Embed presentation
Download as PDF, PPTX

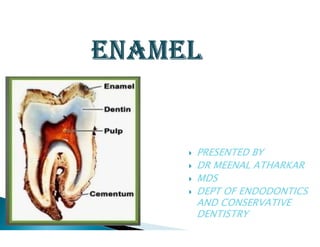


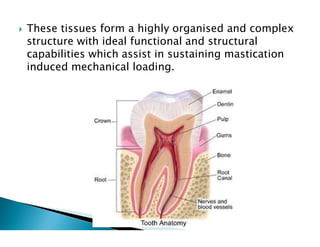
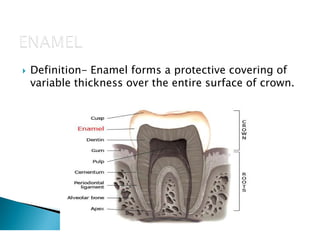
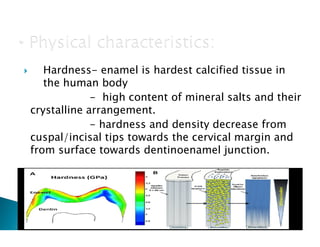

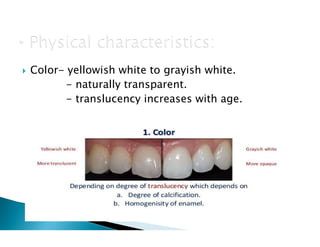

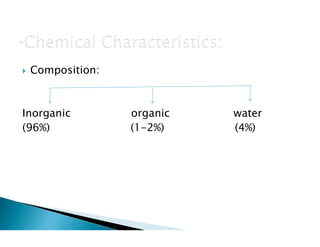
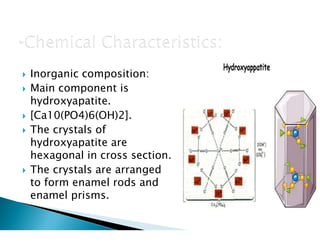



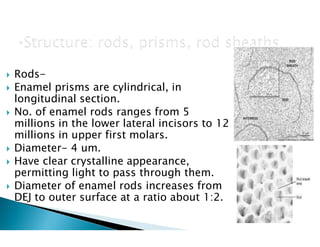

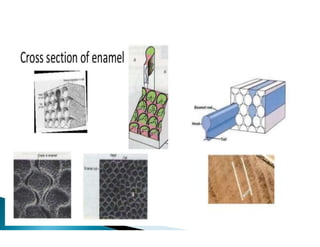


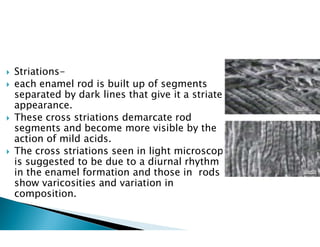
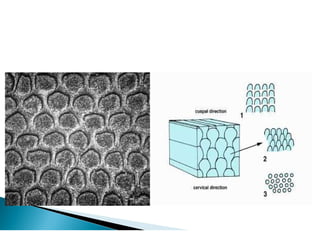
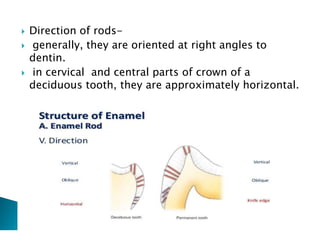
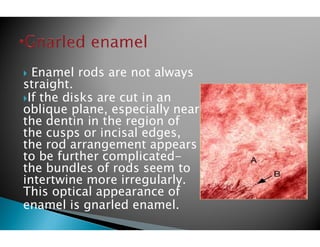
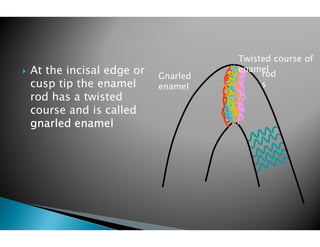

