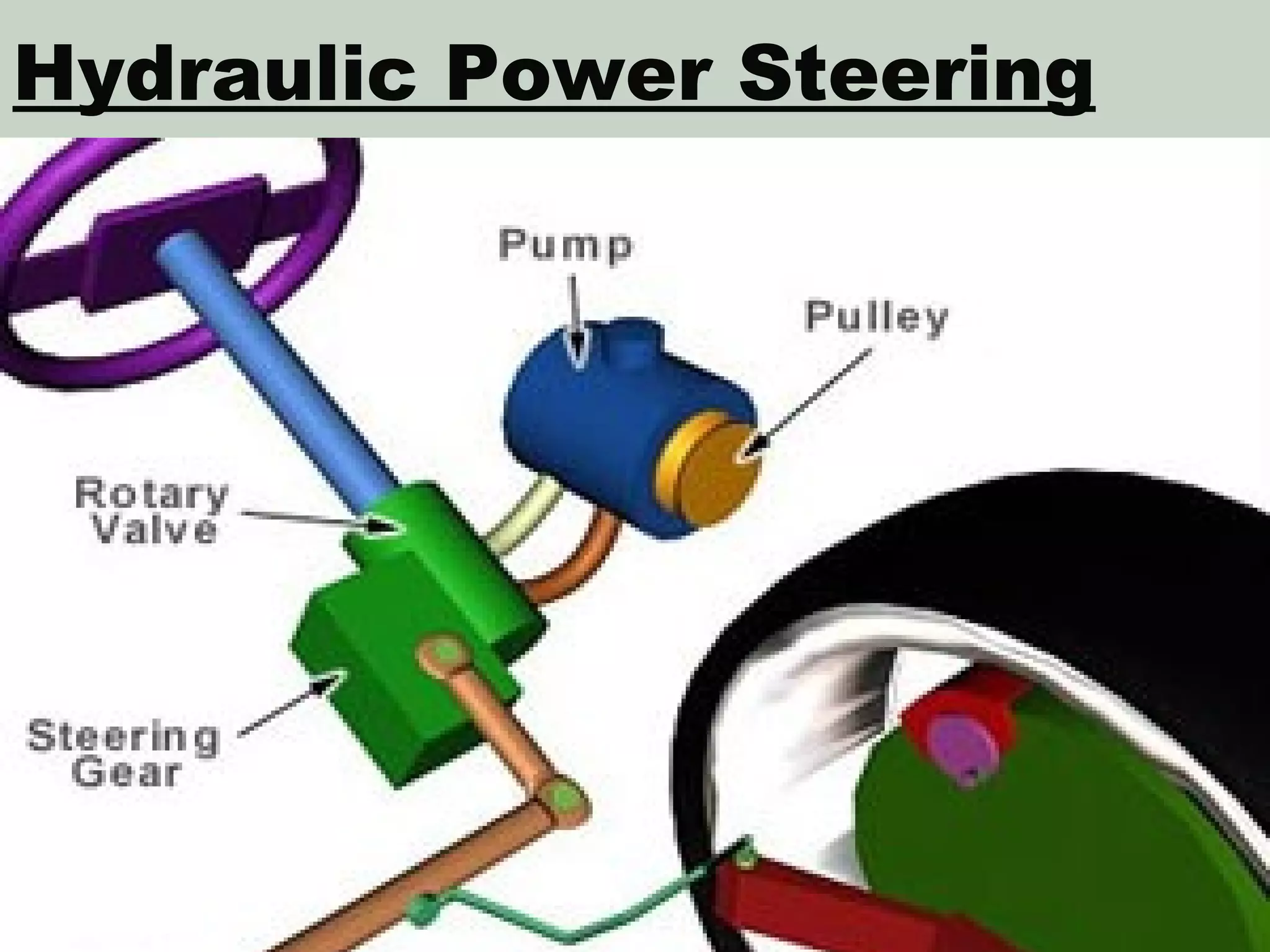
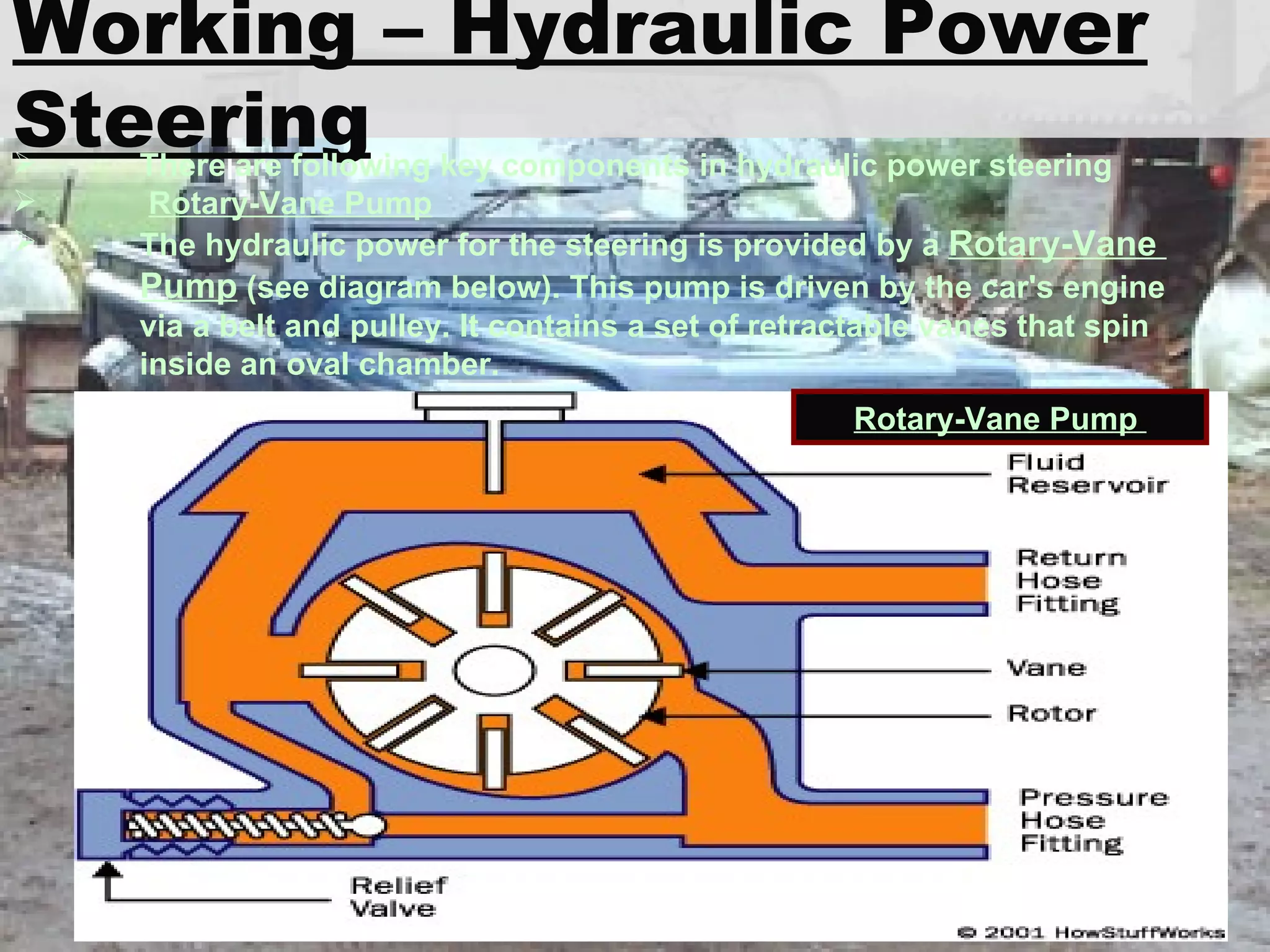
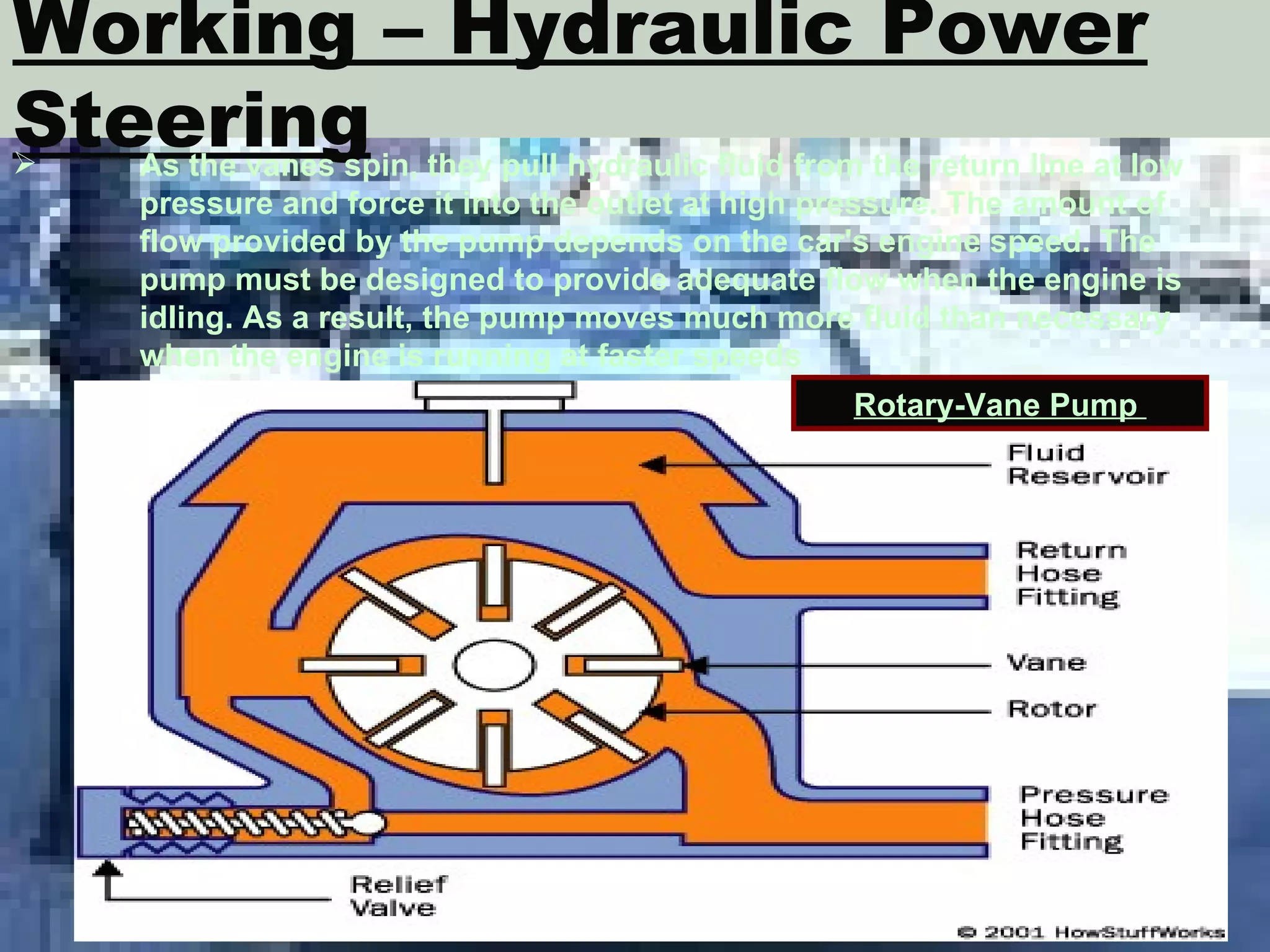
