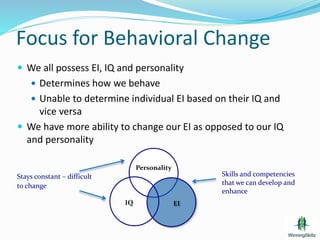
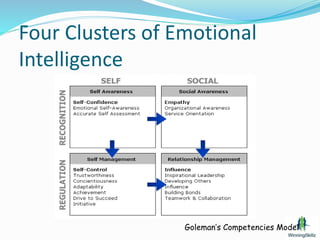
This document discusses emotional intelligence (EI) and its importance. It defines EI as the ability to understand one's own and other people's feelings and to use this awareness to motivate oneself and manage relationships effectively. The document notes that while IQ is important, EI may contribute more to success. It outlines four clusters of EI abilities - self awareness, self management, social awareness, and relationship management. The document provides details on self awareness competencies like emotional awareness and tips for improving self awareness skills.