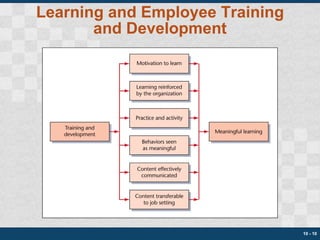
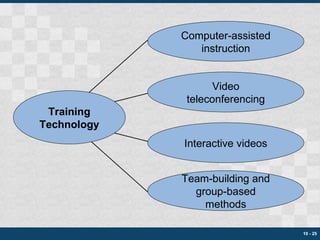
This chapter discusses training, development, and organizational learning. It covers the purposes of training and development including new employee orientation. It describes how to assess training needs, design programs, and use various techniques like on-the-job training. Management development and organizational development are also discussed. The chapter concludes by addressing how to evaluate the effectiveness of training and development programs.