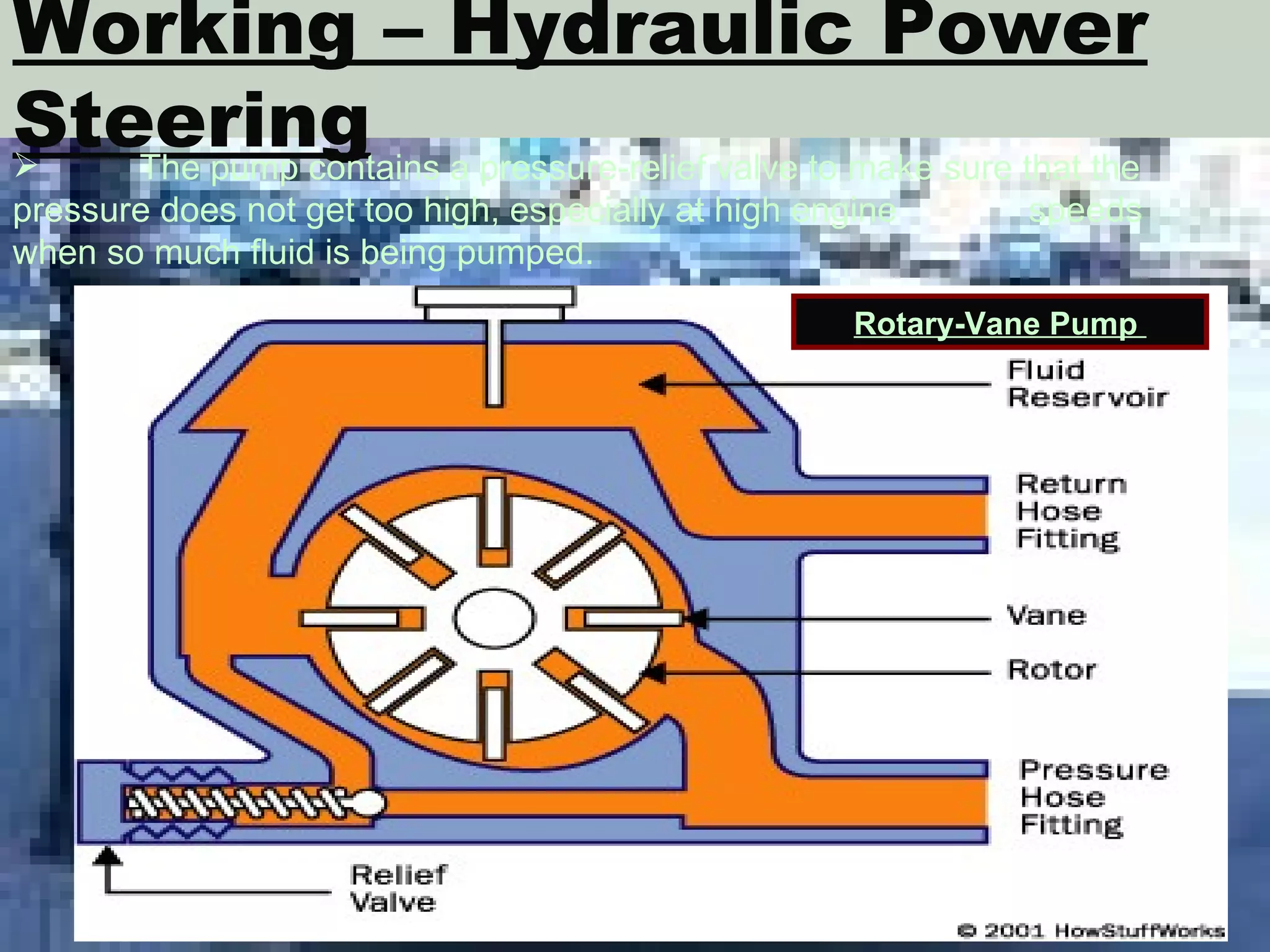
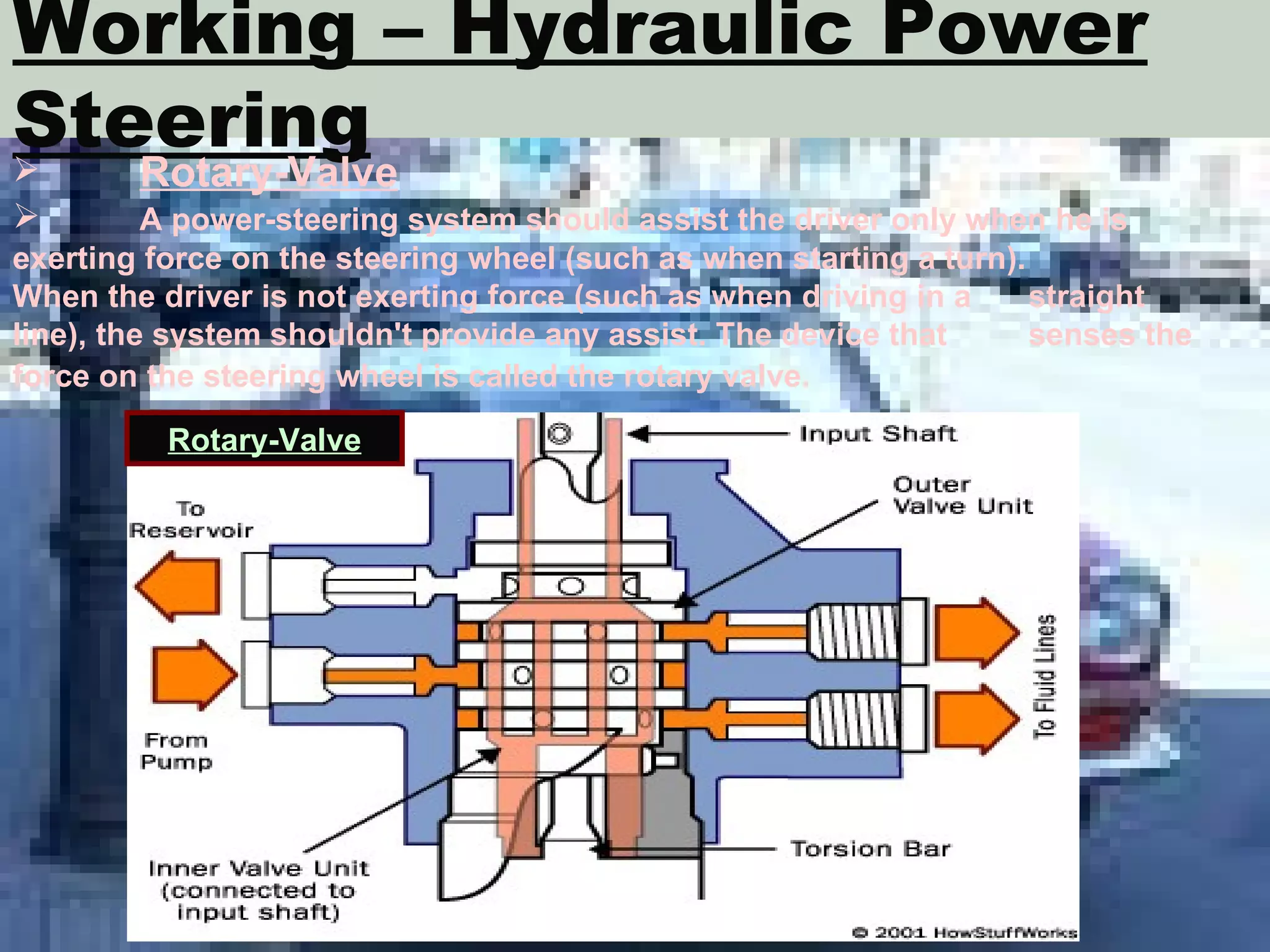
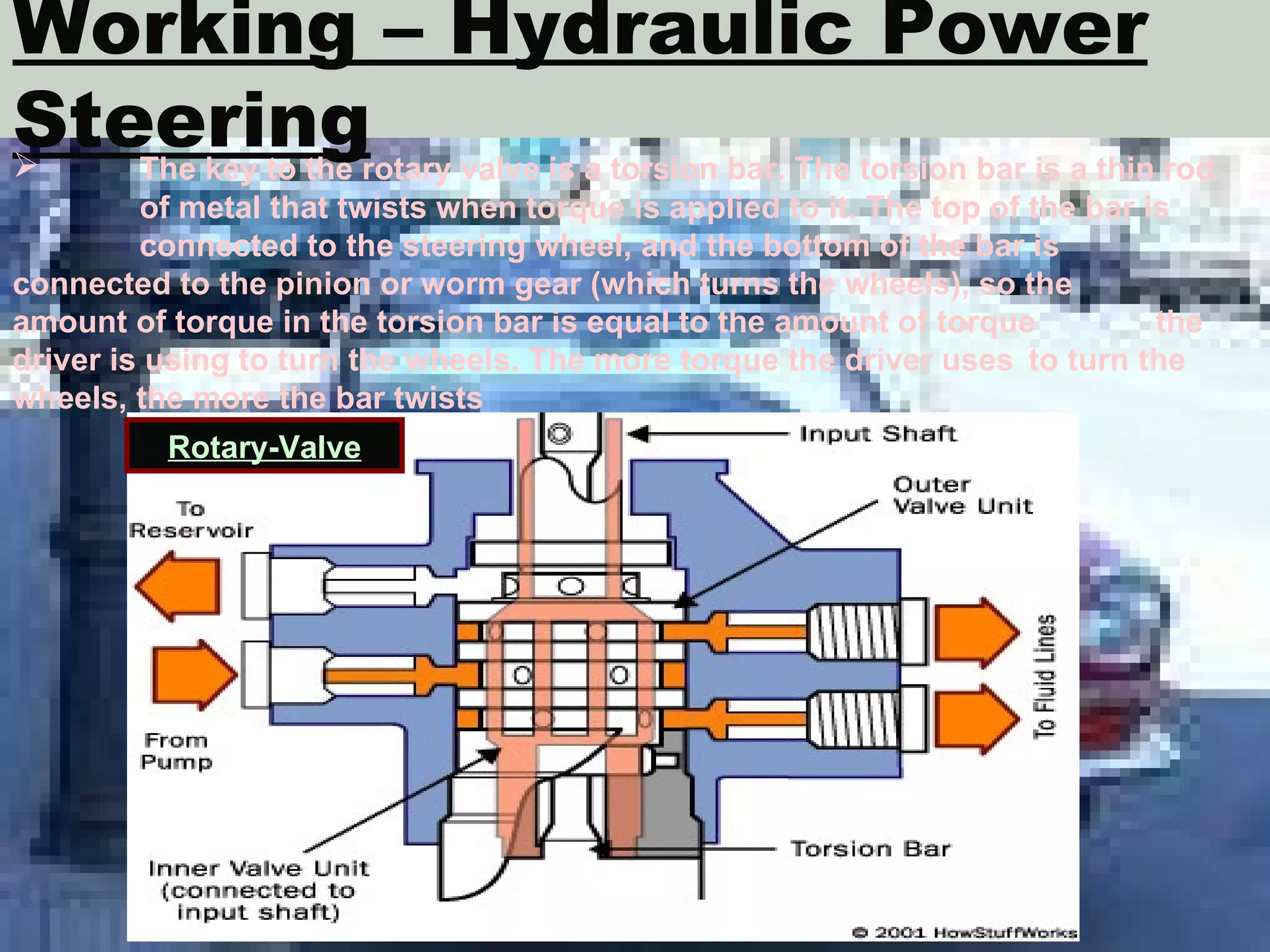
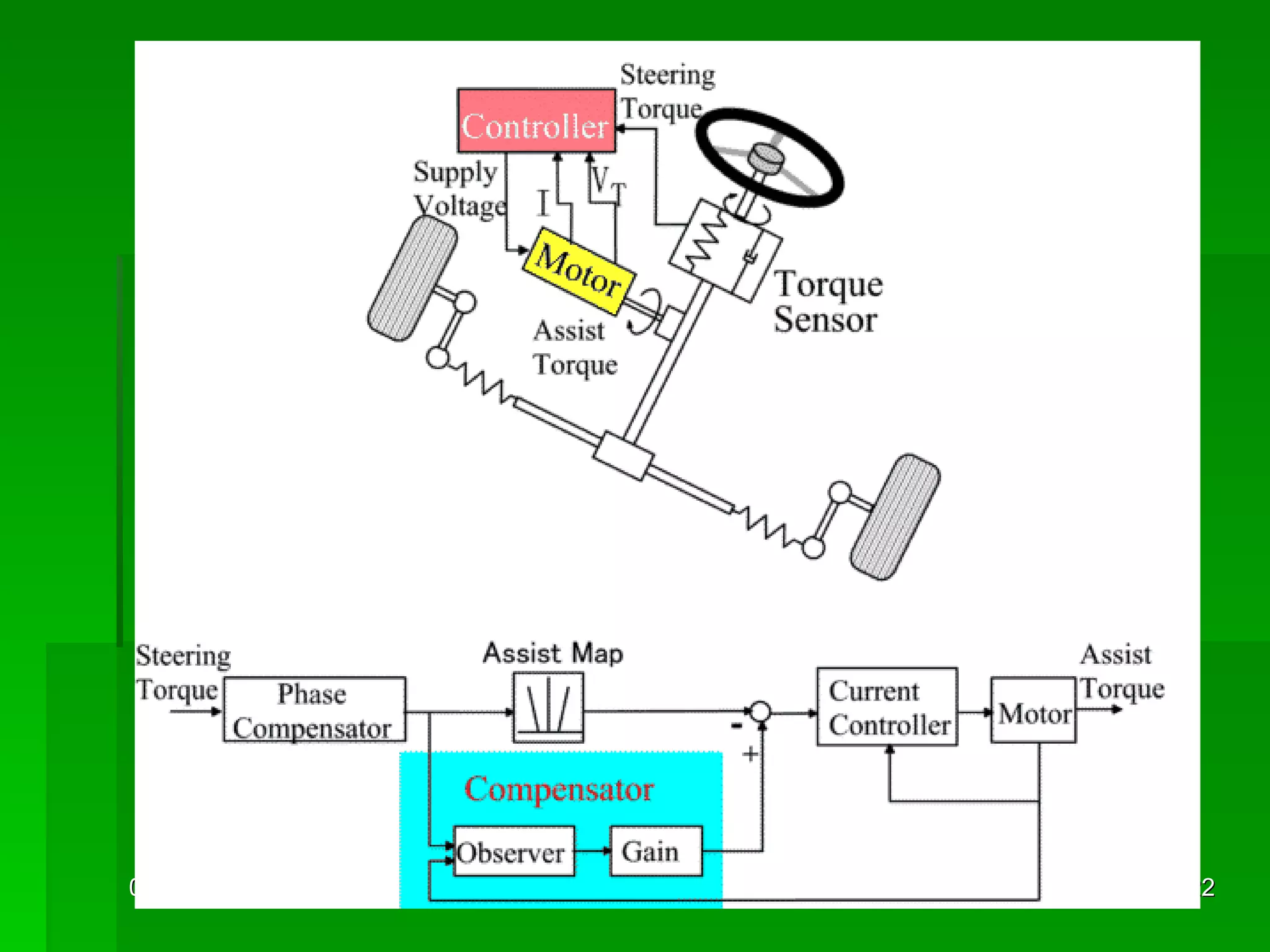