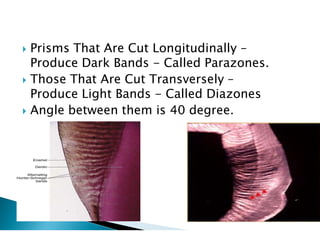

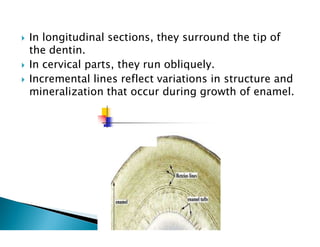

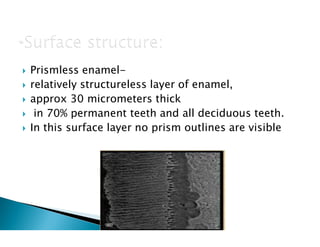




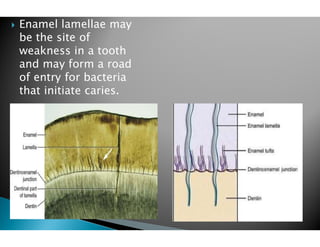
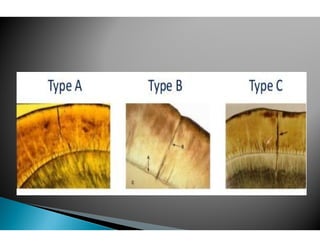
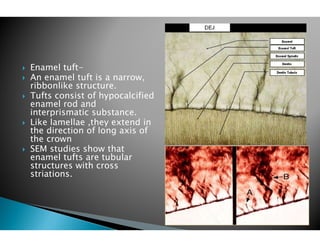
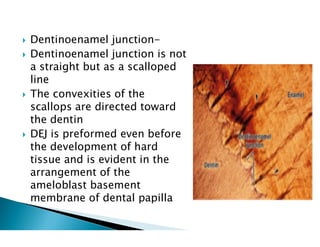
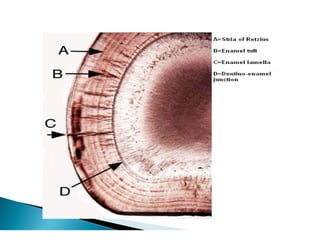
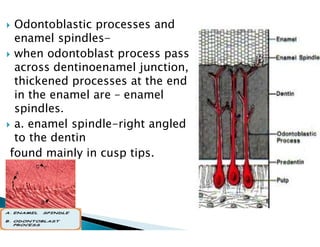
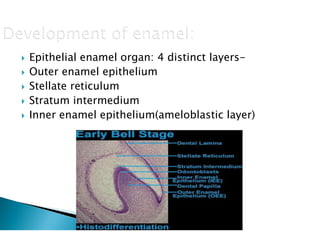








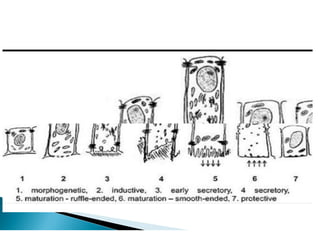


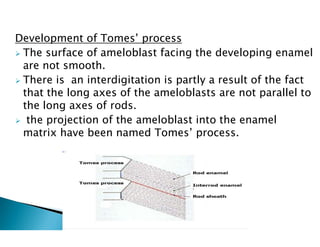

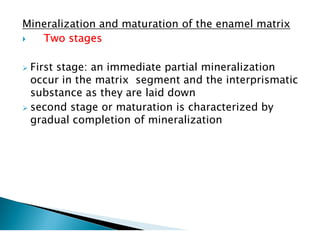

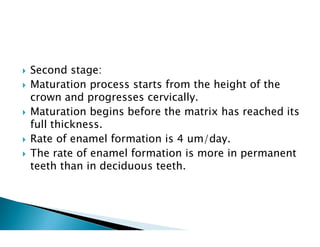




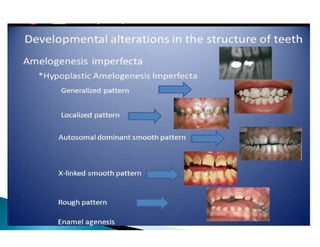

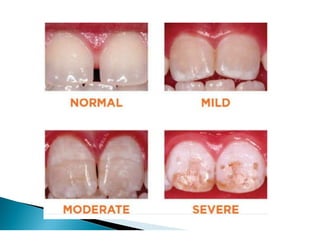
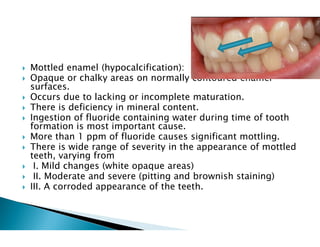
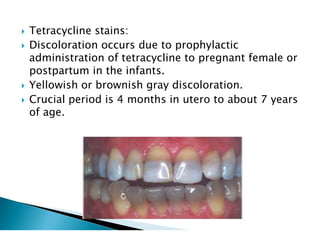
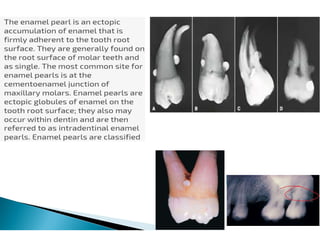
The document discusses the structure and composition of dental hard tissues, focusing on enamel. It describes enamel as the outermost rigid tissue that covers the tooth crown. Enamel is composed primarily of hydroxyapatite crystals arranged in rods that run from the dentin-enamel junction toward the outer surface. The rods are arranged to provide strength and withstand forces during chewing. Enamel hardness allows it to function in mastication but renders it brittle, requiring the underlying dentin as support.













































































