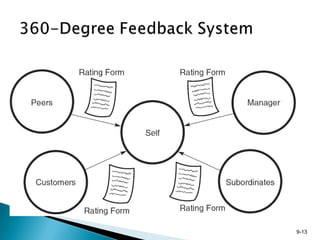
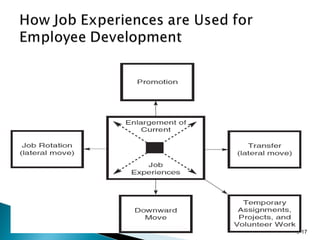
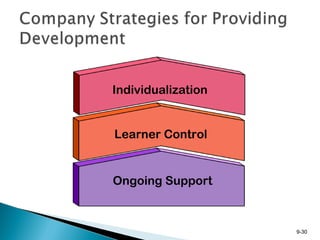
This document discusses employee development in organizations. It describes various formal education programs, assessments, and job experiences that companies use to develop employees' skills and prepare them for current or future roles. These development activities aim to improve quality, meet competitive challenges, and incorporate new technologies. The document outlines tools like the Myers-Briggs Type Indicator for assessment, and experiences like job rotation, transfers, and mentoring relationships that facilitate employee learning. Finally, it stresses that development is most effective when it is individualized, gives the employee control over their growth, and provides ongoing support.