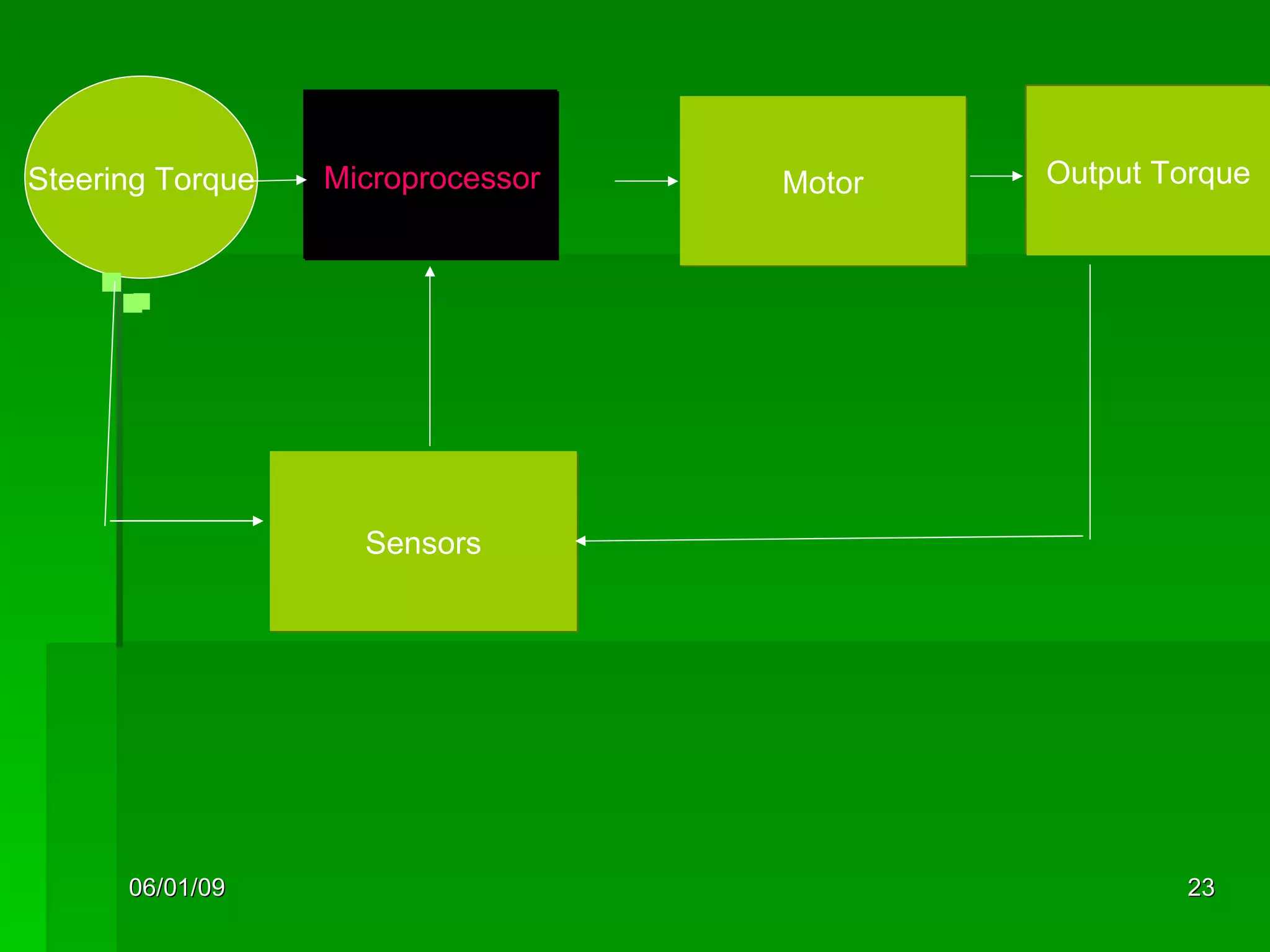
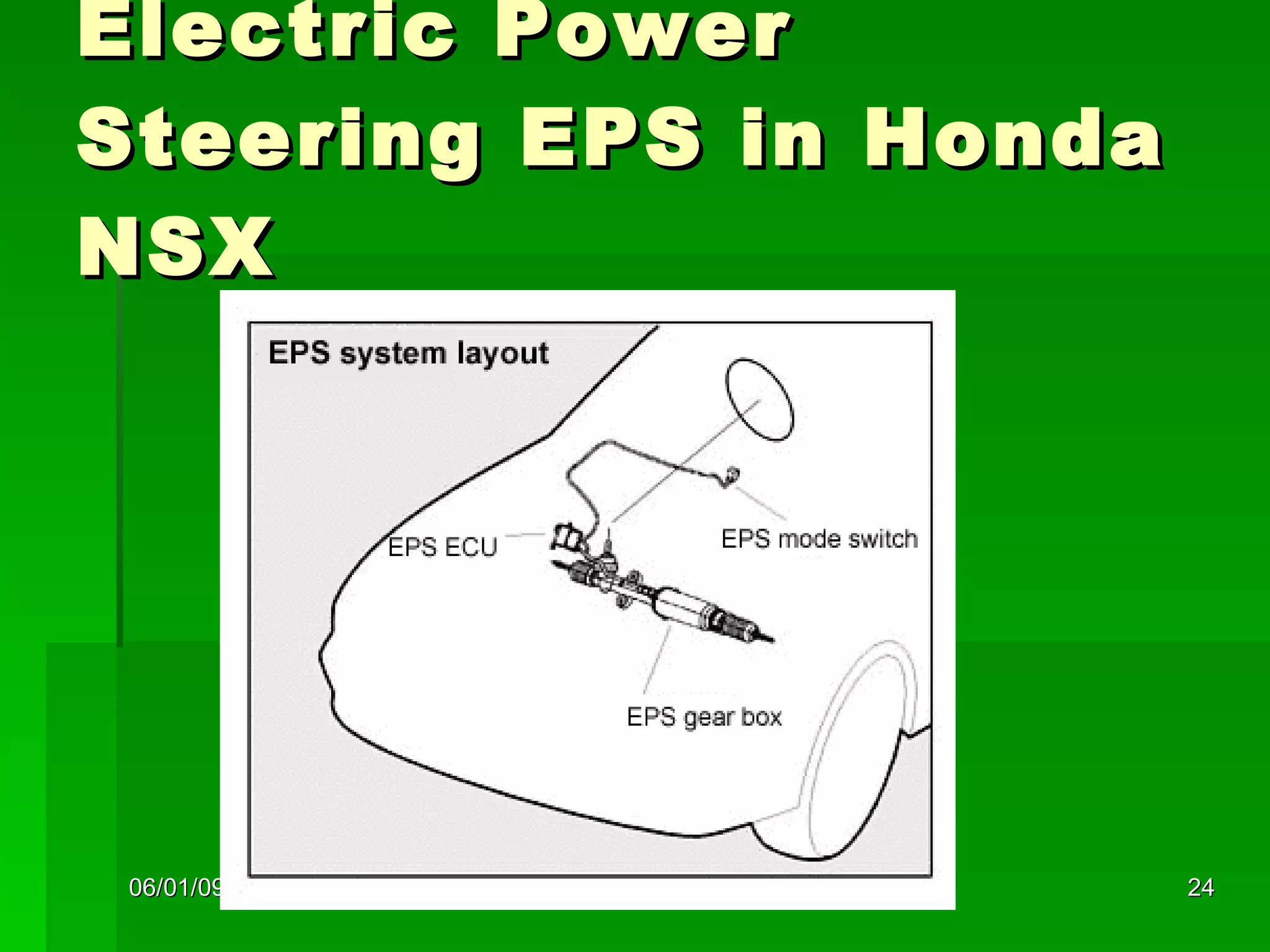
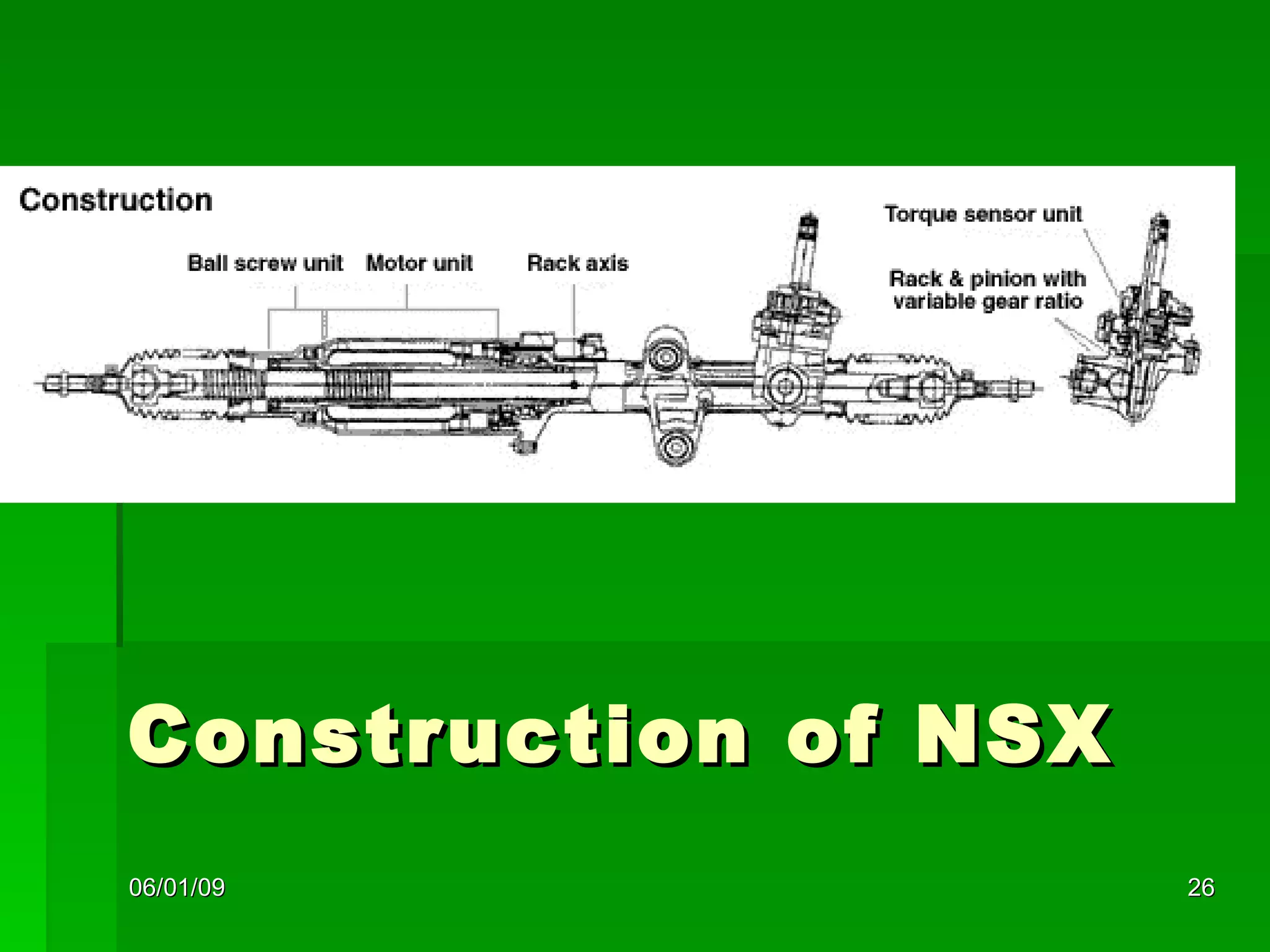
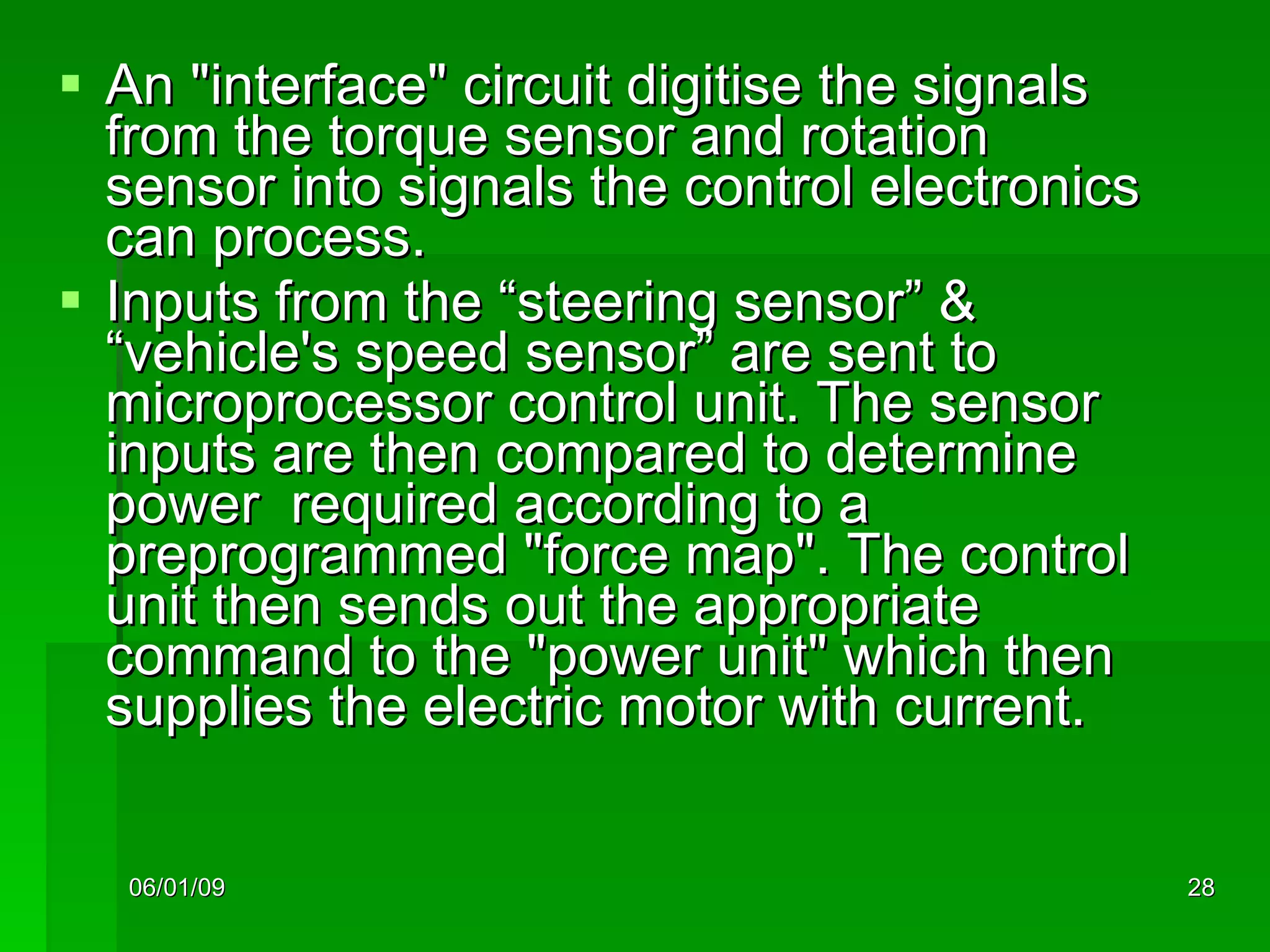
The document discusses different types of power steering systems used in vehicles. It describes hydraulic power steering systems which use a belt-driven pump to provide hydraulic pressure to assist steering. Electro-hydraulic systems use an electric motor instead of a belt to power the hydraulic pump. Electric power steering systems have sensors and a computer module that apply electric motor assist directly to the steering gear or column without hydraulics. The document also discusses Honda's electric power steering system used in the NSX which has precise control from an electric motor around the steering rack.